Concept explainers
What alcohol can be oxidized to each carboxylic acid?
a. 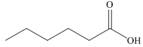 b.
b. 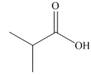 c.
c. 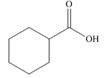
(a)
Interpretation: Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is to be identified.
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids are the carbon compounds that contain carboxyl group as a major functional group. They are polar in nature due to electronegativity difference between the atoms in a compound. They sometimes exist as a dimer. Dimers are the compounds that consist of two monomer units connected by bonds or forces. Carboxylic acids can be synthesized from alkynes, alkene, benzene derivatives, alcohol and allylic halides by using different reagents.
Answer to Problem 19.10P
Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is shown below.
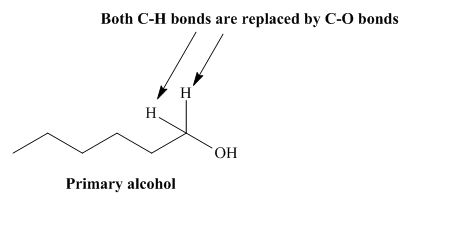
Figure 1
The compound in the figure is
Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is
(b)
Interpretation: Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is to be identified.
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids are the carbon compounds that contain carboxyl group as a major functional group. They are polar in nature due to electronegativity difference between the atoms in a compound. These sometimes exist as a dimer. Dimers are the compounds that consist of two monomer units connected by bonds or forces. Carboxylic acids can be synthesized from alkynes, alkene, benzene derivatives, alcohol and allylic halides by using different reagents.
Answer to Problem 19.10P
Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is
Explanation of Solution
The given carboxylic acid is
Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is
(c)
Interpretation: Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is to be identified.
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids are the carbon compounds that contain carboxyl group as a major functional group. They are polar in nature due to electronegativity difference between the atoms in a compound. These sometimes exist as a dimer. Dimers are the compounds that consist of two monomer units connected by bonds or forces. Carboxylic acids can be synthesized from alkynes, alkene, benzene derivatives, alcohol and allylic halides by using different reagents.
Answer to Problem 19.10P
Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is shown below.
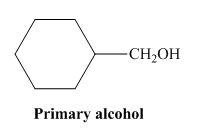
Figure 2
The compound in the figure is
Alcohol that can be oxidized to the given carboxylic acid is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Package: Organic Chemistry with Connect 2-year Access Card
- Draw the organic products formed when attached allylic alcohol A is treated with following reagent. PCCarrow_forwardexplain the following observations a. propanol is more water soluble than propane b. propanol is more water soluble than propanonearrow_forwardPredict whether Tolualdehyde will test positive for a) Tollens’ test, b) Benedict’s test. Pls explain why.arrow_forward
- Thiols have lower boiling points and are less water soluble than the corresponding alcohol e.g., CH3CH2OH and CH3CH2SH. Explain why.arrow_forwardExplain why the ether with formula C2H6O is very slightly soluble in water, whereas the alcohol with the same formula is infinitely soluble in water.arrow_forwardNot all aldehyde give a positve Bendicts test. Which of the follwing aldehydes do? a. d. b. e. c.arrow_forward
- What unsaturated carbonyl compound is formed by dehydration of each β-hydroxy carbonyl compound?arrow_forwardDraw a stepwise mechanism for the attached reaction that forms ether D. D can be converted to the antidepressant fluoxetine (trade name Prozac) in a single steparrow_forwardWhich of the following area. hemiacetals? b. acetals? c. hydrates?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




