
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The distance between
Concept introduction:
The bond length or bond distance is the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. When two similar atoms are bonded together, half of the bond length is known as the covalent radius. The bond length depends on the number of bonded of two atoms. The unit of bond length is picometer.
In single, double and triple bonds, the order of bond length is as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.95P
Explanation of Solution
The total number of electrons in
So
The Lewis structure of

The two hydrogen atoms are separated by two
The total distance between
The bond length between the two atoms in a molecule depends not only on the atoms but also on other factors like orbital hybridization and the steric nature of the substituents.
(b)
Interpretation:
The distance between
Concept introduction:
The bond length or bond distance is the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. When two similar atoms are bonded together, half of the bond length is known as the covalent radius. The bond length depends on the number of bonded of two atoms. The unit of bond length is picometer.
In single, double and triple bonds, the order of bond length is as follows:
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.95P
Explanation of Solution
The total number of electrons in
So
The Lewis structure of
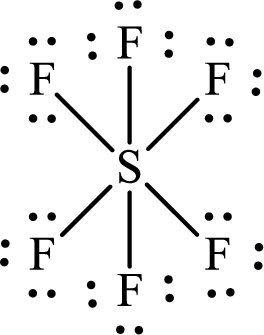
The two fluorine atoms that are opposite to the sulfur atom are separated by two
The total distance between
The adjacent fluorine atoms are present at the two corners of a right-angled triangle. The two sides of the triangle are the bond lengths of
The distance between the adjacent
Or,
Substitute
The bond length between the two atoms in a molecule depends not only on the atoms but also on other factors like orbital hybridization and the steric nature of the substituents.
(c)
Interpretation:
The distance between equatorial
Concept introduction:
The bond length or bond distance is the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. When two similar atoms are bonded together, half of the bond length is known as the covalent radius. The bond length depends on the number of bonded of two atoms. The unit of bond length is picometer.
In single, double and triple bonds, the order of bond length is as follows:
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.95P
Explanation of Solution
The total number of electrons in
So
The Lewis structure of
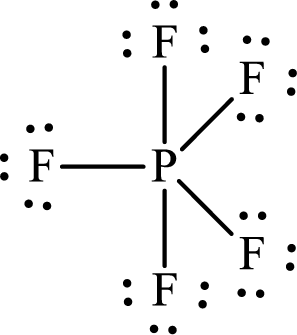
The adjacent fluorine atoms are present at the corners of a triangle with
The distance between the adjacent
Or,
Substitute
The bond length between the two atoms in a molecule depends not only on the atoms but also on other factors like orbital hybridization and the steric nature of the substituents.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
GEN CMB CHEM; CNCT+;ALEKS 360
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





