In this market, the equilibrium hourly wage is %24 , and the equilibrium quantity of labour is workers. Suppose a member of Parliament introduces a bill to legislate a minimum hourly wage of $6. This type of price control is called a For each of the wages listed in the following table, determine the quantity of labour demanded, the quantity of labour supplied, and the direction of pressure exerted on wages in the absence of any price controls. Wage Labour Demanded Labour Supplied (Dollars per hour) (Thousands of workers) (Thousands of workers) Pressure on Wages 12 True or False: A minimum wage below $10 per hour is not a binding minimum wage in this market. (Economists call a minimum wage that prevents the labour market from reaching equilibrium a binding minimum wage.) O True O False
In this market, the equilibrium hourly wage is %24 , and the equilibrium quantity of labour is workers. Suppose a member of Parliament introduces a bill to legislate a minimum hourly wage of $6. This type of price control is called a For each of the wages listed in the following table, determine the quantity of labour demanded, the quantity of labour supplied, and the direction of pressure exerted on wages in the absence of any price controls. Wage Labour Demanded Labour Supplied (Dollars per hour) (Thousands of workers) (Thousands of workers) Pressure on Wages 12 True or False: A minimum wage below $10 per hour is not a binding minimum wage in this market. (Economists call a minimum wage that prevents the labour market from reaching equilibrium a binding minimum wage.) O True O False
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Course List)
16th Edition
ISBN:9781305506893
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Chapter12: The Supply Of And Demand For Productive Resources
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7CQ
Related questions
Question
Choices for the following labelled numbers—- 1. Price ceiling , quota, price floor , tax
2. Up ward or downward
3. Upward or downward
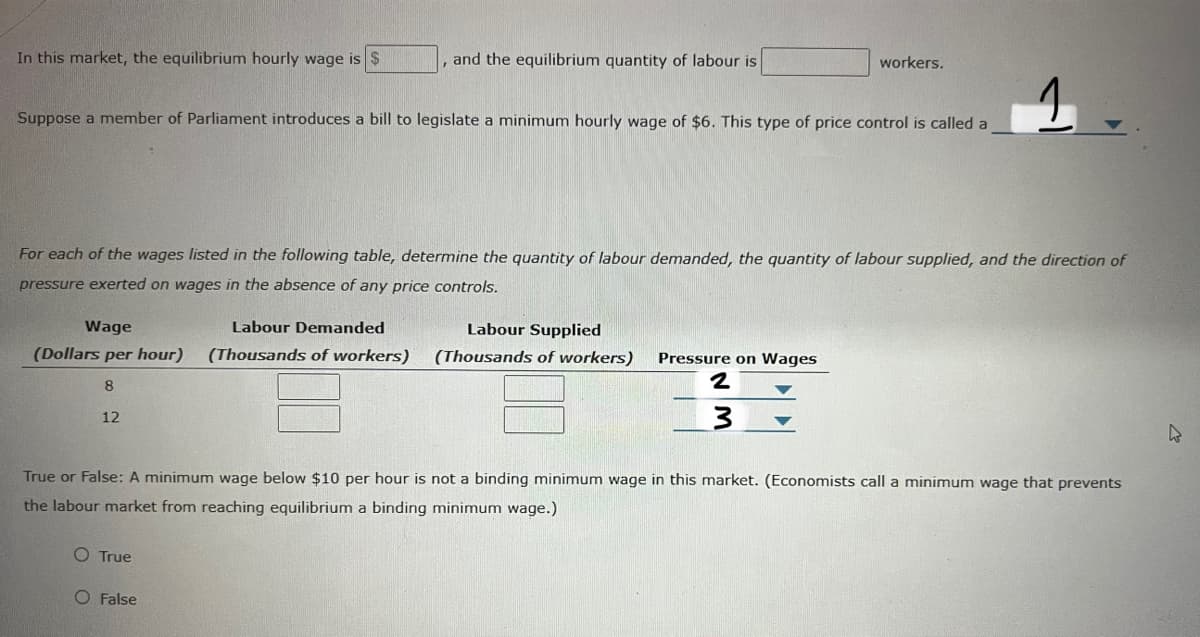
Transcribed Image Text:In this market, the equilibrium hourly wage is $
and the equilibrium quantity of labour is
workers.
Suppose a member of Parliament introduces a bill to legislate a minimum hourly wage of $6. This type of price control is called a
For each of the wages listed in the following table, determine the quantity of labour demanded, the quantity of labour supplied, and the direction of
pressure exerted on wages in the absence of any price controls.
Wage
Labour Demanded
Labour Supplied
(Dollars per hour)
(Thousands of workers)
(Thousands of workers)
Pressure on Wages
8.
12
True or False: A minimum wage below $10 per hour is not a binding minimum wage in this market. (Economists call a minimum wage that prevents
the labour market from reaching equilibrium a binding minimum wage.)
O True
O False
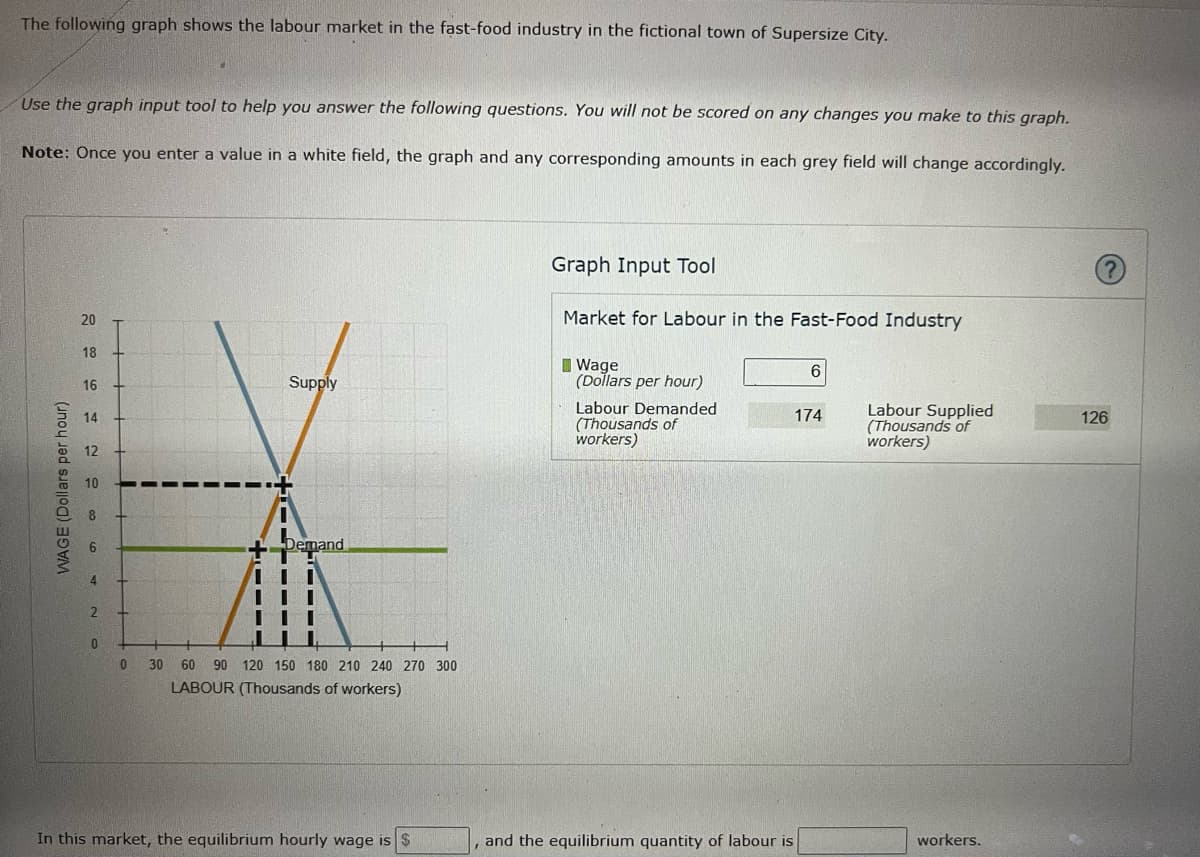
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph shows the labour market in the fast-food industry in the fictional town of Supersize City.
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be scored on any changes you make to this graph.
Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.
Graph Input Tool
20
Market for Labour in the Fast-Food Industry
18
Supply
I Wage
(Dollars per hour)
16
Labour Demanded
(Thousands of
workers)
Labour Supplied
(Thousands of
workers)
14
174
126
12
10
6.
Demand
4.
0
30
60
90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300
LABOUR (Thousands of workers)
In this market, the equilibrium hourly wage is $
and the equilibrium quantity of labour is
workers.
WAGE (Dollars per hour)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc
