
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction with detailed mechanism for the formation of the given compound from the corresponding
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene occurs through formation of a more stable carbocation. The electrophilic addition of water across the double bond in an acidic condition produces the alcohol product. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation, followed by the action of water as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 11.33P
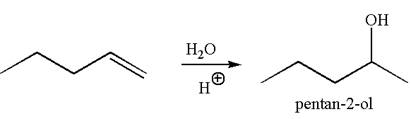
The reaction equation and the detailed mechanism for the formation of
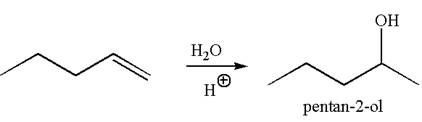
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
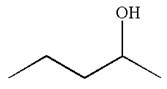
To form the given alcohol by electrophilic addition of water, the double bond must be between the carbon where the
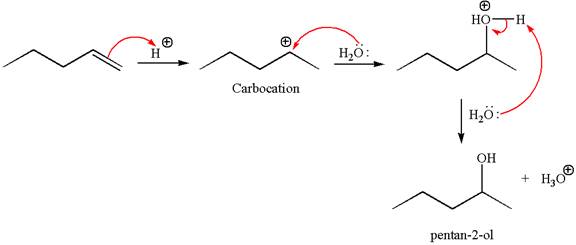
The reaction occurs in acidic condition. Thus the first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted carbon, forming a more stable carbocation.
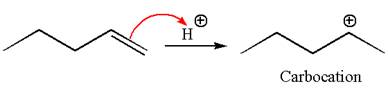
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming the desired product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
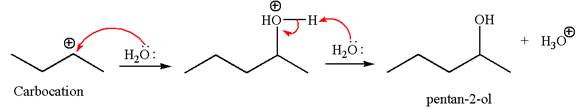
The reaction equation and detailed mechanism are drawn for the formation of
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction with detailed mechanism for the formation of the given compound from the corresponding alkene by single electrophilic addition reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene occurs through formation of a more stable carbocation. The electrophilic addition of water across the double bond in an acidic condition produces the alcohol product. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation, followed by the action of water as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 11.33P
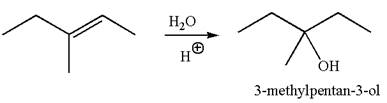
The reaction equation and the detailed mechanism for the formation of
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
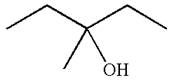
To form the given alcohol by electrophilic addition of water, the double bond must be between the carbon where the
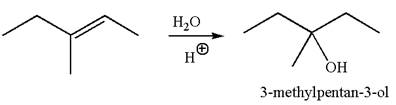
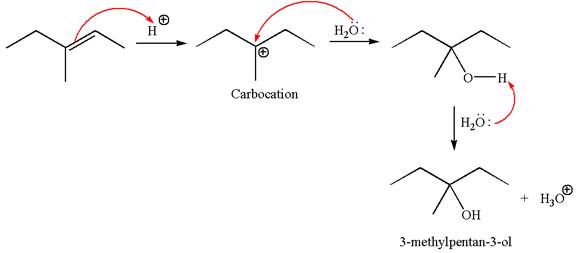
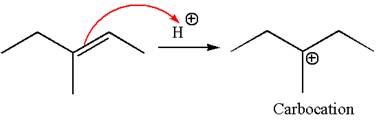
The reaction occurs in acidic condition. Thus the first step is the formation of a tertiary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted carbon, forming a more stable carbocation.
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming the desired product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
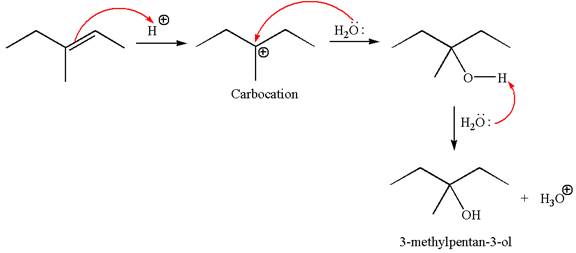
The reaction equation and detailed mechanism are drawn for the formation of
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction with detailed mechanism for the formation of the given compound from the corresponding alkene by single electrophilic addition reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene occurs through formation of a more stable carbocation. The electrophilic addition of water across the double bond in an acidic condition produces the alcohol product. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation, followed by the action of water as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 11.33P
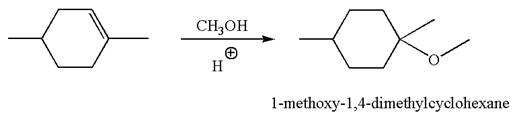
The reaction equation and the detailed mechanism for the formation of
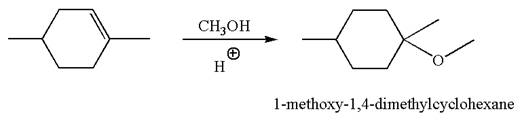
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
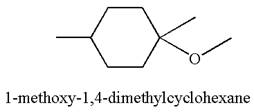
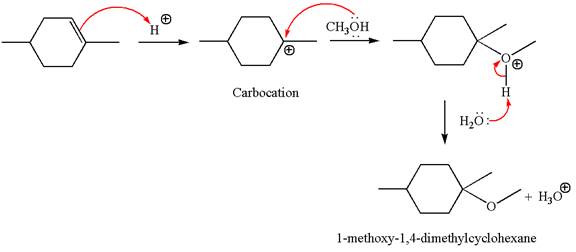
To form the given ether by electrophilic addition of alcohol, the double bond must be between the carbon where the
The reaction occurs in acidic condition. Thus the first step is the formation of a tertiary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted carbon, forming a more stable carbocation.
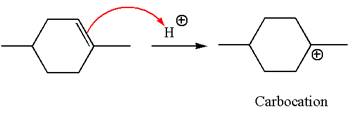
In the second step, the methanol molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming the desired product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
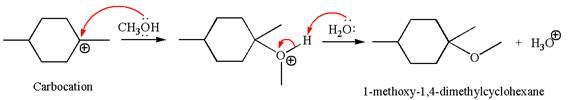
The reaction equation and detailed mechanism are drawn for the formation of
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction with detailed mechanism for the formation of the given compound from the corresponding alkene by single electrophilic addition reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene occurs through formation of a more stable carbocation. The electrophilic addition of water across the double bond in an acidic condition produces the alcohol product. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation, followed by the action of water as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 11.33P
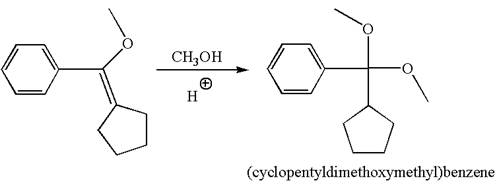
The reaction equation and the detailed mechanism for the formation of (cyclopentyldimethoxymethyl) benzene from alkene are
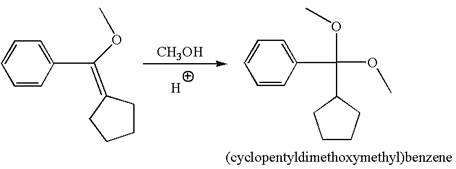
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound (cyclopentyldimethoxymethyl) benzene is
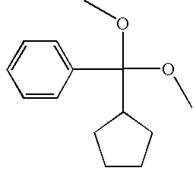
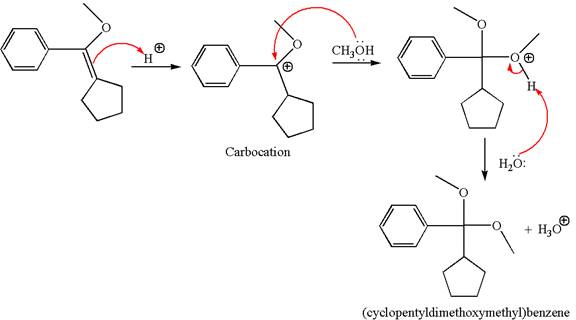
To form the given ether by single electrophilic addition of alcohol, the double bond must be between the carbon where the
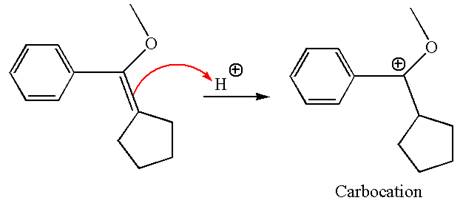
The reaction occurs in acidic condition. Thus the first step is the formation of a tertiary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted carbon, forming a more stable carbocation.
In the second step, the methanol molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation, forming the desired product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
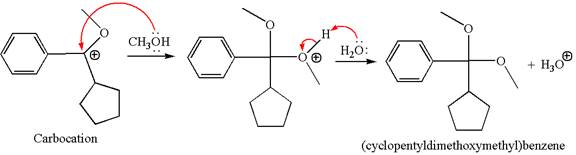
The reaction equation and detailed mechanism are drawn for the formation of (cyclopentyldimethoxymethyl) benzene by identifying the corresponding alkene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Please provide detailed mechanism of this reaction. Thanks so much.arrow_forwardPlease provide a complete, detailed curved-arrow mechanism for the following reaction. Include ALL lone pairs and formal charges. Using the mechanism and a few words, explain why the NaOH deprotonates at the a-position and not the b-position or the aldehyde hydrogen. Also, explain why the indicated alkene is formed in the 2nd second rather than the other possible alkene product.arrow_forwardA student found that heating any one of the isomers shown here resulted in scrambling of the deuterium to all three positions on the five-membered ring. Propose a mechanism to account for this observation.arrow_forward
- please explain what happens in this reaction mechanism. be as DETAILED as possible. acetylene + bromide reactionarrow_forwardRepresent a structure of product A (bicyclic molecule) and propose a detailed mechanism for its preparation.arrow_forwardWhich of the folloqing best describes the major product for the following substitution reaction? (Only the major product of this reaction I will add as a photo!) Please show all steps for how you get to this for my full understanding!arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





