
Concept explainers
16-6 Answer true or false.
- te/7-Butylamine is a 3°
amine .
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: tert-Butylamine is
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 16.6P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of a tert-butylamine is given below:
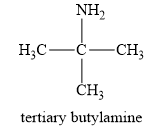
In a tert-butylamine, the carbon atom is bonded to three methyl groups, while nitrogen is attached to only one carbon group. Therefore, the tert-butyl amine is a primary amine. Therefore, this statement is false.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement about the aromatic amine is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 16.6P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
If in an amine, the nitrogen is directly bonded to one or more aryl groups or aromatic rings, and then the amine is known as an aromatic amine.
For example, aniline is an aromatic amine, as it is attached to one aromatic ring benzene. The structure of aniline is given below:
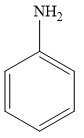
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: In a heterocyclic amine, the main nitrogen is the part of the ringis true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 16.6P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In a heterocyclic amine, the carbon group of the ring structure is replaced by the nitrogen atom. For example, in pyridine, the nitrogen atom replaces one —CH group of the benzene ring.
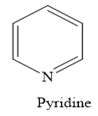
Thus, the heterocyclic amine is an amine in which nitrogen is one of the atoms of a ring. Therefore, this statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The NH4+ and CH4have the same number of valence electrons and both have tetrahedral geometry as per the VSEPR model is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
The VSEPR (Valence-shell electron pair repulsion) model predicts the shape of the molecules or ions by identifying the position of atoms connected to the central atom.
Answer to Problem 16.6P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory determines the shapes and the geometry of a molecule. In a CH4 molecule, one carbon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms with a single bond. In NH4+, one nitrogen atom is singly bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
According to the VSEPR model, each bond represents a pair of electrons. Since both compounds have four bonds around the central atom, they contain eight valence electrons. Also, according to the VSEPR model, these four bonding regions are arranged in a tetrahedral manner so that they are as far away from one another as possible, giving the molecule a tetrahedral geometry. Therefore, this statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: There are four constitutional isomers with the molecular formulaC3H9N, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Constitutional isomers are those compounds which have same molecular formula, but they differ in the arrangement of atoms in the molecules.
Answer to Problem 16.6P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula is given as C3H9N. Therefore, the possible constitutional isomers for this molecular formula are given below:
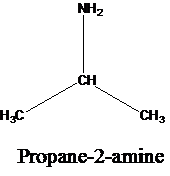
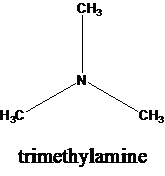
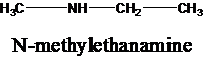
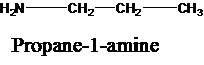
Thus, there are four constitutional isomers possible with the molecular formula C3H9N. Therefore, this statement is true.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- 16-15 There are eight primary amines with the molecular formula C5H13N. (a) Name and draw a structural formula for each amine. (b > Which of these amines are chiral?arrow_forward16-17 Propylamine (bp 48°C), ethylmethylamine (bp 37°C), and trimethylamine (bp 3°C) are constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C3HgN. Account for the fact that trimethylamine has the lowest boiling point of the three and propylamine has the highest.arrow_forward16-26 The p/fb of amphetamine is approximately 3.2 Amphetamine (a) Which form of amphetamine (the free base or its conjugate acid) would you expect to be present at pH 1.0, the pH of stomach acid? (b ) Which form of amphetamine would you expect to be present at pH 7.40, the pH of blood plasma?arrow_forward
- 16-13 Classify each amino group as primary, secondary, or tertiary and as aliphatic or aromatic. Serotonin (a neurotransmitter) Diphenhydramine (the hydrochloride salt is the antihistamine Benadryl) Lysine (an amino acid)arrow_forward17-27 Pentane, 1-butanol, and butanal all have approximately the same molecular weights but different boiling points. Arrange them in order of increasing boiling point. Explain the basis for your ranking.arrow_forward17-69 Propanal (bp 49°C) and 1-propanol (bp 97°C) have about the same molecular weight, yet their boiling points differ by almost 50°C. Explain this fact.arrow_forward
- 18-26 Answer true or false. (a) Carboxylic acids are weak acids compared to mineral acids such as HCI, H2SO4, and HNO3. (b) Phenols, alcohols, and carboxylic acids have in common the presence of an —OH group. (c) Carboxylic acids are stronger acids than alcohols but weaker acids than phenols. (d) The order of acidity of the following carboxylic acids is: (e) The order of acidity of the following carboxylic acids is: (f) The reaction of benzoic acid with aqueous sodium hydroxide gives sodium benzoate. (g) A mixture of the following compounds is extracted in order with (1) 1 M HCI, (2) 1 M NaOH, and (3) diethyl ether. Only compound II is extracted into the basic layer. (h) Conversion of compound I to compound II is best accomplished by reduction with NaBH4. (i) The following ester can be prepared by treating benzoic acid with 1-butanol in the presence of a catalytic amount of H2SO4: (j) Thermal decarboxylation of this ((-ketoacid gives benzoic acid and carbon dioxide: (k) Thermal decarboxylation of this (-ketoacid gives 2-pentanone and carbon dioxide.arrow_forward8 In Chapter 22, we will discuss a class of compounds called amino acids, so named because they contain both an amino group and a carboxyl group. Following is a structural formula for the amino acid alanine. What would you expect to be the major form of alanine present in aqueous solution (a) at pH 2.0, (b) at pH 5—6, and (c) at pH 11.0? Explain.arrow_forwardCalculate [OH-] of NaBrO, 0.810M; KaHBrO = 2.0 x 10-9. Group of answer choices 4.5 x 10-4 2.0 x 10-5 2.0 x 10-3 4.5 x 10-5arrow_forward
- Fix each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the structure it would have if it were dissolved in a 0.1 (aq) solution of NaOH 3-hydroxypropanoic acid and 1,3-dihydroxy-2-propanone .arrow_forwardCarboxylic acids are acidic enough to dissolve in both 10% NaOH and NaHCO3. Phenols, ArOH, are weak acids and most phenols will not dissolve in 10% NaHCO3. How would you separate a mixture of a carboxylic acid (RCOOH), an amine (RNH2), a phenol (ArOH) and a hydrocarbon (RH) using chemically active extraction? Draw a flow chart to illustrate your separation. Show each species in the aqueous and organic layers.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
