
Nitryl fluoride is an explosive compound that can be made by oxidizing nitrogen dioxide with fluorine:
2 NO2(g) + F2(g) → 2 NO2F(g)
Several kinetics experiments, all done at the same temperature and involving formation of nitryl fluoride, are summarized in this table:
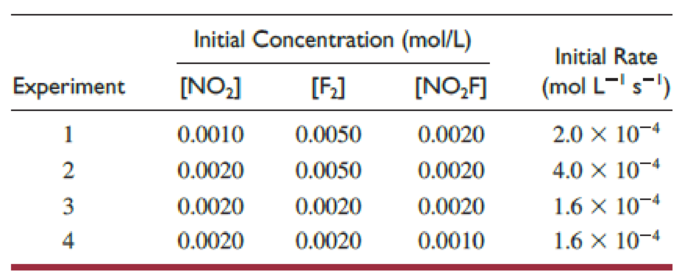
- (a) Write the rate law for the reaction.
- (b) Determine what the order of the reaction is with respect to each reactant and each product.
- (c) Calculate the rate constant k and express it in appropriate units.
(a)
Interpretation:
The rate law for the reaction has to be written.
Explanation of Solution
Suppose the rate law of the above reaction is as follows,
Where,
Carefully examining the table, it can be said that
Now, on dividing both the equations, the value of j can be found out.
Similarly, carefully examining the table, it can be said that
Now, on dividing both the equations, the value of i can be found out.
Similarly, carefully examining the table, it can be said that
Now, on dividing both the equations, the value of h can be found out.
Therefore, the rate law for the reaction is
(b)
Interpretation:
The order of the reaction with respect to each reactant and each product has to be determined.
Explanation of Solution
The rate law for the reaction is
Therefore, the order of the reaction with respect to
(c)
Interpretation:
The rate constant
Answer to Problem 95QRT
The average of the rate constant is
Explanation of Solution
The rate constant can be expressed as shown below.
For first experiment the rate constant can be calculated by plugging all the data given in the table.
In the first experiment, the initial concentration of
Now, the rate constant for first experiment is given below.
Similarly, the rate constant for rest of the experiments can be calculated. The calculated rate constant values are given in the table below.
|
Initial rate |
Rate constant | ||
The average of the rate constant is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science, Hybrid Edition (with OWLv2 24-Months Printed Access Card)
- Chlorine dioxide, ClO2, is a reddish-yellow gas that is soluble in water. In basic solution it gives ClO3 and ClO2 ions. 2ClO2(aq)+2OH(aq)ClO3(aq)+ClO2(aq)+H2O To obtain the rate law for this reaction, the following experiments were run and, for each, the initial rate of reaction of ClO2 was determined. Obtain the rate law and the value of the rate constant.arrow_forwardThe isomerization of cyclopropane, C3H6, is believed to occur by the mechanism shown in the following equations: C3H6+C3H5k1C3H6+C3H6(Step1)C3H6k2C2=CHCH3(Step2) Here C3H6 is an excited cyclopropane molecule. At low pressure, Step 1 is much slower than Step 2. Derive the rate law for this mechanism at low pressure. Explain.arrow_forwardExpress the rate of the reaction 2N2O(g)2N2(g)+O2(g) in terms of (b) [ N2O ] (a) [ O2 ]arrow_forward
- The thermal decomposition of nitryl chloride, NO2Cl, 2NO2Cl(g)2NO2(g)+Cl2(g) is thought to occur by the mechanism shown in the following equations: NO2Clk1NO2+Cl(slowstep)NO2Cl+Clk2NO2+Cl2(faststep) What rate law is predicted by this mechanism?arrow_forwardGiven the following mechanism for a chemical reaction: H2O2+IH2O+IOH2O2+IOH2O+O2+I a Write the overall reaction. b Identify the catalyst and the reaction intermediate. c With the information given in this problem, can you write the rate law? Explain.arrow_forwardOne possible mechanism for the decomposition of nitryl chloride, NO2CI, is What is the overall reaction? What rate law would be derived from this mechanism? What effect does increasing the concentration of the product NO2 have on the reaction rate?arrow_forward
- Nitrosyl bromide, NOBr, is formed from NO and Br2: 2 NO(g) + Br2(g) 2 NOBr(g) Experiments show that this reaction is second-order in NO and first-order in Br2. (a) Write the rate equation for the reaction. (b) How does the initial reaction rate change if the concentration of Br2 is changed from 0.0022 mol/L to 0.0066 mol/L? (c) What is the change in the initial rate if the concentration of NO is changed from 0.0024 mol/L to 0.0012 mol/L?arrow_forwardIsomerization of CH3NC occurs slowly when CH3NC is heated. CH3NC(g) CH3CN(g) To study the rate of this reaction at 488 K, data on [CH3NC] were collected at various times. Analysis led to the following graph. (a) What is the rate law for this reaction? (b) What is the equation for the straight line in this graph? (c) Calculate the rate constant for this reaction. (d) How long does it take for half of the sample to isomerize? (e) What is the concentration of CH3NC after 1.0 104 s?arrow_forwardFor the reaction A+BC, explain at least two ways in which the rate law could be zero order in chemical A.arrow_forward
- At 573 K, gaseous NO2(g) decomposes, forming NO(g) and O2(g). If a vessel containing NO2(g) has an initial concentration of 1.9 102 mol/L, how long will it take for 75% of the NO2(g) to decompose? The decomposition of NO2(g) is second-order in the reactant and the rate constant for this reaction, at 573 K, is 1.1 L/mol s.arrow_forwardThe rate of the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, depends on the concentration of iodide ion present. The rate of decomposition was measured at constant temperature and pressure for various concentrations of H2O2and of KI. The data appear below. Determine the order of reaction for each substance, write the rate law, and evaluate the rate constant. Rate [H2OJ [Kll (mL min-’) (mol L ’) (mol L ’) 0.090 0.15 0.033 0.178 0.30 0.033 0.184 0.15 0.066arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





