
To analyze:
In the given table, the partial diploid genotypes are tested for the following aspescts:
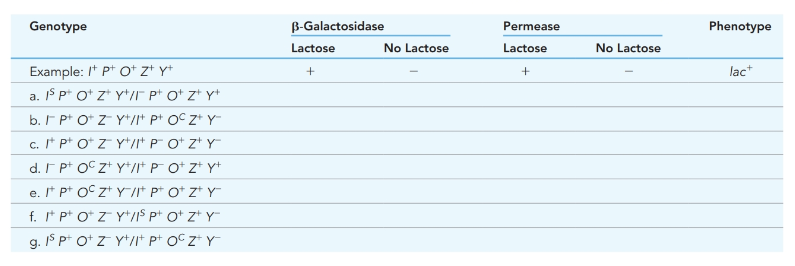
Complete the following table for production of
Introduction:
In the lac operon, the partial diploids are produced by conjugation between
Based on the studies of structural gene mutations, Jacob, Monod, and Colleagues concluded that lac
These two wild type alleles are always dominant to the mutant type alleles.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 12 Solutions
Study Guide And Solutions Manual For Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach
- What are the two main mechanisms by which cells repair doublestrandbreaks? Briefly describe each one.arrow_forwardA number of auxotrophic mutant strains were isolated from wild-type haploid Neurospora crassa. These strains responded to the addition of certain nutritional supplements to minimal culture medium either by growth (+) or no growth (0) The data from this experiment are presented in the table below. Diagram a biochemical pathway, complete with positions of intermediates, that is consistent with the data. Indicate where in the pathway each mutant strain is blocked.arrow_forwardWhy do E. coli cells with a defective lacZ gene fail to show galactoside permease activity after the addition of lactose in the absence of glucose?arrow_forward
- Which of the following correctly describes the regulation and activity of HIF-1? Group of answer choices VHL is required for preventing degradation of HIF-1alpha and promoting translocation to the nucleus In normoxia, HIF-1alpha is ubquitinated and degraded in the proteasome Hypoxic conditions result in increase hydroxylation of prolines in HIF-1alpha The primary function of HIF-1 is to phosphorylate and activate glycolytic enzymesarrow_forwardWhat is/are the possible genotype(s) of an individual who is lactose tolerant?arrow_forwardHow many of these strains of E. coli would have no ß-galactosidase activity?arrow_forward
- Why is Molisch's test used for the determination of the presence of pentose in the yeast RNA hydrolysate and what other tests could be used for this?arrow_forwardHow many functional copies of ɑAA reductase does a yeast cell need in order to perform lysine biosynthesis in a haploid cell? In a diploid cell?arrow_forwardIn studies of the amino acid sequence of wild-type and mutant forms of tryptophan synthetase in E. coli, the following changes have been observed: Determine a set of triplet codes in which only a single-nucleotide change produces each amino acid change.arrow_forward
- How many different types of mutations can result in lactase persistence and what are their names?arrow_forwardCompounds A, B, C, and D are known to be intermediates in the pathway for production of protein E. To determine where the block in protein-E production occurred in each individual, the various intermediates were given to each individual’s cell in culture. After a few weeks of growth with the intermediate, the cells were assayed for the production of protein E. The results for each individual’s cells are given in the following table. A plus sign means that the protein E was produced after the cells were given the intermediate listed at the top of the column. A minus sign means that the cells still could not produce protein E even after being exposed to the intermediate at the top of the column. a) If an individual who is homozygous for the mutation found in individual 2 and heterozygous for the mutation found in individual 4 mates with an individual who is homozygous for the mutation found in individual 4 and heterozygous for the mutation found in individual 2, what could the…arrow_forwardA mutant has no activity for the enzyme isocitrate lyase.Does this result prove that the mutation is in the geneencoding isocitrate lyase?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
