
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
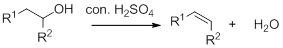
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
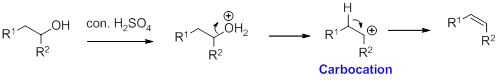
In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkene should be identified from the dehydration of given alcohol.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
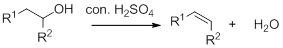
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
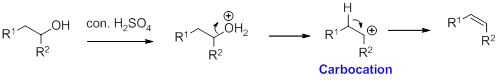
In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkene should be identified from the dehydration of given alcohol.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
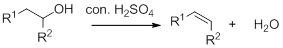
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
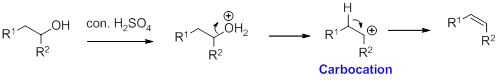
In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction.
(d)
Interpretation:
The alkene should be identified from the dehydration of given alcohol.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
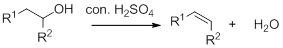
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
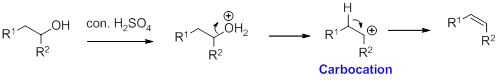
In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction.
(e)
Interpretation:
The alkene should be identified from the dehydration of given alcohol.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
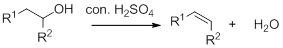
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
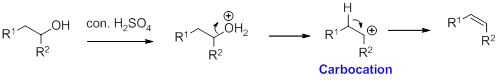
In dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamentals Of General, Organic, And Biological Chemistry Volume 1 Second Custom Edition For Washington State University, 2/e
- What is the ionisable group of phenazopyridine? With illustrationsarrow_forwardIdentify the functional groups in the following compoundsarrow_forwardCompare the densities of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density poly- ethylene (HDPE) with the densities of the liquid alkanes.How might you account for the differences between them?arrow_forward
- The explosive trinitrotoluene (TNT) is made by carrying out three successive nitration reactions on toluene. If these nitrations only occur in the ortho and para positions relative to the methyl group, what is the structure of TNT?arrow_forwardThe reaction of methoxy benzene with hydrogen iodide will yield a phenol and an alkyl halide. Which of following choices is the correct combination of the products?arrow_forwardSalicylic acid (o-hydroxybenzoic acid) is used as starting material to prepare aspirin. Draw the structure of salicylic acid.arrow_forward
- what is the crystallinity of phenazopyridine? with illustationarrow_forwardFor the first part, draw a Fischer projection formula for the enantiomer of each of the following monosaccharides. For the second part, identify whether the images are in D- or L-configuration. Write your answers first on a piece of bond paper.arrow_forwardWhat is the empirical formula for C3H6O3? C3H6O3 C6H12O6 CH2O None of thesearrow_forward
