
Concept explainers
The equilibrium constant for the reaction
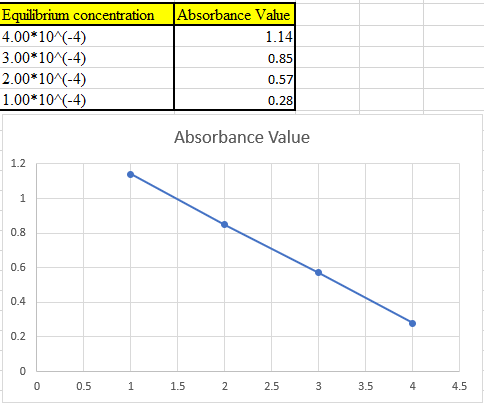
Four solutions were preparedby dissolving 4.00 × 10-4, 3.00 × 10-4, 2.00 × 10-4,and 1.00 × 10-4 moles of K2 Cr2 O7 in water and diluting to 1.00 L with a pH 5.60 buffer. Derive theoretical absorbance values (1.00-cm cells) for each solution and plot the data for (a) 345 nm, (b) 370 nm, and (c) 400 nm.
(a)
Interpretation:
The theoretical absorbance value for 345 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below:
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
(b)
Interpretation:
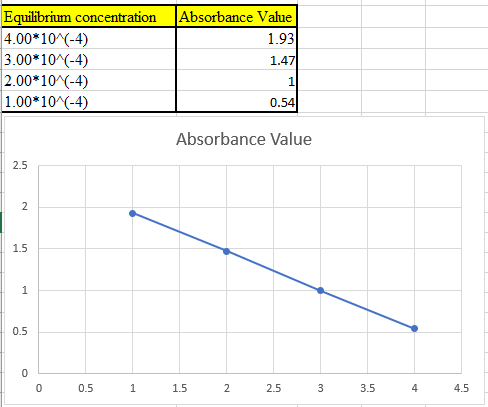
The theoretical absorbance value for 370 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
(c)
Interpretation:
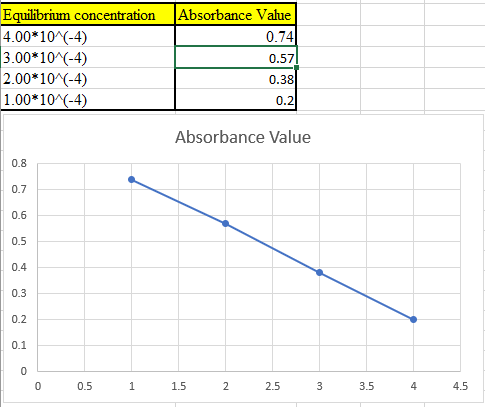
The theoretical absorbance value for 400 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
Theoretical absorbance value of first solution can be calculated as below
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
- The acid-dissociation constant for benzoic acid (C6H5COOH)is 6.3 x 10-5. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations ofH3O+, C6H5COOH-, and C6H5COOH in the solution if the initialconcentration of C6H5COOH is 0.050 M.arrow_forwardDetermine the solubility of cadmium in equilibrium with cadmium hydroxide, Cd(OH)^2 as a function of pH. Kp = 5.33 x 10^-15.arrow_forwardThe value of Ksp for Cd(OH)2 is 2.5 x 10-14. (a) Whatis the molar solubility of Cd1OH22? (b) The solubilityof Cd(OH)2can be increased through formation of thecomplex ion CdBr42 - (Kf = 5 x 103). If solid Cd(OH)2 isadded to a NaBr solution, what is the initial concentrationof NaBr needed to increase the molar solubility of Cd(OH)2to 1.0 x 10-3 mol/L?arrow_forward
- Calculate the molar solubility of Ag2S (pKsp = 48.70) in a solution maintained at pH 9.00 and where the concentration of ammonia is 0.200 M.H2S: Ka1 = 1.0 x 10-7, Ka2 = 1.2 x 10-15[Ag(NH3)2]+ : Kf1 = 2.04 x 103, Kf2 = 8.13 x 103arrow_forward1) The following reaction was allowed to reach equilibrium at 25oC. Enclosed with the phase of each species is the equilibrium concentration. Calculate the equilibrium constant (Kc and Kp) for this reaction. 2 NOCl(g, 2.6 M) = 2 NO(g, 1.4 M) + Cl2(g, 0.34 M) 2) Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M hypochlorous acid solution. Ka = 3.5 x 10-8.arrow_forwardConsider a biochemical reaction that is taking place in a 0.1 M buffer. The initial pH is 7.4, and the pKa of the buffer is 7.2. If, in a final reaction volume of 1.0 mL, 10 micromol of protons are generated, what would be the final pH of the solution?arrow_forward
- In following these steps . Complete the table and provide th given chemical reactions in the qualitative analaysis of Group 3 Cations. Procedure 1. Place 20 drops of each of the following aqueous solutions to separate centrifuge tubes: 0.1M Cr (NO3)3, 0.1M Al (NO3)3, 0.1M Co (NO3)2, 0.1M Zn (NO3)2, 0.1M Mn (OH)2, 0.1M Ni (NO3)2, 0.1 M Fe (NO3)3. Make each solution basic by adding few drops of 6M NH4OH. Confirm using a litmus paper. 2. Add 5 drops of freshly prepared 6M (NH4)2S to each centrifuge tube. Place the samples in thecentrifuge machine for 3 mins. After centrifuge record results. Decant the supernatant liquid of all the samples. 3. Add one drop of NH4OH in each centrifuge tubes. Add 20 drops of distilled water in eachcentrifuge tubes. Then add a few drops of 6M HCl in each solution. Place the samples in the water bath for 10 mins. After water bath, centrifuge the samples for 3 mins. 4. After centrifuge, add a few drops of 6M NH4Cl in each sample. Decant the supernatant liquid…arrow_forwardAt what pH will Mg(OH)2 (Ksp = 5.61 x 10–12) begin precipitating from a 0.750 M MgCl2 solution?arrow_forwardIf the equilibrium constant for A + B C is 0.175, then the equilibrium constant for 2C 2A + 2B isarrow_forward
- The Ksp value for Cu(OH)2 is 1.6x10‑19 at 25oC, what will the equilibrium concentration of [Cu2+] in a solution with pH = 8.0?arrow_forwardWhat is the equilibrium between solid Ag2CrO4 and its ions in a saturated solution and what is the mathematical Ksp expression for Ag2CrO4(s)?arrow_forwardCalculate the activity of La3+ in a saturated solution of La(IO3)3. Ksp = 1.0 x 10-11 1.2 x 10-3 1.7 x 10-4 2.8 x 10-3 4.8 x 10-4arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning


