
(a)
Interpretation:
Molecular formula for Hyponitrous acid and nitroxyl has to be determined using the given data.
Concept-Introduction:
Molecular formula can be determined using the given formula,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given data is shown below:
Empirical mass is calculated as follows,
Empirical mass of
Molecular formula for Hyponitrous acid can be determined using the given formula,
Molecular formula for Hyponitrous acid is
Molecular formula for nitroxyl can be determined using the given formula,
Molecular formula for nitroxyl is
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of Hyponitrous acid and nitroxyl has to be determined.
Concept-Introduction:
Lewis structure
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Draw Lewis structure of Hyponitrous acid:
Outer valence electrons of Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen are one, six and five respectively.
Here, one double bond between two nitrogen atoms is required to complete the complete the octets of all the atoms.
After the distribution of electrons, both Nitrogen atoms gets a lone pair of electrons and both oxygen atoms get two pair of lone electrons.
The Lewis structure of Hyponitrous acid follows as,
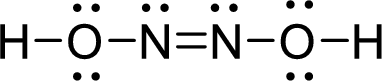
Draw Lewis structure of nitroxyl:
Outer valence electrons of Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen are one, six and five respectively.
Here, one double bond between is required to complete the complete the octets of all the atoms.
After the distribution of electrons, Nitrogen atom gets a lone pair of electrons and oxygen atom gets two pair of lone electrons.
The Lewis structure of nitroxyl follows as,
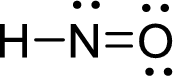
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of Hyponitrous acid and nitroxyl has to be determined.
Concept-Introduction:
According to VSEPR theory, the geometry is predicted by the minimizing the repulsions between electron-pairs in the bonds and lone-pairs of electrons. The VSEPR theory is summarized in the given table as,
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of Hyponitrous acid follows as,
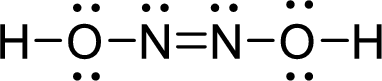
The Lewis structure of nitroxyl follows as,
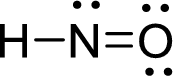
Nitrogen atom present in both Hyponitrous acid and nitroxyl has two bond pair and one lone pair (3 electron domains). Therefore, the molecular geometry of Hyponitrous acid and nitroxyl is bent.
(d)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of Hyponitrous acid and nitroxyl has to be determined.
Concept-Introduction:
Geometric isomers: Two compounds are considered as geometric isomers of each other if both contain same number of atoms but different in their arrangement.
- Trans configuration: In trans configuration, similar groups are placed on opposite sides of the double bond.
- Cis configuration: In cis configuration, similar groups are placed on same sides of the double bond.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of Hyponitrous acid follows as,
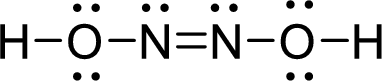
The similar groups are placed on opposite sides of the double bond in trans configuration whereas similar groups are placed on same sides of the double bond in cis configuration.
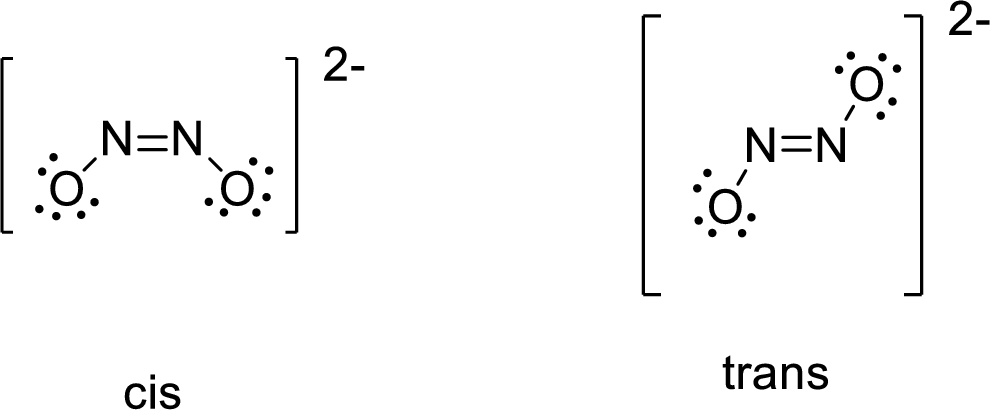
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





