
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(a)
Answer to Problem 23E
Molecular structure = Tetrahedral
Polarity = Non-polar
Hybridization = sp3
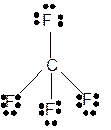
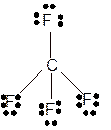
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(b)
Answer to Problem 23E
Molecular structure = pyramid
Polarity = polar
Hybridization = sp3
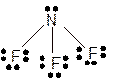
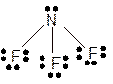
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(c)
Answer to Problem 23E
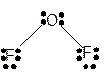
Molecular structure = bent
Polarity = polar
Hybridization = sp3
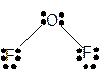
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(d)
Answer to Problem 23E
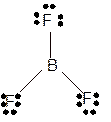
Molecular structure = trigonal planer
Polarity = non-polar
Hybridization = sp2
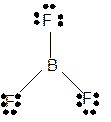
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(e)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(e)
Answer to Problem 23E
Molecular structure = linear
Polarity = non-polar
Hybridization = sp
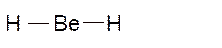
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
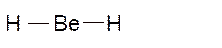
(f)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(f)
Answer to Problem 23E
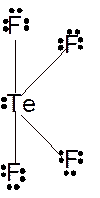
Molecular structure = see-saw
Polarity = polar
Hybridization = sp3d
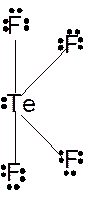
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(g)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(g)
Answer to Problem 23E
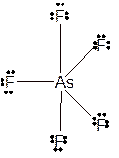
Molecular structure = trigonal bipyramid
Polarity = non-polar
Hybridization = sp3d
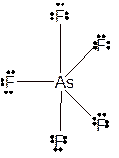
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(h)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(h)
Answer to Problem 23E
Molecular structure = linear
Polarity = non-polar
Hybridization = sp3d
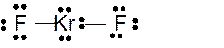
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
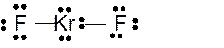
(i)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(i)
Answer to Problem 23E
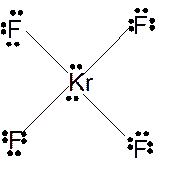
Molecular structure = square planer
Polarity = non-polar
Hybridization = sp3d2
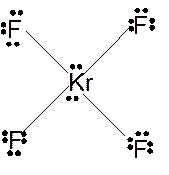
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(j)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(j)
Answer to Problem 23E
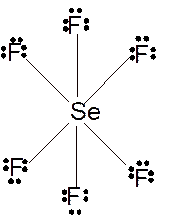
Molecular structure = octahedral
Polarity = non-polar
Hybridization = sp3d2
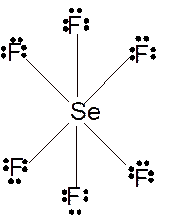
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(k)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
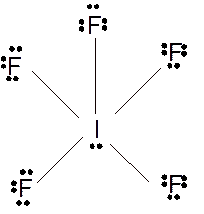
(k)
Answer to Problem 23E
Molecular structure = square pyramid
Polarity = polar
Hybridization = sp3d2
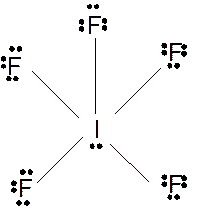
Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for
(l)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure and expected hybrid orbitals on central atom, polarity of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
The polarity of molecule is determined with the help of presence of polar bond and symmetrical geometry.
(l)
Answer to Problem 23E
Molecular structure = T-shape
Polarity = polar
Hybridization = sp3d

Explanation of Solution
The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons. To draw the Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in each atom and draw the structure in such a way that each atom gets its octet configuration.
Total number of valence electrons in
Hence the best Lewis structure for

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
CHEM.PRINC.W/OWL2+REBATE+2 SUPPL.>IP<
- For each of the following molecules, write the Lewis structure(s), predict the molecular structure (including bond angles), give the expected hybrid orbitals of the central atom, and predict the overall polarity. a. CF4 b. NF3 c. OF2 d. BF3 e. BeH2 f. TeF4 g. AsF5 h. KrF2 i. KrF4 j. SeF6 k. IF5 l. IF3arrow_forwardThe sulfamate ion, H2NSO3, can be thought of as having been formed from the amide ion, NH2, and sulphur trioxide, SO3. (a) What are the electron-pair and molecular geometries or the amide ion and or SO3? What are the hybridizations of the N and S atoms, respectively? (b) Sketch a structure for the sulfamate ion, and estimate the bond angles. (c) What changes in hybridization do you expect for N and S in the course of the reaction NH2 + SO3 H2NSO3? (d) Is SO3 the donor of an electron pair or the acceptor of an electron pair in the reaction with amide ion? Does the electrostatic potential map shown below confirm your prediction?arrow_forwardThe three most stable oxides of carbon are carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and carbon suboxide (C3O2). The space-filling models for these three compounds are For each oxide, draw the Lewis structure, predict the molecular structure, and describe the bonding (in terms of the hybrid orbitals for the carbon atoms).arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





