
Concept explainers
Target service costs, value engineering, activity-based costing. Lagoon is an amusement park that offers family-friendly entertainment and attractions. The park boasts more than 25 acres of fun. The admission price to enter the park, which includes access to all attractions, is $35. To earn the required
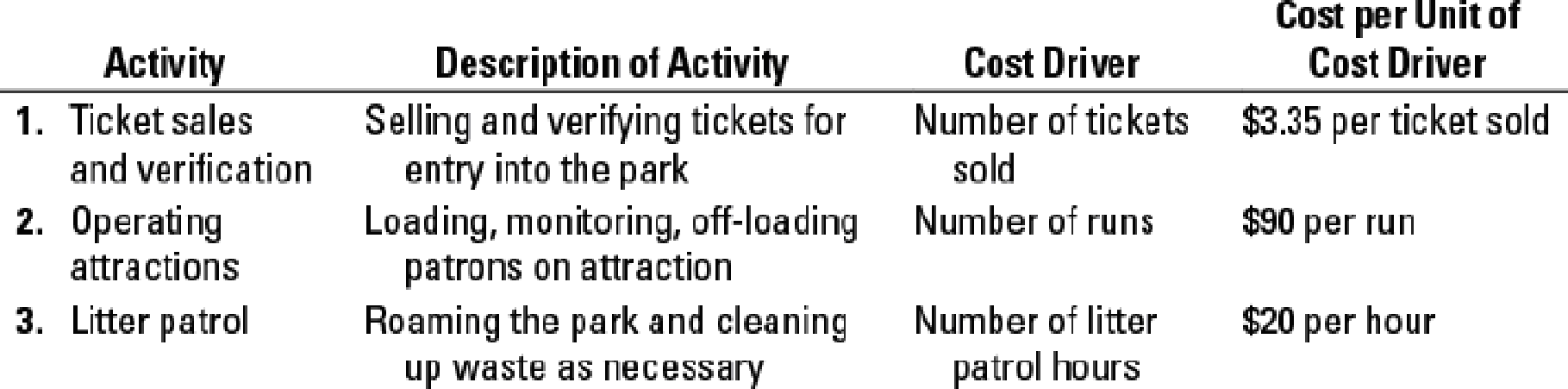
The following information describes the existing operations:
- a. The average number of patrons per week is 55,000.
- b. The total number of runs across all attractions is 11,340 runs each week.
- c. It requires 1,750 hours off litter patrol hours to keep the park clean.
In response to competitive pressures and to continue to attract 55,000 patrons per week, Lagoon has decided to lower ticket prices to $33 per patron. To maintain the same level of profits as before, Lagoon is looking to make the following changes to reduce operating costs:
- a. Reduce the cost of selling and verifying tickets by $0.35 per ticket sold.
- b. Reduce the total number of runs across all attractions by 1,000 runs by reducing the operating hours of some of the attractions that are not very popular.
- c. Increase the number of refuse containers in the park at an additional cost of $250 per week. This will decrease the litter patrol hours by 20%.
The cost per unit of cost driver for all other activities will remain the same.
- 1. Will Lagoon achieve its target operating income of 35% of revenues at ticket prices of $35 per ticket before any operating changes?
- 2. After Lagoon reduces ticket prices and makes the changes and improvements described above, will Lagoon achieve its target operating income in dollars calculated in requirement 1? Show your calculations.
- 3. What challenges might managers at Lagoon encounter in achieving the target cost? How might they overcome these challenges?
- 4. A new carbon tax of $3 per run is proposed to be levied on the energy consumed to operate the attractions. Will Lagoon achieve its target operating income calculated in requirement 1? If not, by how much will Lagoon have to reduce its costs through value engineering to achieve the target operating income calculated in requirement 1?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
HORNGREN'S COST ACCT >IA<
- A local picnic table manufacturer has budgeted these overhead costs: They are considering adapting ABC costing and have estimated the cost drivers for each pool as shown: Recent success has yielded an order for 1,000 tables. Assume direct labor costs per hour of $20. Determine how much the job would cost given the following activities:arrow_forwardKagle design engineers are in the process of developing a new green product, one that will significantly reduce impact on the environment and yet still provide the desired customer functionality. Currently, two designs are being considered. The manager of Kagle has told the engineers that the cost for the new product cannot exceed 550 per unit (target cost). In the past, the Cost Accounting Department has given estimated costs using a unit-based system. At the request of the Engineering Department, Cost Accounting is providing both unit-and activity-based accounting information (made possible by a recent pilot study producing the activity-based data). Unit-based system: Variable conversion activity rate: 100 per direct labor hour Material usage rate: 20 per part ABC system: Labor usage: 15 per direct labor hour Material usage (direct materials): 20 per part Machining: 75 per machine hour Purchasing activity: 150 per purchase order Setup activity: 3,000 per setup hour Warranty activity: 500 per returned unit (usually requires extensive rework) Customer repair cost: 25 per repair hour (average) Required: 1. Select the lower-cost design using unit-based costing. Are logistical and post-purchase activities considered in this analysis? 2. Select the lower-cost design using ABC analysis. Explain why the analysis differs from the unit-based analysis. 3. What if the post-purchase cost was an environmental contaminant and amounted to 10 per unit for Design A and 40 per unit for Design B? Assume that the environmental cost is borne by society. Now which is the better design?arrow_forwardYoung Company is beginning operations and is considering three alternatives to allocate manufacturing overhead to individual units produced. Young can use a plantwide rate, departmental rates, or activity-based costing. Young will produce many types of products in its single plant, and not all products will be processed through all departments. In which one of the following independent situations would reported net income for the first year be the same regardless of which overhead allocation method had been selected? a. All production costs approach those costs that were budgeted. b. The sales mix does not vary from the mix that was budgeted. c. All manufacturing overhead is a fixed cost. d. All ending inventory balances are zero.arrow_forward
- Product costing and decision analysis for a service company Blue Star Airline provides passenger airline service, using small jets. The airline connects four major cities: Charlotte, Pittsburgh, Detroit, and San Francisco. The company expects to fly 170,000 miles during a month. The following costs are budgeted for a month: Blue Star management wishes to assign these costs to individual flights in order to gauge the profitability of its service offerings. The following activity bases were identified with the budgeted costs: The size of the companys ground operation in each city is determined by the size of the workforce. The following monthly data are available from corporate records for each terminal operation: Three recent representative flights have been selected for the profitability study. Their characteristics are as follows: Instructions Determine the fuel, crew, and depreciation cost per mile flown. Determine the cost per arrival or departure by terminal city. Use the information in (1) and (2) to construct a profitability report for the three flights. Each flight has a single arrival and departure to its origin and destination city pairs.arrow_forwardHarriman Industries manufactures engines for the aerospace industry. It has completed manufacturing the first unit of the new ZX-9 engine design. Management believes that the 1,000 labor hours required to complete this unit are reasonable and is prepared to go forward with the manufacture of additional units. An 80 percent cumulative average-time learning curve model for direct labor hours is assumed to be valid. Data on costs are as follows: Required: 1. Set up a table with columns for cumulative number of units, cumulative average time per unit in hours, and the cumulative total time in hours. Complete the table for 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 units. (Round hours to one significant digit.) 2. What are the total variable costs of producing 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 units? What is the variable cost per unit for 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 units?arrow_forwardThe management of Hartman Company is trying to determine the amount of each of two products to produce over the coming planning period. The following information concerns labor availability, labor utilization, and product profitability: a. Develop a linear programming model of the Hartman Company problem. Solve the model to determine the optimal production quantities of products 1 and 2. b. In computing the profit contribution per unit, management does not deduct labor costs because they are considered fixed for the upcoming planning period. However, suppose that overtime can be scheduled in some of the departments. Which departments would you recommend scheduling for overtime? How much would you be willing to pay per hour of overtime in each department? c. Suppose that 10, 6, and 8 hours of overtime may be scheduled in departments A, B, and C, respectively. The cost per hour of overtime is 18 in department A, 22.50 in department B, and 12 in department C. Formulate a linear programming model that can be used to determine the optimal production quantities if overtime is made available. What are the optimal production quantities, and what is the revised total contribution to profit? How much overtime do you recommend using in each department? What is the increase in the total contribution to profit if overtime is used?arrow_forward
- Kelson Sporting Equipment, Inc., makes two types of baseball gloves: a regular model and a catchers model. The firm has 900 hours of production time available in its cutting and sewing department, 300 hours available in its finishing department, and 100 hours available in its packaging and shipping department. The production time requirements and the profit contribution per glove are given in the following table: Assuming that the company is interested in maximizing the total profit contribution, answer the following: a. What is the linear programming model for this problem? b. Develop a spreadsheet model and find the optimal solution using Excel Solver. How many of each model should Kelson manufacture? c. What is the total profit contribution Kelson can earn with the optimal production quantities? d. How many hours of production time will be scheduled in each department? e. What is the slack time in each department?arrow_forwardPatz Company produces two types of machine parts: Part A and Part B, with unit contribution margins of 300 and 600, respectively. Assume initially that Patz can sell all that is produced of either component. Part A requires two hours of assembly, and B requires five hours of assembly. The firm has 300 assembly hours per week. Required: 1. Express the objective of maximizing the total contribution margin subject to the assembly-hour constraint. 2. Identify the optimal amount that should be produced of each machine part and the total contribution margin associated with this mix. 3. What if market conditions are such that Patz can sell at most 75 units of Part A and 60 units of Part B? Express the objective function with its associated constraints for this case and identify the optimal mix and its associated total contribution margin.arrow_forwardCape Cod Adventures makes foam noodles with sales of 3,000,000 units per year and retractable boat oars with sales of 50,000 pairs per year. What information would Cape Cod Adventures need in order to change from traditional to ABC costing? What are the limitations to activity-based costing?arrow_forward
- Pinter Company had the following environmental activities and product information: 1. Environmental activity costs 2. Driver data 3. Other production data Required: 1. Calculate the activity rates that will be used to assign environmental costs to products. 2. Determine the unit environmental and unit costs of each product using ABC. 3. What if the design costs increased to 360,000 and the cost of toxic waste decreased to 750,000? Assume that Solvent Y uses 6,000 out of 12,000 design hours. Also assume that waste is cut by 50 percent and that Solvent Y is responsible for 14,250 of 15,000 pounds of toxic waste. What is the new environmental cost for Solvent Y?arrow_forwardAdvent Software uses standards to manage the cost of the programming staff. There are two programmer levels, Level 1 and Level 2. Level 1 programmers normally work on the easier projects. Level 1 and Level 2 programmers are paid 25 and 35 per hour, respectively. It has been determined from experience that Level 2 programmers can complete 50 lines of code per hour. If a Level 1 programmer is assigned to a Level 2 task, the programming work will be slower than the Level 2 time standard, but will be accomplished at a lower labor rate. During a recent week, a Level 2 project was assigned to a Level 1 programmer. The programmer worked 40 hours and completed 1,400 lines of code. a. Determine the direct labor time variance for this worker. b. Determine the direct labor rate variance for this worker. c. Using the information in (a) and (b), is it more cost effective to use a Level 1 worker or a Level 2 worker on a Level 2 project?arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





