
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
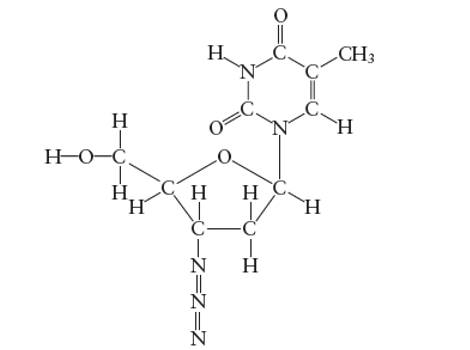
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(a)
Answer to Problem 29E
There are 6 carbon atoms in
Explanation of Solution
A
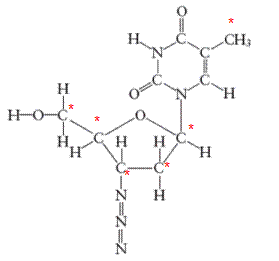
All the asterisk C atoms are
(b)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
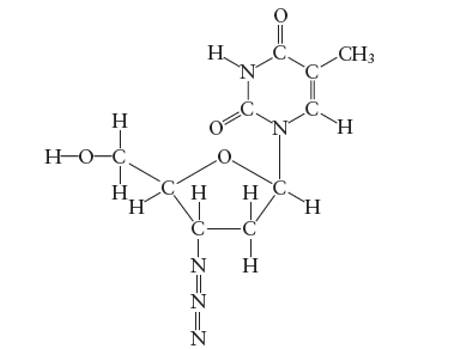
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(b)
Answer to Problem 29E
There are 4 carbon atoms in
Explanation of Solution
A
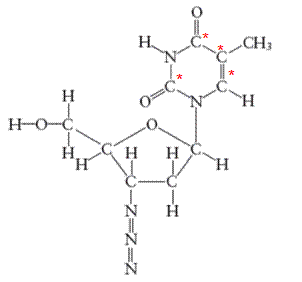
All the asterisk C atoms are
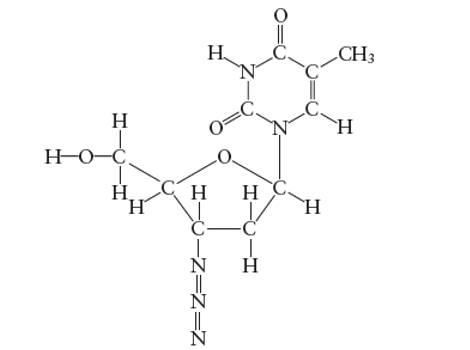
(c)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(c)
Answer to Problem 29E
The N atoms which forms two double covalent bond is sp-hybridized only.
Explanation of Solution
A
There is no
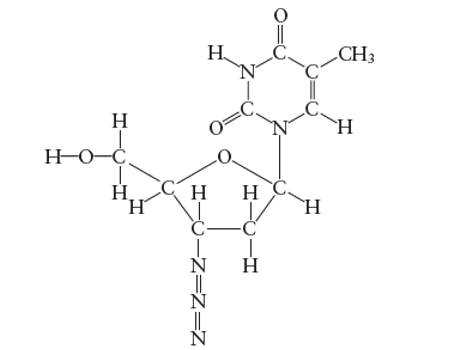
(d)
Interpretation: The number of σ-bonds in AZT molecule needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(d)
Answer to Problem 29E
The total number of σ bonds are 33 in AZT molecule
Explanation of Solution
There are two types of covalent bonds; σ bond and π-bonds. A σ-bond is formed by head-to head overlapping of hybridized orbitals. It is a strong bond and can exist between two bonded atoms. On the contrary, a π-bond is a weak covalent bond as it forms by side-way-overlapping of un-hybridized orbitals.
Since it is a weak bond therefore it is always exist with σ-bond in a double and triple covalent bond. A double covalent bond is formed by 1σ and 1 π bond whereas a triple covalent bond is formed by 1σ and two π bonds. In the given molecule, all single bonds are σ-bonds and all double bonds have 1 σ bonds. Therefore total number of σ bonds are 33 in AZT molecule.
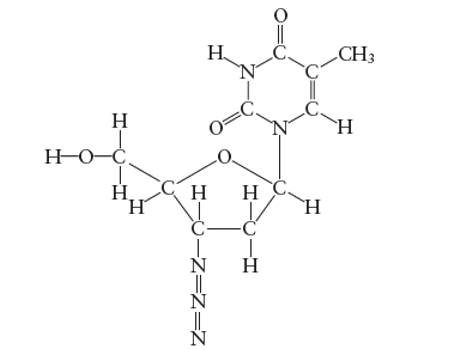
(e)
Interpretation: The number of π-bonds in AZT molecule needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(e)
Answer to Problem 29E
The total number of π bonds are 5 in AZT molecule
Explanation of Solution
There are two types of covalent bonds; σ bond and π-bonds. A σ-bond is formed by head-to head overlapping of hybridized orbitals. It is a strong bond and can exist between two bonded atoms. On the contrary, a π-bond is a weak covalent bond as it forms by side-way-overlapping of un-hybridized orbitals.
Since it is a weak bond therefore it is always exist with σ-bond in a double and triple covalent bond. A double covalent bond is formed by 1σ and 1 π bond whereas a triple covalent bond is formed by 1σ and two π bonds. In the given molecule, total number of π bonds are 5 in AZT molecule.
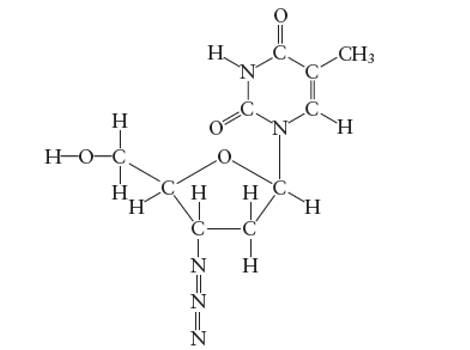
(f)
Interpretation: The bond angle in the N-N-N (azide group) of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(f)
Answer to Problem 29E
With sp-hybridization, the bond angle must be 180°.
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of central N atom in azide group is:
With sp-hybridization, the bond angle must be 180°.
(g)
Interpretation: The bond angle in the H-O-C in the side group attached to the five membered ring of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
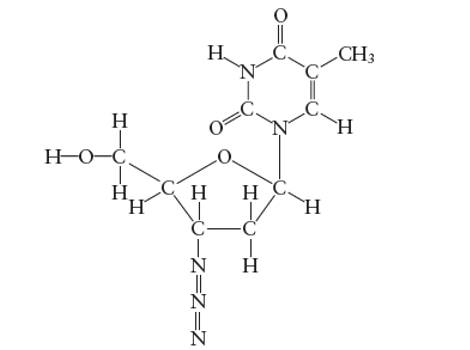
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(g)
Answer to Problem 29E
With
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of central C atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring:
With
(h)
Interpretation: The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
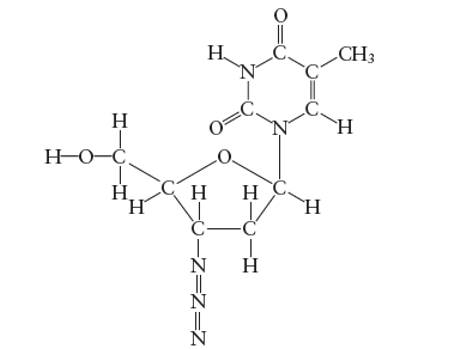
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(h)
Answer to Problem 29E
The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring is
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring:
The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
CHEM.PRINC.W/OWL2+REBATE+2 SUPPL.>IP<
- Give the hybridization of each central atom in the following molecules. (a) cyclohexene (b) phosgene, Cl2CO (c) glycine, H2NC(1)H2C(2)OOH (Note: Numbers in parentheses label each carbon atom.)arrow_forwardGamma hydroxybutyric acid, GHB, infamous as a date rape drug, is used illicitly because of its effects on the nervous system. The condensed molecular formula for GHB is HO(CH2)3COOH. (a) Write the Lewis structure for GHB. (b) Identify the hybridization of the carbon atom in the CH2 groups and of the terminal carbon. (c) Is hydrogen bonding possible in GHB? If so, write Lewis structures to illustrate the hydrogen bonding. (d) Which carbon atoms are involved in sigma bonds? In pi bonds? (e) Which oxygen atom is involved in sigma bonds? In pi bonds?arrow_forwardThere are two compounds with the molecular formula HN3. One is called hydrogen azide; the other is cyclotriazene. (a) Write the Lewis structure for each compound. (b) Designate the hybridization of each nitrogen in hydrogen azide. (c) What is the hybridization of each nitrogen in cyclotriazene? (d) How many sigma bonds are in hydrogen azide? In cyclotriazene? (e) How many pi bonds are in hydrogen azide? In cyclotriazene? (f) Give approximate values for the N-to-N-to-N bond angles in each molecule.arrow_forward
- The hybridization of the two carbon atoms differs in an acetic acid, CH3COOH, molecule. (a) Designate the correct hybridization for each carbon atom in this molecule. (b) What is the approximate bond angle around each carbon?arrow_forwardConsider the polyatomic ion IO65-. How many pairs of electrons are around the central iodine atom? What is its hybridization? Describe the geometry of the ion.arrow_forwardIn each of the following polyatomic ions, the central atom has an expanded octet. Determine the number of electron pairs around the central atom and the hybridization in (a) SF22- (b) AsCl6- (c) SCl42-arrow_forward
- The structure of amphetamine, a stimulant, is shown below. (Replacing one H atom on the NH2, or amino, group with CH3 gives methamphetamine a particularly dangerous drug commonly known as speed.) (a) What are the hybrid orbitals used by the C atoms of the C6 ring. by the C atoms of the side chain, and by the N atom? (b) Give approximate values for the bond angles A, B, and C. (c) How many bonds and bonds are in the molerule? (d) Is the molecule polar or nonpolar? (e) Amphetamine reacts readily with a proton (H+) in aqueous solution. Where does this proton attach to the molecule? Explain how the electrostatic potential map predicts this site of protonation.arrow_forwardBoron trifluoride, BF3, reacts with ammonia, NH3, to form an addition compound, BF3NH3. Describe the geometries about the B and the N atoms in this compound. Describe the hybridization on these two atoms. Now describe the bonding between the B and N atoms, using valence bond theory. Compare the geometries and hybridization of these atoms in this addition compound with that in the reactant molecules BF3 and NH4.arrow_forwardMinoxidil (C9H15N15O) is a compound produced by the Pharmacia Upjohn Company that has been approved as a treatment for some types of male pattern baldness. Note that in such shorthand ring structures, each point where lines meet is a carbon atom and that the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atoms in the rings have been omitted. There will be four bonds to each carbon atom. a. Give the hybridization of the five nitrogen atoms in minoxidil. b. Give the hybridization of each of the nine carbon atoms in minoxidil. c. Give the approximate values for the bond angles marked a, b, c, d, e, and f. d. Including all the hydrogen atoms, how many bonds exist in minoxidil? e. How many bonds exist in minoxidil?arrow_forward
- Draw the Lewis structure for 1, 1-dimethylhydrazine [(CH3)2NNH2, a compound used as a rocket fuel]. What: is the hybridization for the two nitrogen atoms in this molecule? What orbitals overlap to form the bond between the nitrogen atoms?arrow_forwardThe sulfamate ion, H2NSO3, can be thought of as having been formed from the amide ion, NH2, and sulphur trioxide, SO3. (a) What are the electron-pair and molecular geometries or the amide ion and or SO3? What are the hybridizations of the N and S atoms, respectively? (b) Sketch a structure for the sulfamate ion, and estimate the bond angles. (c) What changes in hybridization do you expect for N and S in the course of the reaction NH2 + SO3 H2NSO3? (d) Is SO3 the donor of an electron pair or the acceptor of an electron pair in the reaction with amide ion? Does the electrostatic potential map shown below confirm your prediction?arrow_forwardCalcium cyanamide, CaNCN, is used both to kill weeds and as a fertilizer. Give the Lewis structure of the NCN2 ion and the bonded-atom lone-pair arrangement and hybridization of the carbon atom.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





