
Concept explainers
Answer the following questions about B, depicted in the ball-and-stick model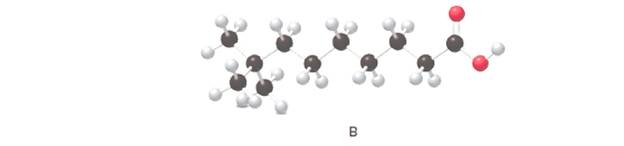
a. What is the IUPAC name for B?
b. Draw an isomer of B that has the same
c. Draw an isomer of B that has a different functional group.
d. What products are formed when B is treated with NaOH?
e. Predict the solubility properties of B in
f. What product is formed when B is treated with
g. What product is formed when B is heated with
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given ball and stick model should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
8,8-dimethylnonanoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
In the given ball and stick model of the compounds;
Black ball = C atom
White ball = H atom
Red ball = O atom
Blue ball = N atom
To assign the acceptable name to the compound, the IUPAC rules must be followed:
- Check the longest C chain and assign root word for that.
- Add prefix for the branch or side chain with its position.
- Add di, tri, tetra prefix for more than one prefix.
- The primary suffix indicates the single, double and triple bond in the molecule.
- Secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
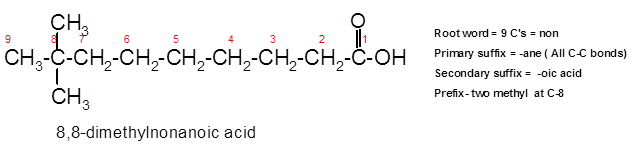
(b)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer of 8,8-dimethylnonanoic acid which has same functional group should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
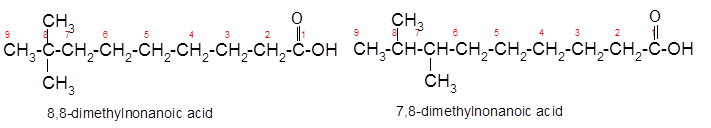
Explanation of Solution
Constitutional isomers are the isomers with same molecular formula but different arrangement of bonded atoms in the molecule. The constitutional isomer of 5-methylhexanoic acid which has same functional group must have same molecular formula but different structural arrangement of bonded atoms.
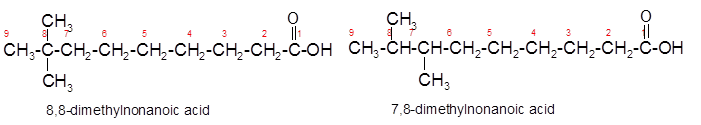
(c)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid which has different functional group should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
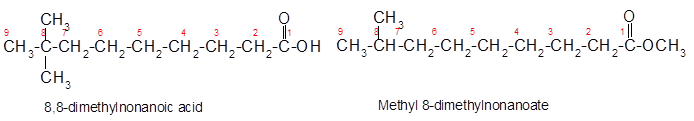
Explanation of Solution
Constitutional isomers are the isomers with same molecular formula but different arrangement of bonded atoms in the molecule. The constitutional isomer of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid which has different functional group must have same molecular formula but different functional group like ester as ester and carboxylic acid are functional isomers of each other.
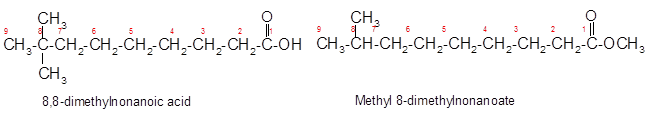
(d)
Interpretation:
The products formed when the given carboxylic 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid react with NaOH should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Amines are the organic compounds with general chemical formula of R-NH2 or R-NH-R whereas carboxylic acids are the organic molecules with R-COOH as general chemical formula.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
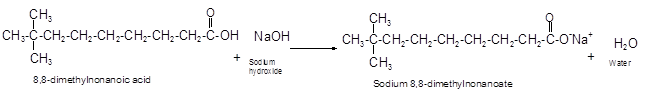
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of carboxylic acid with base like NaOH is an acid-base reaction that leads to the formation of salt and water.
It is also called as neutralization reaction. In these reactions the carboxylic acid gives H+ ions that combines with OH- ion from base and forms water. The carboxylate ion converts to sodium salt due to presence of Na+ ions in the solution.
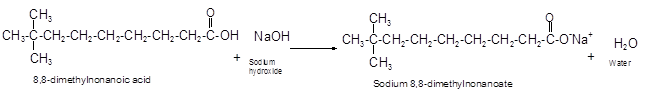
(e)
Interpretation:
The solubility of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid in water and organic solvent should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid is less soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Explanation of Solution
Organic compounds like hydrocarbons are composed of C and H atoms. They mainly have C-C and C-H bonds in their structure.
Since both C-C and C-H bonds are non-polar in nature therefore hydrocarbons like alkanes are non-polar compounds therefore it is soluble in non-polar solvents like organic solvents.
The 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid is a polar compound due to −COOH group and must form hydrogen bonds with water molecule but due to bulky alkyl group in the molecule it is very difficult for the molecule to form hydrogen bonds with water molecule. Therefore 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid is insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of H2SO4 should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Alcohols are the organic compounds with general chemical formula of R-OH whereas carboxylic acids are the organic molecules with R-COOH as general chemical formula.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
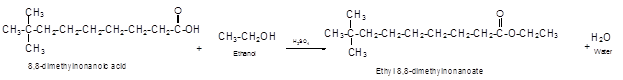
Explanation of Solution
The German chemist Emil Fischer purposed the reaction of carboxylic acid with alcohol in acidic medium to form ester and water. The reaction occurs in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid. In this reaction the alcohol carbon atom react with carbonyl carbon atom of carboxylic acid to form ester.
The reaction of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid with ethanol leads to formation of water and ester that must have −COO- group in the molecule.
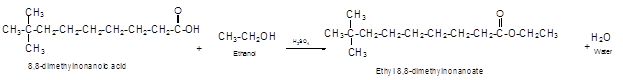
(g)
Interpretation:
The reaction of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid with ethylamine should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Alcohols are the organic compounds with general chemical formula of R-OH whereas carboxylic acids are the organic molecules with R-COOH as general chemical formula.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
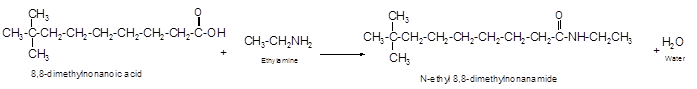
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of carboxylic acid with ammonia or amines forms amide molecules. It involves the formation of water molecule. In this reaction the amine nitrogen atom react with carbonyl carbon atom of carboxylic acid to form amide.
The reaction of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid with ethylamine leads to formation of water and amide that must have −CONH- group in the molecule.
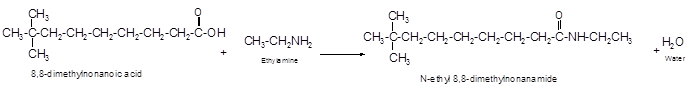
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
GENERAL ORGANIC+BIOCHEM (LL)W/CONNECT
- Molecule Type Boiling point (°C) CH3CH2CH3 Alkane -42 CH3CHO Aldehyde +21 CH3CH2OH Alcohol +78 i. Why is the boiling point of the aldehyde greater than that of the alkane?ii. Why is the boiling point of alcohol the highest?iii. Explain why the solubility of aldehydes and alcohols falls as the molecules get bigger.arrow_forward3. a. What is the chemical structure of benzoic acid, circle functional groups different than alkane,alkene, alkyne? b. Is it polar or nonpolar? _______________________ c. What is its water solubility in g/L? __________________________arrow_forwardALCOHOLS 1. WHY IS ETHANOL MORE SOLUBLE IN WATER THAN 1-HEXANOL? 2. WHAT IS DENATURED ALCOHOL? AND WHY IS ALCOHOL DENATURED? ETHER 1. WHY DOES DIETHYL ETHER HAVE MUCH LOWER BOILING POINT THAN 1-BUTANOL?arrow_forward
- 1.) What is the structure and IUPAC name of tert-butyl isopropyl acetylene? 2.) What is the structure of 2 methyl- dimethyl-alpha-hexylene? 2.) What is the structure of 3 methyl- dimethyl-beta-hexylene?arrow_forwardWhat alkenes are formed when each alcohol is dehydrated with TsOH? Label the major product when a mixture resultsarrow_forwardWhich member of each pair has the lower boiling point? Explain your choice. ***When you draw the diagrams, how do you draw the dipoles when you have CH3 CH2CH2CH3? Like how do you determine the CH3 or CH2 have the dipole. Thank you.arrow_forward
- 1) identify the reactant/s in the chemical equation and circle it, also name its major functional group 2) identify the product/s in the chemical equation (circle it) and name its functional group 3) is the a reversible reaction or not? How do we knowarrow_forward___ is an example of an alkyl halide. Select one: a. KCl b. CHCl3 c. NaCl d. CF2=CF2arrow_forwardDraw the missing starting material. Reagent 1 is benzene and AlCl3. Reagent B is Zn(Hg) and HCl.arrow_forward
- -What is the IUPAC name of the product? a. Pentanoyl chloride b.Pentanoic acid chloride c. Pentanone chloride d. Pentanyl chloride -What type of reaction is illustrated in the reaction mechanism? a. Nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction b. Electrophilic substitution reaction c. Electrophilic acyl substitution reaction d. Nucleophilic addition reaction -What is the main functional group of the organic molecule? a. Carboxyl functional group b. Aldehyde functional group c. Carbonyl functional group d. Alcohol functional group -Aside from the organic molecule, what product is formed in the reaction? a. Hydronium ion b. Hydroxide anion c. Water molecule d. Hydroxyl group -The illustrated reaction mechanism is considered __________. a. Step-wise b. Unfavorable c. Concerted d. Continuous -Which atom in the reaction mechanism is the nucleophile? a. Chloride anion b. Carboxyl carbon c. Hydroxyl group d. Methyl group -What is the type of hybridization of the carboxyl carbon in the mechanism?…arrow_forwardIdentify the IUPAC name of the given structure. A. 2 - methylhexan-5-one B. 5 - methylhexan-2-one C. 2 - heptanone D. 5 - heptanone Identify the IUPAC name of the given structure. A. 4 - bromopentan-3-one B. 1 - bromobutan-2-one C. 2 - bromobutan-one D. None of the abovearrow_forwardCircle all molecules that contain acetals.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
