Template DNA Region of interest that will be copied Cycle 4 Mix together template DNA, present in low amounts, and 2 primers, present in high amounts, with DNTPS and Taq polymerase. During each cycle, the DNA strands are separated via heating. Cycle 1 The temperature is then lowered to allow the primers to bind, and a complementary strand is made. Cycle 2 Cycle 3 With each successive cycle, the relative amount of this type of DNA fragment increases. Therefore, after many cycles, the vast majority of DNA fragments contain only the region that is flanked by the 2 primers. FIGURE 21.6 The technique of PCR carried out for four cycles. During each cycle, oligonucleotides (green) that are comple- mentary to the ends of the targeted DNA sequence bind to the DNA and act as primers for the synthesis of this DNA region. Note: The original DNA strands are purple, and those strands made during the first, second, third, and fourth cycles are blue, red, gray, and orange, respectively. ONLINE ANIMATION
Template DNA Region of interest that will be copied Cycle 4 Mix together template DNA, present in low amounts, and 2 primers, present in high amounts, with DNTPS and Taq polymerase. During each cycle, the DNA strands are separated via heating. Cycle 1 The temperature is then lowered to allow the primers to bind, and a complementary strand is made. Cycle 2 Cycle 3 With each successive cycle, the relative amount of this type of DNA fragment increases. Therefore, after many cycles, the vast majority of DNA fragments contain only the region that is flanked by the 2 primers. FIGURE 21.6 The technique of PCR carried out for four cycles. During each cycle, oligonucleotides (green) that are comple- mentary to the ends of the targeted DNA sequence bind to the DNA and act as primers for the synthesis of this DNA region. Note: The original DNA strands are purple, and those strands made during the first, second, third, and fourth cycles are blue, red, gray, and orange, respectively. ONLINE ANIMATION
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter28: Dna Metabolism: Replication, Recombination, And Repair
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17P
Related questions
Question
After four cycles of PCR, which type of PCR product predominates? Explain why.
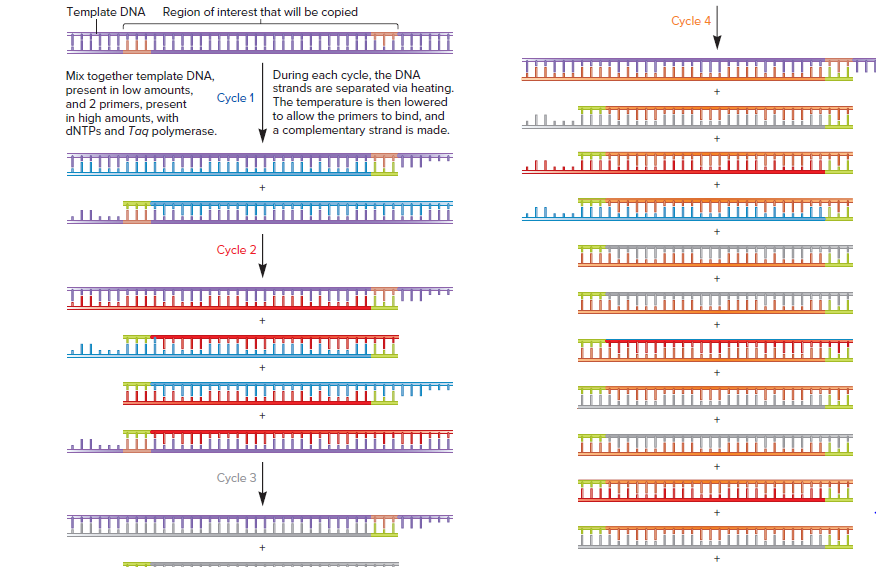
Transcribed Image Text:Template DNA Region of interest that will be copied
Cycle 4
Mix together template DNA,
present in low amounts,
and 2 primers, present
in high amounts, with
DNTPS and Taq polymerase.
During each cycle, the DNA
strands are separated via heating.
Cycle 1 The temperature is then lowered
to allow the primers to bind, and
a complementary strand is made.
Cycle 2
Cycle 3
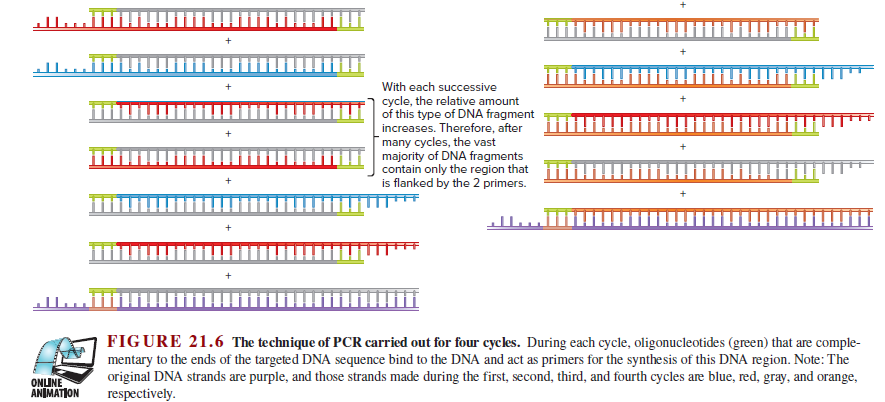
Transcribed Image Text:With each successive
cycle, the relative amount
of this type of DNA fragment
increases. Therefore, after
many cycles, the vast
majority of DNA fragments
contain only the region that
is flanked by the 2 primers.
FIGURE 21.6 The technique of PCR carried out for four cycles. During each cycle, oligonucleotides (green) that are comple-
mentary to the ends of the targeted DNA sequence bind to the DNA and act as primers for the synthesis of this DNA region. Note: The
original DNA strands are purple, and those strands made during the first, second, third, and fourth cycles are blue, red, gray, and orange,
respectively.
ONLINE
ANIMATION
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax