
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a type of spectroscopy in which number of different kind of protons present in different environment can be detected. The
Answer to Problem 13.13P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
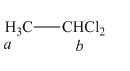
Figure 1
In the given structure of
The
(b)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a type of spectroscopy in which number of different kind of protons present in different environment can be detected. The
Answer to Problem 13.13P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
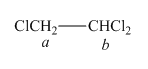
Figure 2
In the given structure of
The
(c)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a type of spectroscopy in which number of different kind of protons present in different environment can be detected. The
Answer to Problem 13.13P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
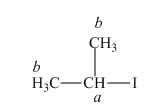
Figure 3
In the given structure of
The
(d)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a type of spectroscopy in which number of different kind of protons present in different environment can be detected. The
Answer to Problem 13.13P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
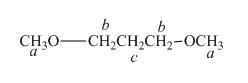
Figure 4
In the given structure of
The
(e)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a type of spectroscopy in which number of different kind of protons present in different environment can be detected. The
Answer to Problem 13.13P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of oxetane ring is shown below in Figure 5.
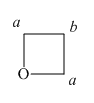
Figure 5
In the given structure of oxetane ring, two types of hydrogens are present. The hydrogen
The
(f)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a type of spectroscopy in which number of different kind of protons present in different environment can be detected. The
Answer to Problem 13.13P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
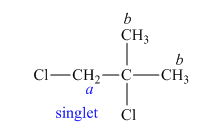
Figure 6
In the given structure of
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Compound I (C11H14O2) is insoluble in water, aqueous acid, and aqueous NaHCO3, but dissolves readily in 10% Na2CO3 and 10% NaOH. When these alkaline solutions are acidified with 10% HCl, compound I is recovered unchanged. Given this information and its 1H-NMR spectrum, deduce the structure of compound I.arrow_forwardUse the 1H-NMRs to determine the structure for the compound with formula: C4H10Oarrow_forwardDefine the 1H NMR spectrum of 2-bromopropane, (CH3)2CHBrarrow_forward
- The treatment of (CH3)2C=CHCH2Br with H2O forms B (molecular formulaC5H10O) as one of the products. Determine the structure of B from its 1H NMR and IR spectra.arrow_forwardAn aromatic compound K, whose molecular formula is C8H11N, is examined in the laboratory to elucidate its structure. The following observations were made: A) Compound K is soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid but insoluble in sodium hydroxide solution. B) Treatment of compound K with excess potassium hydroxide and benzenesulfonyl chloride, C(6)H(5)SO(2)Cl, results in the formation of a heterogeneous mixture. The NMR spectrum of compound K is shown below. C) Compound K when treated with acetic anhydride[CH3-C(O)-O-C(O)-CH3], gives compound L, whose molecular formula is C(10)H(13)ON. Compound L is insoluble in dilute acid or dilute base at room temperature, heating compound L in dilute acid or base, however, regenerates compound K. D) When compound L is heated with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid, a single product, compound M, with the molecular formula C(10)H(12)O(3)N(2) is formed in excellent yields. On the basis of these observations draw the structures of…arrow_forwardCalculate the IHD of C7H6XNO and explain (elucidate) the structure using the 1H and 13C NMR data.arrow_forward
- Nicotine is a diamino compound isolated from dried tobacco leaves. Nicotine has two rings and M+=162.1157 by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Give a molecular formula for nicotine, and calculate the number of double bonds.arrow_forwardy-Butyrolactone (C4H6O2, GBL) is a biologically inactive compound that is converted to the biologically active recreational drug GHB (Section 19.5) by a lactonase enzyme in the body. Since y-butyrolactone is more fat soluble than GHB, it is more readily absorbed by tissues and thus produces a faster onset of physiological symptoms. y-Butyrolactone shows an absorption in its IR spectrum at 1770 cm-1 and the following 1H NMR spectral data: 2.28 (multiplet, 2 H), 2.48 (triplet, 2 H), and 4.35 (triplet, 2 H) ppm. What is the structure of y-butyrolactone?arrow_forwardAnts emit tiny amounts of chemicals called alarm pheromones to warn other ants (of the same species) of the presence of an enemy. Several of the components of the pheromone in one species have been identified, and two of their structures follow. Which compound has the infrared spectrum shown? -0 -O Citral Citronellal 12025 1720 cm"1 2. The main constituent of cinnamon oil has the formula C9H8O. From the following infrared spectrum, deduce the structure of this component. 1677 cm 1200 1000 3. The infrared spectra of cis- and trans-3-hexen-1-ol follow. Assign a structure to each spectrum.arrow_forward
- Suggest structures given the 1H NMR spectra and formulas for each of the compounds below. C9H10Oarrow_forwardBased on this IR spectrum and 1H NMR spectrum and the given chemical formula is C9H10O2, what would be the chemical structure of the compound? Please give a full analysis of the NMR spectra for given compound.arrow_forwardWhich of the following molecules best describes the IR spectrum given with a molecular formula of C6H12O2?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

