
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.4, Problem 3bT
The photograph at right shows the diffraction pattern produced by laser light incident on a narrow slit.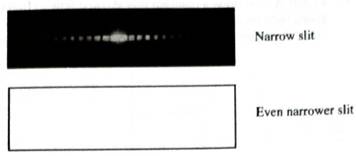
Use the model that we have developed to predict how the pattern would change it the slit were made even,narrower. Explain your reasoning and sketch your prediction in the space provided at right.
Ask a tutorial instructor for the photograph showing diffraction patterns produced by light Incident on a narrow slit and on an even narrower slit so that you may check your predictions.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A thin beam of white light is directed at a flat sheet of silicate flint glass at an angle of 20° to the surface of the sheet. Due to dispersion in the glass, the beam is spread out in a spectrum as shown in the figure. The refractive index of silicate flint glass versus wavelength is graphed in figure to the right. (a) The rays (A and B) shown in the figure correspond to the extreme wavelengths. Which corresponds to red and which to violet? Explain your reasoning. (b) For what thickness of the glass sheet will the spectrum be 1.0 mm wide, as shown (see Problem 7)? Hint: you must first solve Problem 7 first before doing Problem 8). Answer: 93.5 mm
A narrow beam of light is incident on the left side of the prism shown in the figure below. The prism is a right triangle, with two of its angles measuring 45°.
A) The transmitted beam that exits the hypotenuse of the prism makes an angle of
? = 17.5° with the direction of the incident beam. What is the index of refraction of the prism?
B) In part (a), we assumed the beam was monochromatic. Consider instead the case where the beam was composed of white light. Because the index of refraction differs for different wavelengths, the white light would be dispersed into constituent colors. Assume the index of refraction for blue wavelengths is 1.01n and for red wavelengths it is 0.99n, where n is the index of refraction found in part (a). What is the angular spread (in degrees) between red and blue light exiting the prism?
A plane wave hits a piece of glass whose front surface is spherical and whose back surface is plane. The radius of the lens is 10 cm and the thickness of the glass is 1 cm at the center, as shown in the diagram at right. At time t1, the center of the plane wavefront has just reached the lens. A short time later, at time t2, the center of the wavefront will have passed completely through the glass, as shown.
a) Find the time that elapses between t1 and t2, the time it takes the center of the wavefront to pass thorugh the middle 1 cm of the glass.
b) Find the amount by which the edges of the wavefront at t2 will be ahead of the cetner of the wavefront, due to the fact that these edges passed through empty space, with no glass in their paths.
Chapter 11 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 1TCh. 11.1 - Prob. 2aTCh. 11.1 - Prob. 2bTCh. 11.1 - Prob. 2cTCh. 11.1 - The representation that we have been using...Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 2eTCh. 11.1 - Prob. 2gTCh. 11.1 - Each of the photographs at right shows a part of a...Ch. 11.1 - Obtain a piece of paper and a transparency with...Ch. 11.2 - Obtain a pan of water and form a barrier in it...
Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 2aTCh. 11.2 - Obtain an enlargement of the diagram at right that...Ch. 11.2 - Suppose that the width of one of the slits were...Ch. 11.2 - Red light from a distant point source is incident...Ch. 11.2 - Compare the situation in part II (in which a...Ch. 11.2 - For each of the lettered points, determine D (in...Ch. 11.2 - Suppose that one of the slits were covered. At...Ch. 11.2 - The pattern produced by red light passing through...Ch. 11.2 - Consider point B, the first maximum to the left of...Ch. 11.3 - Red light from a distant point source is incident...Ch. 11.3 - In a previous homework, you found an expression...Ch. 11.3 - Suppose that the screen were semicircular, as...Ch. 11.3 - Consider a point M on the distant screen where...Ch. 11.3 - Consider a point N on the screen where there is a...Ch. 11.3 - Obtain a set of transparencies of sinusoidal...Ch. 11.3 - Suppose that coherent red light were incident on a...Ch. 11.3 - Generalize your results from the 2-slit, 3-slit,...Ch. 11.3 - Coherent red light is incident on a mask with two...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 3dTCh. 11.4 - Red light from a distant point source is incident...Ch. 11.4 - Suppose that point X marks the location of the...Ch. 11.4 - Suppose that only slit 1 is uncovered, and all...Ch. 11.4 - Show how you could group all ten slits into five...Ch. 11.4 - Suppose that the number of slits is doubled and...Ch. 11.4 - If we continued to add slits in this way (i.e.,...Ch. 11.4 - How is this pattern different from what you would...Ch. 11.4 - Consider the following dialogue: Student 1: "l...Ch. 11.4 - The photograph at right shows the diffraction...Ch. 11.4 - The photograph at right shows the diffraction...Ch. 11.4 - Describe what you would see on the screen if the...Ch. 11.4 - If a diffraction pattern has several minima (like...Ch. 11.4 - In part A, you drew a diagram that showed how find...Ch. 11.4 - Use the model that we have developed to write an...Ch. 11.5 - The minima that occur in the case of a single slit...Ch. 11.5 - Consider the following dispute between two physics...Ch. 11.5 - A second slit, identical in size to the first, is...Ch. 11.5 - Both slits are now uncovered. For what angles will...Ch. 11.5 - Suppose that the width of both slit, a, were...Ch. 11.5 - Suppose instead that the distance between the...Ch. 11.5 - The four graphs from part C that show relative...Ch. 11.5 - Consider the relative intensity graph shown at...Ch. 11.5 - Consider the following comment made by a student:...Ch. 11.5 - You may have already noticed that the maxima are...Ch. 11.6 - Prob. 1TCh. 11.6 - Prob. 2aTCh. 11.6 - When comparing two materials of different indices...Ch. 11.6 - Consider light incident on a thin soap film, as...Ch. 11.6 - Light of frequency f=7.51014Hz is incident on the...Ch. 11.6 - Suppose that an observer were located on the left...Ch. 11.6 - Observer A is looking at the part of the film that...Ch. 11.6 - Observer B is looking at the part of the film that...Ch. 11.6 - Observer C is looking at the thinnest part of the...Ch. 11.6 - Describe the appearance of the film as a whole.Ch. 11.6 - What are the three smallest film thickness for...Ch. 11.6 - The thickness of the film is 1650 nm at the bottom...Ch. 11.7 - Look at the room lights through one of the...Ch. 11.7 - Hold a second polarizing filter in front of the...Ch. 11.7 - Do the room lights produce polarized light?...Ch. 11.7 - Suppose that you had two marked polarizers (i.e.,...Ch. 11.7 - Suppose that you had a polarizer with its...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 2dTCh. 11.7 - An observer is looking at a light source through...Ch. 11.7 - Consider a beam of unpolarized light that is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
As an oil well is drilled, each new section of drill pipe support its own weight and the weight of the pipe and...
University Physics Volume 1
How could you determine which pole of an electromagnet is north and which pole is south?
University Physics Volume 2
40.(II) If 21.0 V is applied across the whole network of Fig. 19-63, calculate (a) the voltage across each capa...
Physics: Principles with Applications
Two identical bubbles of gas form at the bottom of a lake, then rise to the surface. Because the pressure is mu...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The experiment described in question 2 above is performed, but this time, a strip of transparent plastic is placed over the left slit. Its presence changes the interference between light waves from the two slits, causing the interference pattern to be shifted across the screen from the original pattern. Explain, clearly but briefly, which way (right or left) the original pattern shifts and why this shift occurs.arrow_forwardA beam of white light, containing wavelengths from 400 nm (violet) to 750 nm (red), is directed at a pair of narrow slits 0.002 mm apart. Sketch and label the patterns (i.e., locations and colors) of light which will be seen on a large wall behind the slits. Show any calculations that you use to justify your sketch.arrow_forwardIf light with a wavelength of 480 nm is used in a two-slit experiment with a barrier with slits that are 0.05 mm apart that is 1.6 m from the projection screen. What is the distance from the center of the first and third dark fringes? Show your work.arrow_forward
- Please answer it short and easy to understand.How does a single slit affect the wave pattern? How does a double slit affect the wave pattern?arrow_forwardGiven the light fixture on the picture. In this device you will be able to change the beam angle from 5 to 60 degrees. Assume an isometric distribution of the light on the illuminated surface 1) If the distance to the floor is 3 meters, what will be the beam angle that will produce an Illuminated surface Diameter of 2 meters?arrow_forwardTwo radio antennas separated by d = 270 m, as shown in the figure below, simultaneously broadcast identical signals at the same wavelength. A car travels due north along a straight line at position x = 1,030 m from the center point between the antennas, and its radio receives the signals. Hint: Do not use the small-angle approximation in this problem. (a) If the car is at the position of the second maximum after that at point O when it has traveled a distance of y = 400 m northward, what is the wavelength of the signals? m(b) How much farther must the car travel from this position to encounter the next minimum in reception? marrow_forward
- I need a proper solution for the following ( understandable writing and well explained ) How are reflection and refraction similar and different? and how does a prism affect white light? Plus, how is a rainbow formed?arrow_forwardIn a Young's double-slit experiment, blue light (?λ = 440 m) gives a second-order bright fringe at a certain location on a flat screen. What wavelength of visible light would produce a dark fringe at the same location? Assume that the range of visible wavelengths extends from 380 to 750 nm. Calculate the wavelength that fulfills the problem description. Clearly show all steps, starting from generalized equations. Explain your mathematical work in words. Your explanation should cover both what you did, any approximations you make and the thought process behind why you did that. Evaluate your answer to determine whether it is reasonable or not. Consider all aspects of your answer (the numerical value, sign, and units) in your evaluation.arrow_forwardDirections: Solve the following problems. Show your complete solutions legibly and concisely in the space below each item. Solve the following: (a) What is the width of a single slit that produces its first minimum at 60.0° for 600 nm light? (b) Find the light wavelength with its first minimum at 62.0°.arrow_forward
- For the figure shown below, the two sources are 6cm apart, and they are in phase. Two paths are drawn from the sources to a point. (The picture is to scale, even if the sources are not 6cm apart on the paper.) (a) If the wavelength of the two sources is 2cm, for the picture, figure out whether the point marks a position of constructive or destructive interference. (b) Repeat if the wavelength is 1cm.arrow_forwardWhat angle is needed between the direction of polarized light and the axis of a polarizing filter to reduce its intensity by 68%? Write your pourcentage with 3 sig fig. Please show full work!!arrow_forwardIf the incident ray at point A is at the critical angle between mediums 2 and 3, does the ray incident at point B refract out of medium 2 into 3? If so, what is the (i) angle of refraction at point B? If not, what is the reflected angle at point B? (ii) Draw an accurate ray diagram at point B. (iii) What is the initial angle θ at point C?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Domestic Electric Circuits; Author: PrepOnGo Class 10 & 12;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2ZvWaloQ3nk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY