
College Physics (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780321902788
Author: Hugh D. Young, Philip W. Adams, Raymond Joseph Chastain
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 50P
Figure 15.33 shows a pV diagram for an ideal gas in which its absolute temperature at b is one-fourth of its absolute temperature at a. (a) What volume does this gas occupy at point b? (b) How many joules of work were done by the gas in this process? Was the work positive or negative? (c) Did the internal energy of the gas increase or decrease from a to b?
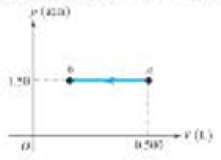
Figure 15.33
Problem 50.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An ideal diatomic gas, with rotation but no oscillation, undergoes an adiabatic compression. Its initial pressure and volume are .20 atm and 1.2 m^3. Its final pressure and volume are 1.5 atm and 2x10^6 cm^3. How much work is done by the gas? Here y=1.4
Sketch a PV diagram and find the work done by the gas during the following stages.(a) A gas is expanded from a volume of 1.0 L to 3.0 L at a constant pressure of 3.0atm. (b) The gas is then cooled at constant volume until the pressure falls to 2.0 atm.(c) The gas is then compressed at a constant pressure of 2.0 atm from a volume of 3.0L to 1.0 L. Note: Be careful of signs. (d) The gas is heated until its pressure increasesfrom 2.0 atm to 3.0 atm at a constant volume. (e) Find the net work done during thecomplete cycle. [203 J]
Suppose 4.00 mol of an ideal diatomic gas, with molecular rotation but not oscillation, experienced a temperature increase of 60.0 K under constant-pressure conditions. What are (a) the energy transferred as heat Q, (b) the change Eint in internal energy of the gas, (c) the work W done by the gas, and (d) the change K in the total translational kinetic energy of the gas?
Chapter 15 Solutions
College Physics (10th Edition)
Ch. 15 - In the ideal-gas equation could you give the...Ch. 15 - True or false? Equal masses of two different gases...Ch. 15 - How does evaporation of perspiration from your...Ch. 15 - The ideal-gas law is sometimes written in the form...Ch. 15 - (a) If you double the absolute temperature of an...Ch. 15 - Chemical reaction rates slow down as the...Ch. 15 - True or false? When two ideal gases are mixed,...Ch. 15 - Is it possible for a gas to expand and lose energy...Ch. 15 - The gas inside a balloon will always have a...Ch. 15 - When a gas expands adiabatically, it does work on...
Ch. 15 - Since Cv is defined with specific reference to a...Ch. 15 - The ratio y found in Equations 15.22 and 15.23...Ch. 15 - Prob. 1MCPCh. 15 - Prob. 2MCPCh. 15 - Prob. 3MCPCh. 15 - Prob. 4MCPCh. 15 - Prob. 5MCPCh. 15 - Prob. 6MCPCh. 15 - Assume you have n moles of an ideal gas initially...Ch. 15 - The formula U = nCvT for the change in the...Ch. 15 - For the process shown in the pV diagram in Figure...Ch. 15 - Prob. 10MCPCh. 15 - The gas shown in Figure 15.29 is in a completely...Ch. 15 - Prob. 12MCPCh. 15 - A cylindrical tank has a tight-fitting piston that...Ch. 15 - Prob. 2PCh. 15 - A 3.00 L tank contains air at 3.00 atm and 20.0C....Ch. 15 - A 20.0 L tank contains 0.225 kg of helium at...Ch. 15 - A room with dimensions 7.00 m by 8.00 m by 2.50 m...Ch. 15 - Three moles of an ideal gas are in a rigid cubical...Ch. 15 - A large cylindrical tank contains 0.750 m3 of...Ch. 15 - A 1.0 L canister contains 0.2 mole of helium gas....Ch. 15 - The gas inside a balloon will always have a...Ch. 15 - Prob. 10PCh. 15 - A diver observes a bubble of air rising from the...Ch. 15 - At an altitude of 11,000 m (a typical cruising...Ch. 15 - If a certain amount of ideal gas occupies a volume...Ch. 15 - Calculate the volume of 1.00 mol of liquid water...Ch. 15 - What volume does 2 mol of hydrogen gas (H2) occupy...Ch. 15 - The atmosphere of the planet Mars is 95.3% carbon...Ch. 15 - Find the mass of a single sulfur (S) atom and an...Ch. 15 - Prob. 18PCh. 15 - In the air we breathe at 72F and 1.0 atm pressure,...Ch. 15 - We have two equal-size boxes. A and B. Each box...Ch. 15 - Prob. 21PCh. 15 - Prob. 22PCh. 15 - A container of helium gas is heated until the...Ch. 15 - If 5 g of liquid helium is converted into a gas at...Ch. 15 - At what temperature is the root-mean-square speed...Ch. 15 - Where is the hydrogen? The average temperature of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 27PCh. 15 - STP. The conditions of standard temperature and...Ch. 15 - Prob. 29PCh. 15 - (a) How much heat does it take to increase the...Ch. 15 - (a) If you supply 1850 J of heat to 2.25 moles of...Ch. 15 - Suppose 100 J of heat flows into a diatomic ideal...Ch. 15 - Perfectly rigid containers each hold n moles of...Ch. 15 - Assume that the gases in this problem can be...Ch. 15 - A metal cylinder with rigid walls contains 2.50...Ch. 15 - A gas under a constant pressure of 1.50 105 Pa...Ch. 15 - Two moles of an ideal gas are heated at constant...Ch. 15 - Three moles of an ideal monatomic gas expand at a...Ch. 15 - Prob. 39PCh. 15 - Prob. 40PCh. 15 - A gas in a cylinder expands from a volume of 0.110...Ch. 15 - A gas in a cylinder is held at a constant pressure...Ch. 15 - Five moles of an ideal monatomic gas with an...Ch. 15 - When a system is taken from state a to state b in...Ch. 15 - An ideal gas expands while the pressure is Kept...Ch. 15 - You are keeping 1.75 moles of an ideal gas in a...Ch. 15 - Prob. 47PCh. 15 - A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3.00 mol...Ch. 15 - Figure 15.32 show a pV diagram for an ideal gas in...Ch. 15 - Figure 15.33 shows a pV diagram for an ideal gas...Ch. 15 - The pV diagram in Figure 15.34 shows a process abc...Ch. 15 - A volume of air (assumed to be an ideal gas) is...Ch. 15 - In the process illustrated by the pV diagram in...Ch. 15 - A cylinder contains 0.250 mol of carbon dioxide...Ch. 15 - Heating air in the lungs. Human lung capacity...Ch. 15 - The graph in Figure 15.37 shows a pV diagram for...Ch. 15 - An ideal gas at 4.00 atm and 350 K is permitted to...Ch. 15 - An experimenter adds 970 J of heat to 1.75 mol of...Ch. 15 - Heat Q flows into a monatomic ideal gas, and the...Ch. 15 - A player bounces a basketball on the floor,...Ch. 15 - In the pV diagram shown in Figure 15.38, 85.0 J of...Ch. 15 - Modern vacuum pumps make it easy to attain...Ch. 15 - Prob. 63GPCh. 15 - The effect of altitude on the lungs. (a) Calculate...Ch. 15 - (a) Calculate the mass of nitrogen present in a...Ch. 15 - An automobile tire has a volume of 0.0150 m3 on a...Ch. 15 - A student in a physics lab course has the task of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 68GPCh. 15 - Atmosphere of Titan. Titan, the largest satellite...Ch. 15 - Helium gas expands slowly to twice its original...Ch. 15 - A cylinder with a piston contains 0.250 mol of...Ch. 15 - You blow up a spherical balloon to a diameter of...Ch. 15 - A bicyclist uses a tire pump whose cylinder is...Ch. 15 - The bends. If deep-sea divers rise to the surface...Ch. 15 - 75. Figure 15.39 shows a pV diagram for 0.0040...Ch. 15 - Figure 15.40 Problem 76. The graph in Figure 15.40...Ch. 15 - A flask with a volume of 1.50 L, provided with a...Ch. 15 - Initially at a temperature of 80.0C, 0.28 m3 of...Ch. 15 - In a cylinder, 4.00 mol of helium initially at...Ch. 15 - Starting with 2.50 mol of N2 gas (assumed to be...Ch. 15 - Insulating windows. One way to improve insulation...Ch. 15 - Estimate the ratio of the thermal conductivity of...Ch. 15 - The rate of effusionthat is, the leakage of a gas...Ch. 15 - Prob. 84PPCh. 15 - In another test, the gas is put into a cylinder...Ch. 15 - You have a cylinder that contains 500 L of the gas...Ch. 15 - In a hospital, pure oxygen may be delivered at 50...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The Sun’s position in the Milky Way is shown in the picture above. What is the approximate distance from the Su...
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Give the metric prefix for each value.
8. 0.000001
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
Societal Reaction. It is frequently said that the detection of a signal by SETI would revolutionize human socie...
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Use the data at the back of this book to determine H for the combustion of a mole of glucose, C6H12O6+6O26CO2+6...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
1. In uniform circular motion, which of the following are constant: speed, velocity, angular velocity, centripe...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. To determine a planets average density...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An ideal gas initially at 300 K undergoes an isobaric expansion at 2.50 kPa. If the volume increases from 1.00 m3 to 3.00 m3 and 12.5 kJ is transferred to the gas by heat, what are (a) the change in its internal energy and (b) its final temperature?arrow_forwardFor a temperature increase of 10 at constant volume, what is the heat absorbed by (a) 3.0 mol of a dilute monatomic gas; (b) 0.50 mol of a dilute diatomic gas; and (c) 15 mol of a dilute polyatomic gas?arrow_forwardA sample of a monatomic ideal gas occupies 5.00 L at atmospheric pressure and 300 K (point A in Fig. P17.68). It is warmed at constant volume to 3.00 atm (point B). Then it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.00 atm (point C) and at last compressed isobarically to its original state. (a) Find the number of moles in the sample. Find (b) the temperature at point B, (c) the temperature at point C, and (d) the volume at point C. (e) Now consider the processes A B, B C, and C A. Describe how to carry out each process experimentally. (f) Find Q, W, and Eint for each of the processes. (g) For the whole cycle A B C A, find Q, W, and Eint. Figure P17.68arrow_forward
- An ideal gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a movable piston on top of it. The piston has a mass of 8 000 g and an area of 5.00 cm2 and is free to slide up and down, keeping the pressure of the gas constant. How much work is done on the gas as the temperature of 0.200 mol of the gas is raised from 20.0C to 300C?arrow_forwardWhen a gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion, which of the following statements is true? (a) The temperature of the gas does not change. (b) No work is done by the gas. (c) No energy is transferred to the gas by heat. (d) The internal energy of the gas does not change. (e) The pressure increases.arrow_forwardIf a gas is compressed isothermally, which of the following statements is true? (a) Energy is transferred into the gas by heat. (b) No work is done on the gas. (c) The temperature of the gas increases. (d) The internal energy of the gas remains constant. (e) None of those statements is true.arrow_forward
- One of a dilute diatomic gas occupying a volume of 10.00 L expands against a constant pressure of 2.000 atm when it is slowly heated. If the temperature of the gas rises by 10.00 K and 400.0 J of heat are added in the process, what is its final volume?arrow_forwardFigure P21.45 shows a cyclic process ABCDA for 1.00 mol of an ideal gas. The gas is initially at Pi = 1.50 105 Pa, Vi = 1.00 103 m3 (point A in Fig. P21.45). a. What is the net work done on the gas during the cycle? b. What is the net amount of energy added by heat to this gas during the cycle? FIGURE P21.45arrow_forwardAn ideal monatomic gas expands isothermally from 0.560 m3 to 1.25 m3 at a constant temperature of 580 K. If the initial pressure is 1.09 ✕ 105 Pa find the following. (a) the work done on the gas J (b) the thermal energy transfer Q J (c) the change in the internal energy Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thermodynamics: Crash Course Physics #23; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4i1MUWJoI0U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY