
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, the atoms must complete their normal valency by bond formation and lone pairs of electrons. Maximum number of covalent bonds formed by any neutral atom with maximum number of lone pairs is
| Atom | Number of bond | Number of lone pairs |
| C | 4 | 0 |
| H | 1 | 0 |
| O | 2 | 2 |
| N | 1 | 1 |
| F | 1 | 3 |
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
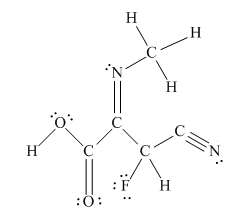
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
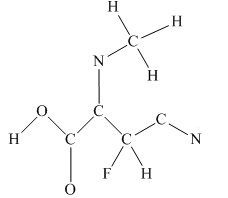
Total valence electron count for the given molecule is
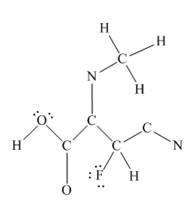
The other oxygen atom has formed only one bond with carbon. This is converted to a double bond and two lone pairs are placed on the oxygen atom so that its octet is complete. A double bond is placed between C and N atom to complete the octet of carbon and a lone pair is placed in nitrogen to complete its octet.
A triple bond is placed between the other C and N to complete the octet of carbon and a lone pair is placed in the nitrogen to complete its octet.

This structure now accounts for all 54 electrons and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogens is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, every carbon atom must form four covalent bonds whereas the hydrogen atom forms one bond.
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
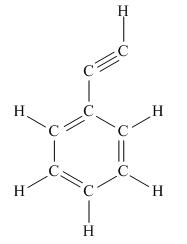
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
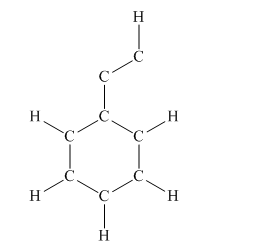
Total valence electron count for the given molecule must be

This structure now accounts for all 38 electrons and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogen atoms is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, the atoms must complete their normal valency by bond formation and lone pairs of electrons. Maximum numbers of covalent bonds formed by any neutral atom with maximum number of lone pair are
| Atom | Number of bond | Number of lone pairs |
| C | 4 | 0 |
| H | 1 | 0 |
| O | 2 | 2 |
| N | 1 | 1 |
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
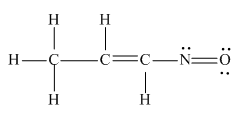
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
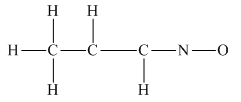
Total valence electron count for the given molecule is
The oxygen atom has formed only one bond with nitrogen. This is converted to a double bond and two lone pairs are placed on the oxygen atom so that its octet is complete. Another lone pair is placed on the nitrogen atom so that its octet is complete.
A double bond is placed between the C atoms attached to one hydrogen each. This completes the octet of both carbon atoms

This structure now accounts for all the 28 electrons, and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogen atoms is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLES & MECHANISM
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





