
Glacier Products Inc. is a wholesaler of rock climbing gear. The company began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to securities acquired by Glacier Products Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
- 1.
Journalize the entries to record the preceding transactions. - 2. Prepare the investment-related asset and stockholders’ equity balance sheet presentation for Glacier Products Inc. on December 31, Year 2, assuming that the
Retained Earnings balance on December 31, Year 2, is $700,000.
(1)
Journalize the stock investment transactions for Company G.
Explanation of Solution
Equity investments: Equity investments are stock instruments which claim ownership in the investee company and pay a dividend revenue to the investor company.
Equity method: Equity method is the method used for accounting equity investments which claim a significant influence of above 20% but less than 50% in the outstanding stock of the investee company.
Available-for-sale securities: These are short-term or long-term investments in debt and equity securities with an intention of holding the investment for some strategic purposes like meeting liquidity needs, or manage interest risk.
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 9,000 shares of Company M, at $40 per share.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| January | 18 | Investments–Company M Stock | 360,000 | ||
| Cash | 360,000 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (1)
- Investments–Company M Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company M for 9,000 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| July | 22 | Cash | 27,000 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 27,000 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (2)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for sale of 500 shares of Company M, at $58, with a brokerage of $100.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| October | 5 | Cash | 28,900 | ||
| Gain on Sale of Investments | 8,900 | ||||
| Investments–Company M Stock | 20,000 | ||||
| (To record sale of shares) | |||||
Table (3)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Gain on Sale of Investments is an expense account. Since expenses and losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Investments–Company M Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are sold, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Calculate the realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Step 1: Compute cash received from sale proceeds.
Step 2: Compute cost of stock investment sold.
Step 3: Compute realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Note: Refer to Steps 1 and 2 for value and computation of cash received and cost of stock investment sold.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company M for 8,500 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 1 | |||||
| December | 18 | Cash | 25,500 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 25,500 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company M’s stock.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of available-for-sale securities transaction.
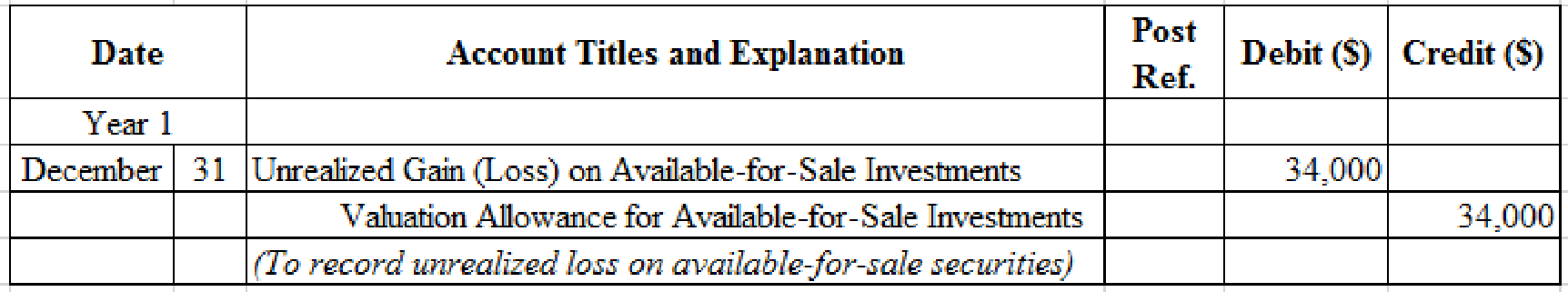
Table (5)
- Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Available-for-Sale Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since loss has occurred and losses reduce stockholders’ equity value, and a decrease in stockholders’ equity value is debited.
- Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is credited because the market price was decreased (loss) to $306,000 from the cost of $340,000.
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31, Year 1.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Available-for-sale investments at fair value, December 31, | $306,000 |
| Less: Available-for-sale investments at cost, December 31, | (340,000) |
| Unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale investments | $(34,000) |
Table (6)
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 75,000 shares out of the outstanding stock of 250,000 shares of Company H at $800,000.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| January | 25 | Investment in Company H Stock | 800,000 | ||
| Cash | 800,000 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares of Company H for cash) | |||||
Table (7)
- Investment in Company H Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company M for 8,500 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| July | 16 | Cash | 25,500 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 25,500 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (8)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company M for 8,500 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| December | 16 | Cash | 27,200 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 27,200 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (9)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company M’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for dividends received from Company H.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| December | 31 | Cash | 38,000 | ||
| Investment in Company H Stock | 38,000 | ||||
| (To record dividends received from Company H) | |||||
Table (10)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Investment in Company H Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are reduced as an effect of receipt of dividends, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare journal entry for share of income received from Company H.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Year 2 | |||||
| December | 31 | Investment in Company H Stock | 51,000 | ||
| Income of Company H | 51,000 | ||||
| (To record income realized from Company H) | |||||
Table (11)
- Investment in Company H Stock is an asset account. Since income of the investee is reported as the increase in the investment, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Income of Company H is a revenue account. Revenues increase stockholders’ equity value, and an increase in stockholders’ equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of income received from Company H.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of available-for-sale securities transaction.
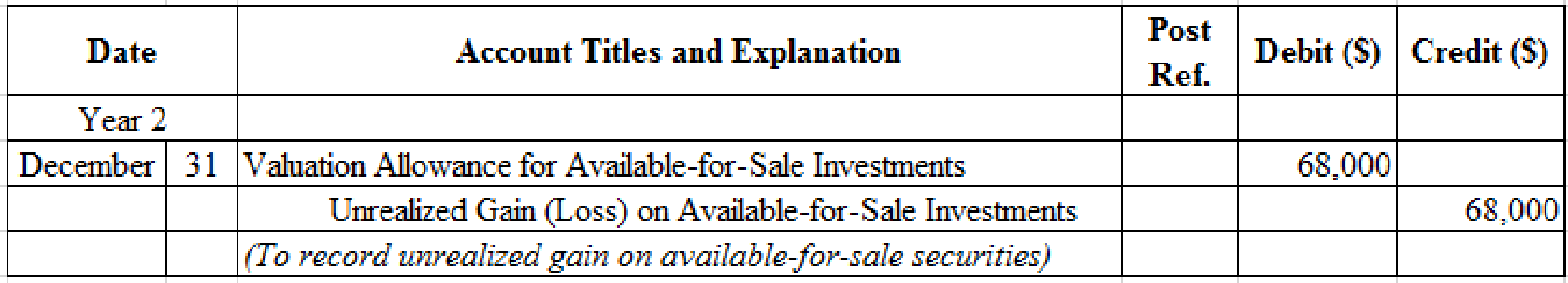
Table (12)
- Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is debited because the market price was increased (loss) to $374,000 from the cost of $306,000.
- Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Available-for-Sale Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since gain has occurred and gains increase stockholders’ equity value, and an increase in stockholders’ equity value is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Available-for-sale investments at fair value, December 31, | $374,000 |
| Less: Available-for-sale investments at cost, December 31, | (306,000) |
| Unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale investments | $68,000 |
Table (13)
(2)
Indicate the presentation of available-for-sale investments, equity method investments, and stockholders’ equity on the balance sheet as on December 31, Year 2.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet presentation:
| Company G | ||
| Balance Sheet (Partial) | ||
| December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | ||
| Available-for-sale investments (at cost) | $340,000 | |
| Add valuation allowance for available-for-sale investments | 34,000 | |
| Available-for-sale investments (at fair value) | $374,000 | |
| Investments: | ||
| Investment in Company I Stock | 813,000 | |
| Stockholders’ equity: | ||
| Retained earnings | 700,000 | |
| Unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale investments | 34,000 | |
Table (14)
Working Notes:
Compute the cost of available-for-sale investments.
Compute valuation allowance balance as on December 31, Year 2.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Valuation allowance credit balance, December 31, Year 1 | $34,000 |
| Valuation allowance debit balance, December 31, Year 2 | 68,000 |
| Valuation allowance balance | $34,000 |
Table (15)
Prepare Investment in Company H Stock account to find the stock investment balance as on December 31, Year 2.
Investment in Company H Stock account
| Investment in Company H Stock | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| Cash | 800,000 | Cash(dividends) | 38,000 | |||
| Income | 51,000 | |||||
| Total | 851,000 | Total | 38,000 | |||
| Balance | $813,000 | |||||
Table (16)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Financial Accounting, Loose-Leaf Version, 15th + LMS Integrated CengageNOWv2, 1 term Printed Access Card
- Forte Inc. produces and sells theater set designs and costumes. The company began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to securities acquired by Forte Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31: Instructions 1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions. 2. Prepare the investment-related asset and stockholders equity balance sheet presentation for Forte Inc. on December 31, Year 2, assuming that the Retained Earnings balance on December 31, Year 2, is 389,000.arrow_forwardRios Financial Co. is a regional insurance company that began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to trading securities acquired by Rios Financial Co., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31: Instructions 1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions. 2. Prepare the investment-related current asset balance sheet presentation for Rios Financial Co. on December 31, Year 2. 3. How are unrealized gains or losses on trading investments presented in the financial statements of Rios Financial Co.?arrow_forwardSoto Industries Inc. is an athletic footware company that began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to debt investments acquired by Soto Industries Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31: Instructions 1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions. 2. If the bond portfolio is classified as available for sale, what impact would this have on financial statement disclosure?arrow_forward
- Rekya Mart Inc. is a general merchandise retail company that began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to debt investments acquired by Rekya Mart Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31: Instructions 1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions. 2. If the bond portfolio is classified as available for sale, what impact would this have on financial statement disclosure?arrow_forwardYerbury Corp. manufactures construction equipment. Journalize the entries to record the following selected equity investment transactions completed by Yerbury during a recent year:arrow_forwardThe following equity investment transactions were completed by Romero Company during a recent year: Journalize the entries for these transactions.arrow_forward
- Entries for selected corporate transactions Morrow Enterprises Inc. manufactures bathroom fixtures. Morrow Enterprises stockholders equity accounts, with balances on January 1, 20Y6, are as follows: The following selected transactions occurred during the year: Instructions 1. Enter the January 1 balances in T accounts for the stockholders equity accounts listed. Also prepare T accounts for the following: Paid-In Capital from Sale of Treasury Stock; Stock Dividends Distributable; Stock Dividends; Cash Dividends. 2. Journalize the entries to record the transactions, and post to the eight selected accounts. Assume that the closing entry for revenues and expenses has been made and post net income of 1,125,000 to the retained earnings account. 3. Prepare a statement of stockholders equity for the year ended December 31, 20Y6. Assume that net income was 1,125,000 for the year ended December 31, 20Y6. 4. Prepare the Stockholders Equity section of the December 31, 20Y6, balance sheet.arrow_forwardYou are the accountant for Trumpet and Trombone Manufacturing, Inc. and you oversee the preparation of financial statements for the year just ended 6/30/2020. You have the following information from the companys general ledger and other financial reports (all balances are end-of-year except for those noted otherwise): Prepare the companys Statement of Retained Earningsarrow_forwardThe accountant of Crane Shoe has compiled the following information from the company’s records as a basis for an income statement for the year ended December 31, 2022. Rent revenue £ 23,200 Interest expense 14,400 Unrealized gain on equity securities designated at fair value through other comprehensive income, net of tax 24,800 Selling expenses 112,000 Income tax 24,480 Administrative expenses 144,800 Cost of goods sold 412,800 Net sales 784,000 Cash dividends declared 12,800 Loss on sale of plant assets 12,000 There were 20,000 ordinary shares outstanding during the year. (a) New attempt is in progress. Some of the new entries may impact the last attempt grading. Your answer is partially correct. Prepare a comprehensive income statement using the combined statement approach. (Round earnings per share to 2 decimal places, e.g. 1.48.) CRANE SHOEStatement of Comprehensive Incomechoose the accounting…arrow_forward
- On November 1 of the current year, Rob Elliot invested $30,500.00 of his cash to form a corporation, GGE Enterprises Inc., in exchange for shares of common stock. No other common stock was issued during November or December. After a very successful first month of operations, the retained earnings as of November 30 were reported at $5,000.00. After all transactions have been entered into the accounting equation for the month of December, the ending balances for selected items on December 31 follow. On that date, the financial statements were prepared. The balance sheet reported total assets of $54,400.00 and total stockholders' equity of $38,955.00. 2. What is the retained earnings amount reported on December 31? 3. How much does GGE Enterprises Inc. owe to its creditors? 4. How much cash is being held by GGE Enterprises Inc.? 5. By what amount did retained earnings increase or decrease during the period? 6. What is the amount of profit or loss during December?arrow_forwardOn November 1 of the current year, Rob Elliot invested $30,500.00 of his cash to form a corporation, GGE Enterprises Inc., in exchange for shares of common stock. No other common stock was issued during November or December. After a very successful first month of operations, the retained earnings as of November 30 were reported at $5,000.00. After all transactions have been entered into the accounting equation for the month of December, the ending balances for selected items on December 31 follow. On that date, the financial statements were prepared. The balance sheet reported total assets of $54,400.00 and total stockholders' equity of $38,955.00. 6. What is the amount of profit or loss during December? 7. What were the total expenses for December? 8. How much was paid for rent?arrow_forwardOn November 1 of the current year, Rob Elliot invested $29,250 of his cash to form a corporation, GGE Enterprises Inc., in exchange for shares of common stock. No other common stock was issued during November or December. After a very successful first month of operations, the retained earnings as of November 30 were reported at $5,000. After all transactions have been entered into the accounting equation for the month of December, the ending balances for selected items on December 31 follow. On that date, the financial statements were prepared. The balance sheet reported total assets of $55,400 and total stockholders' equity of $37,250. By what amount did retained earnings increase or decrease during the period?arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College



