
Concept explainers
a)
Profit maximizing price quantity combination and corresponding profits for the monopolist
a)
Explanation of Solution
Demand curve,
Therefore, profits are,
Differentiating the profit equation with respect to
Second order condition, proves that this price and quantity maximizes the profits for a monopolist.
And profits given this price and quantity is,
b)
Nash equilibrium output for two firms operating in Cournot model. Also to compute
market output, price and firms profits.
b)
Explanation of Solution
From the demand function, we get,
Also,
So, profit for the firm 1 ,
Differentiating with respect to
And similarly, profit equation of the firm 2 reveals,
Solving 1 and 2 we get,
Market output will be,
And market price is,
So, at
The profits for firm 1 is,
The profit for firm 2 is,
c)
To find Nash
c)
Explanation of Solution
In case of a Bertrand model, undercutting of prices by both the firms leads to price becoming approximately nil in the given scenario. Hence the price will tend to zero, and quantity will become tending to 150 .
So, price
And Quantity
As there are no cost to production so firms will undercut to a level that at the end of the day both firms will be willing to provide the quantity at price 0 .
Profits for the firm
And market output is,
However the maximum demand is only for 150 units, therefore market output is 150 .
d)
To graph the demand curve for cases in parts (a), (b), (c).
d)
Explanation of Solution
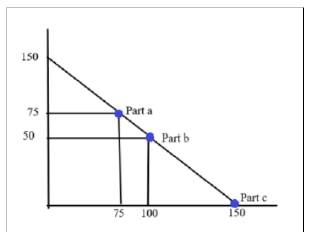
In the above diagram, Price is measured on
In part
In part c, the two firms follows Bertand
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Assume that two companies (C and D) are duopolists that produce identical products. Demand for the products is given by the following linear demand function:P=1000−QC−QDwhere QC and QD are the quantities sold by the respective firms and P is the selling price. Total cost functions for the two companies are TCC=15,000+50QC TCD=10,000+75QD Assume that the firms act independently as in the Cournot model (i.e., each firm assumes that the other firm’s output will not change). Please, find the equilibrium output of firm C.arrow_forwardSuppose that two duopolists (firm A and Firm B) produce identical products. The firms face the following market demand curve P=1250-Q Where Q = Total output in the duopoly market Qa= Firm A’s output Qb = Firm B’s output P = Price in the duopoly market Firm A and Firm B make output decisions sequentially. Firm A is the leading firm that makes the first move, and firm B is the following firm. Firm A rationally anticipates the output reaction of Firm B, as Firm A has the prior knowledge of Firm B’s output-reaction curve, which is Qb = 600-0.5Qa It is assumed that firm B always acts in the same manner. Both firms have constant marginal costs (MC) of production where MCa=MCb=$50. Fixed Costs are nil because expenses have already been fully amortised In this duopoly market, equilibrium level of output is __________, and equilibrium level of price is ___________arrow_forwardAssume that two companies (C and D) are duopolists that produce identical products. Demand for the products is given by the following linear demand function: P=600-Qc-Qd where QCQC and QDQD are the quantities sold by the respective firms and P is the selling price. Total cost functions for the two companies are TCc=25,000=100Qc TCd=20,000=125Qd Assume that the firms act independently as in the Cournot model (i.e., each firm assumes that the other firm’s output will not change). For Company C, the long-run equilibrium output is , and the selling price is $ . For Company D, the long-run equilibrium output is , and the selling price is $ . At the equilibrium output, Company C earns total profits of $ , and Company D earns total profits of $ .arrow_forward
- In the Nash equilibrium of a Cournot game with two firms who have identical marginal costs, each firm chooses to produce half of the quantity that would be produced by a monopolist, given the same aggregate demand and marginal cost.(a) True. (b) False.arrow_forwardIf a duopolist has a linear demand curve of the form Q=400 – P. Assuming each firm has total cost (TC=3000+100Q). Calculate the profit-maximizing price-quantity combinations using the following four oligopoly pricing models listed below demonstrating that: a. Under the Quasi-competitive model, the firm will make a loss equivalent to fixed cost. b. Under the Stackelberg’s model the leader will earn more than twice the profit of the follower and that total industry profits will be lower than under both Cournot and Cartel models. Explain why this is would be the case.arrow_forwardConsider two firms, i = 1; 2, producing differentiated products and engaged in Cournot a. Given the market demands, what are the best-response functions of the two firms? b. Draw the best-response functions both for complements (d 0). c. Compute the Cournot equilibrium quantities and prices in this market. d. Compare the outcome between substitutes and complements goods. e. What are the profit-maximizing quantities and prices if firm i is a monopolist in this market? Compare with part c.arrow_forward
- Cournot’s Model of Duopoly) Joe and Rebecca are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is Qd=5500-25P, where P is the price of a cubic metre of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic metres demanded every year. The marginal cost is $40 per cubic metre. Competition in this market is described by the Cournot model. (a)Given Rebecca’s output is 2000, what is Joe’s residual demand function? What is Joe's output so he maximizes his profit? (b)If Rebecca’s output is qR, what is Joe’s best response function? (c)If Joe’s output is qj, what is Rebecca’s best response function? (d)Plot both Joe and Rebecca’s best response functions on one graph, where the the horizontal axis represents Rebecca’s output qR and the vertical axis represents Joe's output qR. (e)What is the meaning of the interception of the two best response functions?arrow_forwardSuppose two brothers own identical skydiving companies but have decided to experiment with different pricing structures. The older brother’s company, Air Adventures, charges everyone the same price, while the younger brother’s company, Sky Warriors, sets its prices using a twotiered, price-discrimination model. Assuming that both companies face the same market demand curves, marginal costs, and costs of production, and wield significant market power for their service area, which of the following is most likely to occur? a. Air Adventures will generate a similar net revenue to Sky Warriors. b. Sky Warriors will generate a higher net revenue than Air Adventures. c. Sky Warriors will generate a lower net revenue than Air Adventures. d. Air Adventures will generate a higher net revenue than Sky Warriors. e. Sky Warriors will eventually switch to the Air Adventures model.arrow_forwardTry the analysis with an n-firm Cournot oligopoly in which one firm innovates to reduce cost from c to c/2. For this problem, assume n = 2, and use the demand and cost numbers used in the lecture. That is, let inverse market demand be given by P = 100 - Q, and let marginal cost be constant at 50 per unit before the innovation, and 25 per unit after the innovation. (a) Compute what the duopolist stands to gain from innovating. How does it compare to the perfectly competitive firm and to the monopolist? (b) What can you conclude about the relationship between concentration and innovationarrow_forward
- The marginal cost of a product is fixed at MC = 20. The demand for the product is Q = 100 - 2P. (a) Now consider a Cournot model with two firms that are choosing quantities simultaneously. What is the best reply (best response) function for each firm? What is theNash equilibrium? What is the total surplus? (b)What do you expect the total surplus would be with three firms? Why? (You do not need to calculate an exact value. You can say ”total surplus is at least 100”, or ”total surplus is at most 80”)arrow_forwardAssume a market consists of two upstream firms, and they are sole suppliers of their respective products. Each of these monopolists sell at a linear price to one downstream duopolist each. What would be the effect of vertical integration (so that each upstream monopolist owns its retail outlet) on the final good price?arrow_forwardConstruct a numerical example based on a linear demand function and two firms with identical, constant marginal costs. a) Use your model to show that, a Cournot duopolist can "do better" by producing the monopoly output, under the assumption that its competitor reacts and adjusts its output optimally. b) How does this result compare to what the Stackelberg model predicted?arrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning


