
(a)
Interpretation:
It should be determined that the structure of the ammonium ion formed, when the given amine is treated with an acid.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
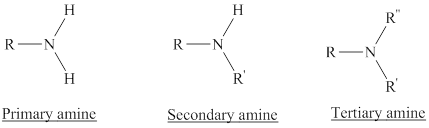
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Reaction of amines and acid will give amine salt an (ammonium ion).
(b)
Interpretation:
It should be determined that the structure of the ammonium ion formed, when the given amine is treated with an acid.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.

From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Reaction of amines and acid will give amine salt an (ammonium ion).
(c)
Interpretation:
It should be determined that the structure of the ammonium ion formed, when the given amine is treated with an acid.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.

From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Aniline is an
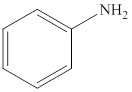
Reaction of amines and acid will give amine salt an (ammonium ion).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
- Consider the following acids and their ionization constant, determine which conjugate base is HCOOH Ka = 1.7 x 10-4 (b) HCN Ka = 4.9 x 10-10arrow_forwardWhat is the m/v % concentration of a solution of LiCl with a density of 2.07 g/mL in 40.0 mL of deionized water with a density of 1 g/mL?arrow_forwardTomato juice has a OH- concentration equal to 1 X 10 -10, what is the pH of this solution?arrow_forward
- What is the pH of a 0.0032 M solution of NaOH?arrow_forwardWhat are the molarity and the normality of a solution made by dissolving 25 g of citric acid (triprotic, C6H5O7H3) in enough water to make 800 mL of solution?arrow_forwardAmmonia, NH3, and phosphorus trihydride, PH3, both have trigonal pyramid geometry. Which one is more polar? Explain.arrow_forward
- What is the pH of a solution of 4.1 x 10-8 M NaOH in otherwise pure water?arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of stomach acid, a solution of HCl with a hydronium ion concentration of 1.2 × 10−3 M?arrow_forwardIf an unknown solution of cobalt (II) chloride has an absorbance of 0.79, what is its concentration? Include proper units, please How did you determine this using the Beer’s Law plot?arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning


