
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The Lewis diagram for
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure shows the connectivity between atoms by identifying the lone pairs of electrons in a compound. Lewis structures are also known as Lewis dot structures. The valence electrons around an atom are shown by dots. Bonds between atoms are shown by lines and the lone pair of electrons is shown by a pair of dots.
Answer to Problem 9E
The Lewis diagram for
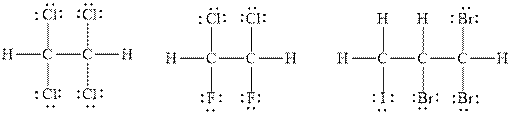
Explanation of Solution
The number of valence electrons in the carbon atom is
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bonds between the carbon atoms and other atoms are drawn. Each bond contains
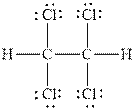
Figure 1
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bonds between the carbon atoms and other atoms are drawn. Each bond contains
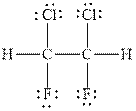
Figure 2
In
Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in
These valence electrons are distributed in the Lewis diagram using bonds and lone pair of electrons.
At first, the single bonds between the carbon atoms and other atoms are drawn. Each bond contains
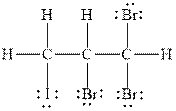
Figure 3
The Lewis diagram for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Bundle: Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach, 6th + Owlv2, 4 Terms (24 Months) Printed Access Card
- PLEASE ANSWER THESE 3 MULTIPLE choices QUESTIONS Q1) What is the total number of electrons in the correct Lewis dot formula of the sulfite ion? a 8 b 24 c 26 d 30 e 32 Q2) In the Lewis structure for the OF2 molecule, the number of lone pairs of electrons around the central oxygen atoms is a 0 b 1 c 2 d 3 e 4 Q1) Francium has a higher electronegativity than fluorine. True Falsearrow_forwardFor each of the following molecules draw the Lewis structure on a separate sheet of paper. MAKE SURE TO FOLLOW THE RULES FROM CLASS (ie do not break the octet rule unless necessary to connect all the atoms). These can all be drawn on one piece of paper. Based on your structure provide the following: the total number of valence electrons. a picture of the Lewis structure (3-D model not required). the total number of structural domains around the CENTRAL atom. the number of bonding domains around the CENTRAL atom. the number of lone pairs around the CENTRAL atom. the electronic and molecular shapes. the hybridization of the CENTRAL atom. (sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, or sp3d2) whether or not the molecule is polar (Enter Y for yes and N for no). Note: The central atom is the first atom listed.arrow_forwardWrite a Lewis structure for each of the following molecules. H2CO (carbon is central) Draw the molecule by placing atoms on the grid and connecting them with bonds. Include all lone pairs of electrons.arrow_forward
- Explain why more C and N atoms are required to form a compound with Ba. It is important to note that all atoms obey the octet rule. Hint generate the Lewis diagram for Ba(CN) 2 to help you answer this question.arrow_forwardConvert the 3-D model of the general anesthetic methoxyfl urane into a Lewis structure and include all nonbonded electron pairs on atoms that contain them.arrow_forwardWrite a Lewis structure for each of the following molecules. H3COCH3 (oxygen is between the two carbon atoms) Draw the molecule by placing atoms on the grid and connecting them with bonds. Include all lone pairs of electrons.arrow_forward
- Draw Lewis structures for each of the following molecules: (a) CH5N (contains a bond between C and N); (b) CH3NO2 (contains a bond between C and N but no bonds between C and O); (c) CH2O; (d) CH2Cl2; (e) BrCNarrow_forward[Molecular shape and polarity] Consider two molecules: XCl3, and YO2 X is an atom in group 5A with electronegativity of 2.0. Y is an atom in group 6A with electronegativity of 2.4. Fill in the blanks. Molecule Lewis structure (Draw an lone pair(s) of electrons, when present) Molecular shape Molecular polarity (Yes: polar or No: nonpolar) XCl3 ? ? ? YO2 ? ? ?arrow_forward1. List 5 covalent compounds that are common in daily man’s life. 2. Complete the table. ELEMENT GROUP NUMBER NUMBER OF VALENCE ELECTRONS NUMBER OF BONDS NUMBER OF ELECTRONS NEEDED TO SHARE TO ATTAIN STABILITY 1. Cl 2. O 3. I 3. Complete the table. Covalent compound TOTAL NUMBER OF ATOMS TOTAL NUMBER OF ELECTRONS SHARED TOTAL NUMBER OF BONDS NUBER OF LONE PAIRS 1. NH3arrow_forward
- Find the total number of valence electrons, lewis structure, name of electron and molecular geometry, and 3D diagram for SEI2 and SbBr3.arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for each of the following:a. NO3-b. NO2+ c. -C2H5d. +C2H5 e. CH3N + H3f. NaOH g. HCO3-h. HCO2-arrow_forwardUsing the symbols and +, indicate the direction of polarity in each polar covalent bond. (a) CN (b) NO (c) CClarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





