
EBK GENETICS: FROM GENES TO GENOMES
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220100255250
Author: HARTWELL
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 43P
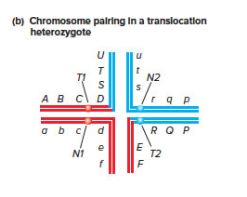
Chromosomes normally associate during meiosis I as bivalents (a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes) because chromosome pairing involves the synapsis of the corresponding regions of two homologous chromosomes. However, Fig. 13.17b shows that in a heterozygote for a reciprocal translocation, chromosomes pair as quadrivalents (that is, four chromosomes are associated with each other). Quadrivalents can form in other ways: For example, in some autotetraploid species, chromosomes can pair as quadrivalents rather than as bivalents.
| a. | How could quadrivalents actually form in these autotetraploids, given that chromosomal regions synapse in pairs? To answer this question, diagram such a quadrivalent. |
| b. | How can these autotetraploid species generate euploid gametes if the chromosomes pair as quadrivalents rather than bivalents? |
| c. | Could quadrivalents form in an amphidiploid species? Discuss. |
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An individual heterozygous for a reciprocal translocation possesses the following chromosomes: A B ● C D E F G, A B • C D V W X, R S •T U E F G, R S•T U V W Xa. Draw the pairing arrangement of these chromosomes in prophase 1 of meiosis. Mention their gametic composition. b. Draw the alternate, adjacent I, and adjacent II segregation patterns in anaphase I of meiosis. Mention their gametic composition.
A diploid individual is heterozygous for a chromosome rearrangement. The original chromosome and its rearranged homolog have the following segments, where ∙ represents a centromere:
A B ∙ C D E F G
A B ∙ C F E D G
While paired in prophase I, a single crossing-over occurs between segment E and segment D of the paired chromosomes. Describe the unusual crossing-over structure that forms as a result.What gamete types will result from crossing over when meiosis is complete?
please asap
An individual is heterozygous for a reciprocal translocation, with the following chromosomes:
A • B C D E F
A • B C V W X
R ST • U D E F
R ST • U V W X
Q. Draw a picture of these chromosomes pairing in prophase I of meiosis.
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK GENETICS: FROM GENES TO GENOMES
Ch. 12 - For each of the terms in the left column, choose...Ch. 12 - Prob. 2PCh. 12 - For each of the following types of chromosomal...Ch. 12 - For the following types of chromosomal...Ch. 12 - One of the X chromosomes in a particular...Ch. 12 - Prob. 6PCh. 12 - Prob. 7PCh. 12 - Prob. 8PCh. 12 - Two wild-type fragments of human genomic DNA from...Ch. 12 - Indicate which of the four major classes of...
Ch. 12 - The recessive, X-linked z1 mutation of the...Ch. 12 - Genes a and b are 21 m.u. apart when mapped in...Ch. 12 - In the following group of figures, the pink lines...Ch. 12 - Three strains of Drosophila Bravo, X-ray, and...Ch. 12 - Prob. 15PCh. 12 - Suppose a haploid yeast strain carrying two...Ch. 12 - In the mating between two haploid yeast strains...Ch. 12 - During ascus formation in Neurospora, any...Ch. 12 - In the following figure, black and pink lines...Ch. 12 - In Drosophila, the gene for cinnabar eye color is...Ch. 12 - Semisterility in corn, as seen by unfilled ears...Ch. 12 - Prob. 22PCh. 12 - Prob. 23PCh. 12 - Prob. 24PCh. 12 - Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD is caused by a...Ch. 12 - Explain how transposable elements can cause the...Ch. 12 - The Drosophila genome normally harbors about 40 P...Ch. 12 - Prob. 28PCh. 12 - Fred and Mary have a child named Bob. The genomic...Ch. 12 - Uniparental disomy is a rare phenomenon in which...Ch. 12 - Among adults with Turner syndrome, it has been...Ch. 12 - In Neurospora, his2 mutants require the amino acid...Ch. 12 - Human geneticists interested in the effects of...Ch. 12 - The incidence of Down syndrome will be very high...Ch. 12 - The Drosophila chromosome 4 is extremely small;...Ch. 12 - Down syndrome is usually caused by having a...Ch. 12 - Common red clover, Trifolium pratense, is a...Ch. 12 - The numbers of chromosomes in the somatic cells of...Ch. 12 - Prob. 39PCh. 12 - Somatic cells in organisms of a particular diploid...Ch. 12 - Prob. 41PCh. 12 - Prob. 42PCh. 12 - Chromosomes normally associate during meiosis I as...Ch. 12 - Using whole-genome sequencing, how could you...Ch. 12 - Prob. 45PCh. 12 - Prob. 46PCh. 12 - Seedless watermelons that you find in the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 48PCh. 12 - What characteristic property of translocations...Ch. 12 - In examining the genome of the rice Oryza sativa...Ch. 12 - Prob. 51PCh. 12 - Prob. 52PCh. 12 - The accompanying figure shows idiograms of human...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- People with Down syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21, for a total of 47 chromosomes. However, in a few cases of Down syndrome, 46 chromosomes are present. This total includes two normal-looking chromosomes 21, one normal chromosome 14, and a longer-than-normal chromosome 14. Interpret this observation. How can these individuals have 46 chromosomes?arrow_forwardAssume that a meiotic-nondisjunction event causes trisomy 8 in a newborn. If two of the three copies of chromosome 8 are absolutely identical, at what point during meiosis did the nondisjunction event take place?arrow_forwardA colleague e-mails you saying that she has identified an interesting chromosome variation at 21q13. In discussing this discovery with a friend who is not a cytogeneticist, explain how you would describe this location, defining each term in the chromosome address 21q13.arrow_forward
- An individual heterozygous for a reciprocal translocation possesses the following chromosomes: A B • C D E F G A B • C D V W X R S • T U E F G R S • T U V W X Q. Draw the pairing arrangement of these chromosomes in prophase I of meiosis.arrow_forwardHere is a depiction of the position of several genes on 2 chromosomes, with a dash "-" depicting the position of the centromere. Chromosome A has genes ABCD-EFGHIJ Chromosome B has genes 1234-56789. Please name the kind of rearrangement that would result in the following derivative chromosomes: 12D-EFGHIJ AB4-56789 O Unbalanced reciprocal translocation Unbalanced nonreciprocal translocation Balanced reciprocal translocation Balanced nonreciprocal translocationarrow_forwardAssume that the diploid number of a certain species is four chromosomes, two large and two small (2n=4). a) Of the following figures, which represents a 3n (triploid) cell in mitotic metaphase? b) For each of the wrong answers from part (a) above, explain briefly why it cannot represent a triploid cell in mitotic metaphase.arrow_forward
- During metaphase I of meiosis, tetrads align along the metaphase plate independently of each other. Therefore, there is a random “shuffle” of maternal and paternal chromosomes in the resulting gametes.The following diagram demonstrates how this works in a diploid cell with four chromosomes . Because there are two pairs of chromosomes and each pair can align in one of two ways during metaphase I, the number of possible variations in the gametes produced is , or .For an organism that is , there are three pairs of chromosomes, so the number of possible variations in the gametes produced due to independent assortment in metaphase I is , or . In an organism with a haploid number of , how many possible combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes can occur in its gametes? Select one: a. 72=49 b. 27=128 c.17=1 d. 214=16 384arrow_forwardThe STR DNA marker DS11 is located on the p arm of the chromosome #8 in humans. Molecular analysis has shown that Charlie Chaplin is a heterozygote for the STR marker (genotype DS11A and DS11B) Using this knowledge, provide a diagram of meiosis showing only the movements of chromosome 8 (assume no nondisjunction). Throughout, indicate where the marker may be found (in other words, label the chromosome to show where the STR markers can be found. (Show ONLY the chromosomes at interphase, metaphase 1, end of meiosis 1, metaphase 2, and end of meiosis 2). Suppose Charlie conceived a son with a chromosome 8 trisomy. Molecular analysis of the STR DS11 marker revealed that his son carried two copies of the DS11A marker and a DS11C marker. Based on the data, determine if the nondisjunction occurred in Charlie or in the mother? Provide your reasoning.arrow_forwardin metaphase 1 of meiosis, the homologous chromosomes line up side by side along the equator so that crossing over can occur between the homologous pairs and the homologous chromosomes can be pulled to opposite poles during anaphase 1. in mitosis, by contrast, homologous chromosomes line up single file along the equator. what benefits are derived from these two different ways that homologous chromosomes are positioned at metaphase in meiosis and mitosis?arrow_forward
- Rice has a chromosome number of 2n = 24. If different aneuploids are available in rice, identifythe specific aneuploidy that shows the following chromosomal configurations at diakinesis ormetaphase I. Also provide the formula and chromosome number of the different aneuploids. Complete the table. Chromosome configuration at diakinesis or metaphase I Specific Type of Aneuploidy Formula (e.g. 2n+1) Chromosome number (2n=24) Types of gametes n, n+1, n+2, n-1, n-2) a. 1 III + 11 II b. 1 IV + 11 II c. 1 I + 11 II d. 11 II e. 2 I + 10 IIarrow_forwardA diploid species has 3 pairs of chromosomes in its somatic cells. In males, the first pair is large submetacentric[1]; the second is medium acrocentric[2], and the third is small telocentric[3]. In females, the first two pairs are like those of the males while the third is large metacentric[4][5], with satellite4 Illustrate the karyograms (drawing/picture of the chromosome) of the following: A triploid cell in females tetrasomic cell in males tetraploid cell in females [1] submetacentric --centrosome is just above the middle of the chromosome [2] acrocentric --centrosome is much higher location than submetacentric so that the “p” arm of the chromosome is much shorter than the q arm [3] telocentric --the centromere is at the end of the chromosome [4] metacentric --centrosome is in the middle of the chromosome; thus the “p-arm” and the “q-arm” or both arms of the chromosome are equal in length [5] satellite-a constriction in an arm of a chromosome, aside…arrow_forwardIn a turtle species, a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle contains 22 picograms of DNA (picogram is a measure of the total mass of the DNA present). How much DNA is present in a cell of the same species at prophase II of meiosis (prophase of the second meiotic division)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Cell Cycle and its Regulation; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eqJqhA8HSJ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Cell Division - Mitosis and Meiosis - GCSE Biology (9-1); Author: Mr Exham Biology;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w7vp_uRA8kw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY