
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The number of rings and number of pi bonds in A is to be determined. And one possible structure is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Degree of unsaturation is used to determine the total number of rings and pi bonds present in compound by just looking at the molecular formula. It does not specify the total number of rings and total number of pi bonds individually.
Answer to Problem 12.35P
The number of pi bonds and number of rings in A is one. The possible structure is given in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
For compound A:
Before hydrogenation, the molecular formula is
The maximum number of
The maximum number of
The number of
Substitute the values of maximum number of
The degree of unsaturation is calculated by the formula,
Hence, the degree of unsaturation before hydrogenation is two.
After hydrogenation, the molecular formula is
The maximum number of
The maximum number of
The number
Substitute the values of maximum number of
The degree of unsaturation is calculated by the formula,
Hence, the degree of unsaturation after hydrogenation is one.
The number of pi bonds in A is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the values of degree of unsaturation before hydrogenation and degree of unsaturation after hydrogenation in the above formula.
Hence, the number of pi bonds is one.
Number of rings is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the values of degree of unsaturation and number of pi bonds in the above formula.
Hence, the number of rings is one.
The possible structure for A is,
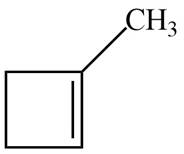
Figure 1
The number of pi bonds and number of rings in A is one. The possible structure is given in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The number of rings and number of pi bonds in B is to be determined. And one possible structure is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Degree of unsaturation is used to determine the total number of rings and pi bonds present in compound by just looking at the molecular formula. It does not specify the total number of rings and total number of pi bonds individually.
Answer to Problem 12.35P
The number of pi bonds and number of rings in B is one and two respectively. The possible structure is given in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
For compound B:
Before hydrogenation, the molecular formula is
The maximum number of
The maximum number of
The number of
Substitute the values of maximum number of
The degree of unsaturation is calculated by the formula,
Hence, the degree of unsaturation before hydrogenation is three.
After hydrogenation, the molecular formula is
The maximum number of
The maximum number of
The number
Substitute the values of maximum number of
The degree of unsaturation is calculated by the formula,
Hence, the degree of unsaturation after hydrogenation is two.
The number of pi bonds in A is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the values of degree of unsaturation before hydrogenation and degree of unsaturation after hydrogenation in the above formula.
Hence, the number of pi bonds is one.
Number of rings is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the values of degree of unsaturation and number of pi bonds in the above formula.
Hence, the number of rings is two.
The possible structure for B is,
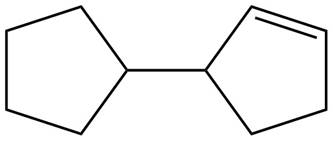
Figure 2
The number of pi bonds and number of rings in B is one and two respectively. The possible structure is given in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The number of rings and number of pi bonds in B is to be determined. And one possible structure is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Degree of unsaturation is used to determine the total number of rings and pi bonds present in compound by just looking at the molecular formula. It does not specify the total number of rings and total number of pi bonds individually.
Answer to Problem 12.35P
The number of pi bonds and number of rings in C is four and one respectively. The possible structure is given in Figure 3.
Explanation of Solution
For compound C:
Before hydrogenation, the molecular formula is
The maximum number of
The maximum number of
The number of
Substitute the values of maximum number of
The degree of unsaturation is calculated by the formula,
Hence, the degree of unsaturation before hydrogenation is five.
After hydrogenation, the molecular formula is
The maximum number of
The maximum number of
The number
Substitute the values of maximum number of
The degree of unsaturation is calculated by the formula,
Hence, the degree of unsaturation after hydrogenation is one.
The number of pi bonds in A is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the values of degree of unsaturation before hydrogenation and degree of unsaturation after hydrogenation in the above formula.
Hence, the number of pi bonds is four.
Number of rings is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the values of degree of unsaturation and number of pi bonds in the above formula.
Hence, the number of rings is one.
The possible structure for C is,
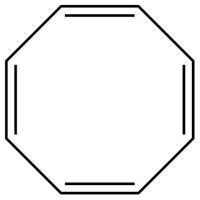
Figure 3
The number of pi bonds and number of rings in C is four and one respectively. The possible structure is given in Figure 3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- An ion with a positively charged nitrogen atom in a three-membered ring is called an aziridinium ion. The following aziridinium ion reacts with sodiummethoxide to form compounds A and B: If a small amount of aqueous Br2 is added to A, the reddish color of Br2 persists, but the color disappears when Br2 is added to B. When the aziridinium ion reacts with methanol, only A is formed. Identify A and B.arrow_forwardRank the following groups in order of decreasing priority. a.−F, −NH2, −CH3, −OH b.−CH3, −CH2CH3, −CH2CH2CH3, −(CH2)3CH3 c.−NH2, −CH2NH2, −CH3, −CH2NHCH3 d.−COOH, −CH2OH, −H, −CHO e.−Cl, −CH3, −SH, −OH f.−C≡CH, −CH(CH3)2, −CH2CH3, −CH=CH2arrow_forwardPGF2α (Section 4.15) is synthesized in cells from arachidonic acid (C20H32O2) using a cyclooxygenase enzyme that catalyzes a multistep radical pathway. Part of this process involves the conversion of radical A to PGG2, an unstableintermediate, which is then transformed to PGF2α and other prostaglandins. Draw a stepwise mechanism for the conversion of A to PGG2. (Hint: The mechanism begins with radical addition to a carbon–carbon double bond to form a resonance-stabilized radical.)arrow_forward
- Treatment of compound A (C8H17Br) with NaOCH2CH3 affords twoconstitutional isomers B and C. Ozonolysis of B affords CH2=O and(CH3CH2CH2)2C=O. Ozonolysis of C affords CH3CH2CH2COCH3 andCH3CH2CHO. What is the structure of A?arrow_forwardPGF2α (Section 4.15) is synthesized in cells from arachidonic acid (C20H32O2) using a cyclooxygenase enzyme that catalyzes a multistep radical pathway. Part of this process involves the conversion of radical A to PGG2, an unstable intermediate, which is then transformed to PGF2α and other prostaglandins. Draw a stepwise mechanism for the conversion of A to PGG2. (Hint: The mechanism begins with radical addition to a carbon–carbon double bond to form a resonance-stabilized radical.)arrow_forwardDraw the structure of a hydrocarbon that has six carbon atoms and a. three vinylic hydrogens and two allylic hydrogens. b. three vinylic hydrogens and one allylic hydrogen. c. three vinylic hydrogens and no allylic hydrogens.arrow_forward
- An optically active unknown compound B, whose molecular formula is C6H10, reacts with H2/Ni produce compound C, whose molecular formula is C6H14. Compound C is optically inactive. What are the structures of compound B and C ?arrow_forwardAccount for the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity observed when 1-methylcyclopentene is treated with reagent. Q) BH3arrow_forwardDraw the structures of the products obtained from the reaction of each enantiomer of cis-1-chloro-2-isopropylcyclopentane with sodium methoxide in methanol. b. Are all the products optically active? c. How would the products differ if the starting material were the trans isomer? Are these products optically active? d. Will the cis enantiomers or the trans enantiomers form substitution products more rapidly? e. Will the cis enantiomers or the trans enantiomers form elimination products more rapidly?arrow_forward
- An unknown compound A of molecular formula C10H18O reacts with H2SO4 to form two compounds (B and C)of molecular formula C10H16. B and C both react with H2 in the presence of Pd-C to form decalin. Ozonolysis of B forms D, and ozonolysis of C forms a diketone E of molecular formula C10H16O2. Identify the structures of compounds A, B, C, and E.arrow_forwardTreatment of compound A (C8H17Br) with NaOCH2CH3 affords two constitutional isomers B and C. Ozonolysis of B affords CH2=O and (CH3CH2CH2)2C=O. Ozonolysis of C affords CH3CH2CH2COCH3 and CH3CH2CHO. What is the structure of A?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

