
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds cyclohexane and
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The cyclohexane gives only a single peak for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the
Explanation of Solution
The compounds cyclohexane and
The structure of
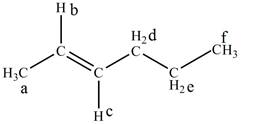
Figure 1
The structure of the cyclohexane along with its all equivalent protons peak data is shown below.
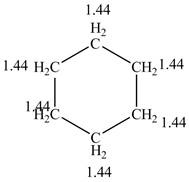
Figure 2
The cyclohexane gives only a single peak for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the
(b)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The structure of
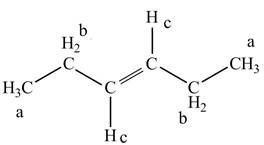
Figure 3
The structure of the
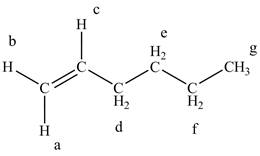
Figure 4
The
(c)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The two compounds
The structure of
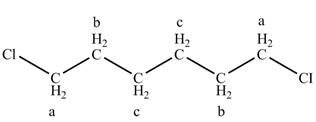
Figure 5
The structure of the
There is one signal at high chemical value at
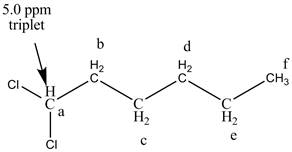
Figure 6
The structure of the
There are two signals at high chemical shift value for the compound. One at
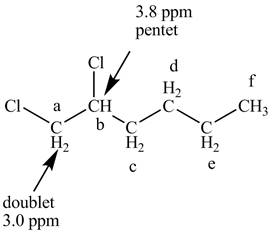
Figure 7
The
(d)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The only signal that is different in both the compounds is for the single hydrogen of methane group attached directly to the oxygen. Also, the splitting of the protons methyl groups into doublet occurs for isopropyl group while in
The structure of
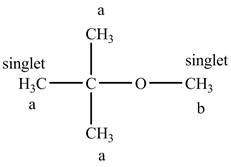
Figure 8
The structure of the isopropyl methyl ether is given below along with three sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
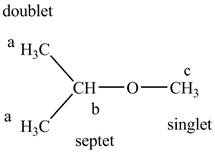
Figure 9
The
(e)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The
Both compounds are distinguished on the basis of the number of NMR signals.
Explanation of Solution
The compounds
The structure of
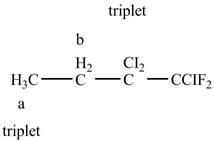
Figure 10
The structure of the
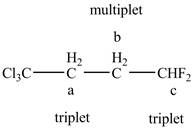
Figure 11
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Propose a structure given the 1H and 13C NMR spectra of the unknown compound. Assign chemical shifts to corresponding hydrogen and carbon atoms Molecular Formula: C5H10O3arrow_forwardThe following is the predicted 1H-NMR spectrum for an unknown compound with molecular formula C6H14O . This compound is a liquid at room temperature, is slightly soluble in water, and reacts with sodium metal with the evolution of a gas.arrow_forwardPredict the 1H NMR spectrum for the compound below and sketch it. Include splitting, and label the protons and their corresponding peaks.arrow_forward
- How could 1H NMR spectroscopy be used to distinguish among isomers A, B, and C?arrow_forwardPredict 1H NMR (with splitting patterns) and 13C NMR chemical shifts for the benzene Alkene derivative below .arrow_forwardThe following compound has a molecular formula of C5H10O and the indicated 13C spectrum. A proton NMR was measured, but the data was lost except for the fact that it showed three distinct signals: a singlet, a doublet, and a septet, all of which appear between 0 and 3 ppm. Identify the compound, and draw its expected 1H NMR.arrow_forward
- Propose structures that are consistent with the following spectra. (Integral ratios are given from left to right across the spectrum.) a. The 1H NMR spectrum of a compound with molecular formula C4H10O2 has two singlets with integral ratios of 2 : 3. b. The 1H NMR spectrum of a compound with molecular formula C6H10O2 has two singlets with integral ratios of 2 : 3. c. The 1H NMR spectrum of a compound with molecular formula C8H6O2 has two singlets with integral ratios of 1 : 2.arrow_forwardAn unknown compound has the formula C5H10O2. Elucidate its structure by scrutinizing its 1H NMR spectra, shown. Specifically, label each different type of H atom in the final structure with its NMR chemical shift in ppm.arrow_forwardFigure 1 shows the following spectrum of a compound with formula C5H10O, with interesting coupling patterns at 2.4 and 9.8 ppm. Expansions of these two peaks are shown in Figure 2. Expansions of the other patterns (not shown) are given as follows: 0.92 ppm(triplet), 1.45 ppm (sextet), and 1.61 ppm (quintet).1.Draw the structure of the compound.2.Assign the proton signals in the 1H NMR spectrum according to the answer in3(a). 3.Draw tree diagrams of the peaks at 2.4 and 9.8 ppm.4.Assign the coupling constants of the peaks at 2.4 and 9.8 ppm in tree diagram3(c).arrow_forward
- Treatment of 2-methylpropanenitrile [(CH3)2CHCN] withCH3CH2CH2MgBr, followed by aqueous acid, affords compound V, whichhas molecular formula C7H14O. V has a strong absorption in its IRspectrum at 1713 cm−1, and gives the following 1H NMR data: 0.91(triplet, 3 H), 1.09 (doublet, 6 H), 1.6 (multiplet, 2 H), 2.43 (triplet, 2 H), and2.60 (septet, 1 H) ppm. What is the structure of V?arrow_forwardThe tabulated 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectral data acquired for an unknown compound with an atomic composition of C11H20O2is detailed below. Using this data, propose a molecular structure for the unknown compound and, based on this structure, hypothesise a molecular structure of at least one major fragment appearing in the corresponding EI mass spectrum of the unknown compound, which is shown below; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 5.55 (s, 1H), 5.11 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H), 4.16 (q, J = 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 2H), 2.18 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 2H), 2.13 (s, 3H), 1.65 (s, 3H), 1.61 (s, 3H), 1.27 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, Common NMR Solvents) δ 166.72 (C), 158.99 (C), 131.99 (C), 123.58 (CH), 116.45 (CH), 59.71 (CH2), 38.94 (CH2), 26.53 (CH2), 24.98 (CH3), 19.87 (CH3), 18.90 (CH3), 14.53 (CH3).arrow_forwardA hydrocarbon, compound B, has molecular formula C6H6, and gave an NMR spectrum with two signals: delta 6.55 pm and delta 3.84 pm with peak ratio of 2:1. When warmed in pyridine for three hr, compound B quantitatively converts to benzene. Mild hydrogenation of B yielded another compound C with mass spectrum of m/z 82. Infrared spectrum showed no double bonds; NMR spectrum showed one broad peak at delta 2.34 ppm. With this information, address the following questions. a) How many rings are in compound C? b) How many rings are probably in B? How many double bonds are in B? c) Can you suggest a structure for compounds B and C? d) In the NMR spectrum of B, the up-field signal was a quintet, and the down field signal was a triplet. How must you account for these splitting patterns?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

