
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reaction should be completed.
Concept introduction:
Hydrobromination:
A hydrobromination reaction is one of the electrophilic additions to

(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction should be completed.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation reaction:
Alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction using oxidising agent like
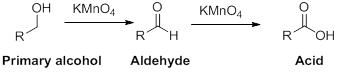
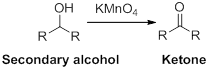
(c)
Interpretation:
The reaction should be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
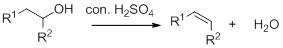
Alcohol is reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, first alcohol gets protonated forms carbocation (more stable carbocation) followed by elimination of proton (
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
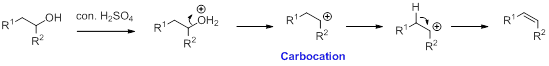 In Dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction. Dehydration reaction will not go without acid (sulfuric acid).
In Dehydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, and which is used to protonate the alcohol and makes carbocation therefore sulfuric acid is the driving force of the reaction. Dehydration reaction will not go without acid (sulfuric acid).
(d)
Interpretation:
The reaction should be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Bromination of alkenes:
Alkene undergoes bromination which yields the dibromo compound (vicinal dibromides or 1,2-dibromides).
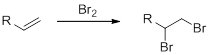
(e)
Interpretation:
The reaction should be completed.
Concept introduction:
Thiols:
The general structure of thiol is
Oxidation of thiols:
Thiol undergoes oxidation using

(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction should be completed.
Concept introduction:
Hydration:
When alkene is undergoes hydration with water in the presence of sulfuric acid which yields the alcohol. In this reaction, the water molecule will behave like a hydrogen halide to the alkene which gives the addition product this reaction is known as a hydration reaction.
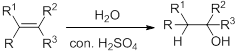
Alkene is reaction with water in the presence of sulfuric acid, first step is proton (
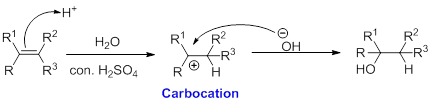
In hydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, which is the driving force of the reaction. Hydration reaction will not go without acid (sulfuric acid).
(g)
Interpretation:
The reaction should be completed.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation reaction:
Alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction using oxidising agent like
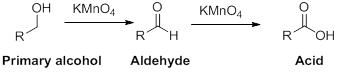
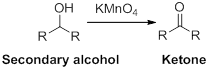
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamentals Of General, Organic, And Biological Chemistry Volume 1 Second Custom Edition For Washington State University, 2/e
- What is the product of the following reaction?arrow_forwardWhere in the periodic table are the best reducing agents found? The best oxidizing agents?arrow_forwardCalculate ΔG for the reaction H2O(l) ⇆ H+(aq) + OH−(aq) at 25°C for the following conditions. [H+] = 3.1 M, [OH−] = 4.7 ×10−4 Marrow_forward
- If you measured the rate of reaction at 20°C to be 1.11 x 10-5 M/s when using 0.080 M I1- and 0.040 M S2O82-. Approximately how long will the reaction take if you were to increase the temperature to 30 °C?arrow_forwardWhich letter represents the ΔG of the reaction?arrow_forwardwhat is the conjugate acid for the following reaction? HC2HO4 + H2O <--> H3O+ + C2HO4- A)C2HO4- B) HC2HO4 C)H2O D) H3O+arrow_forward
- For the following reaction, 4.91 grams of water are mixed with excess chlorine gas. The reaction yields 12.5 grams of hydrochloric acid.chlorine (g) + water (l) hydrochloric acid (aq) + chloric acid (HClO3) (aq) What is the theoretical yield of hydrochloric acid ? grams What is the percent yield of hydrochloric acid ? %arrow_forwardIdentify the major and minor product(s) of the following reaction:arrow_forwardIf the phosphorus atom in 3-phosphoglycerate is radioactively labeled, where will the label be when the reaction that forms 2-phosphoglycerate is over?arrow_forward
