
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The most important Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures represent covalent bonds and describe valence electrons configuration of atoms. The covalent bonds are depicted by lines, and unshared electron pairs by pairs of dots. The sequence to write Lewis structure of some molecule is given as follows:
- The central atom is identified and various other atoms are arranged around it. This central atom so chosen is often the least electronegative.
- Total valence electrons is estimated.
- single bond is first placed between each atom pair.
- The electrons left can be allocated as unshared electron pairs or as multiple bonds around the right
symbol of the element to satisfy the octet (or duplet) for each atom. - Add charge on the overall structure in case of polyatomic cation or anion.
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
Here,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure possible for
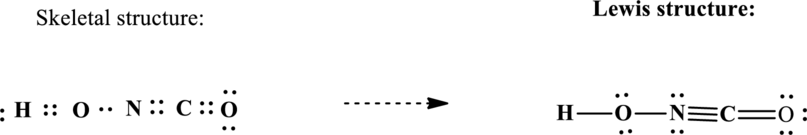
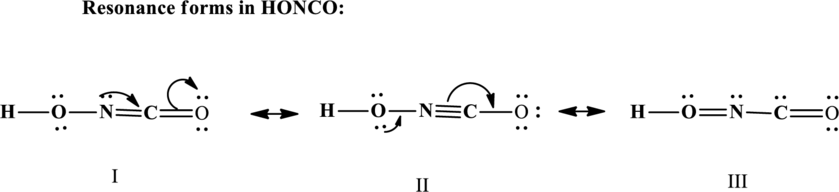
Since the double and triple bonds can conjugate therefore delocalization occurs that results in various equivalent resonance structures as indicated below:
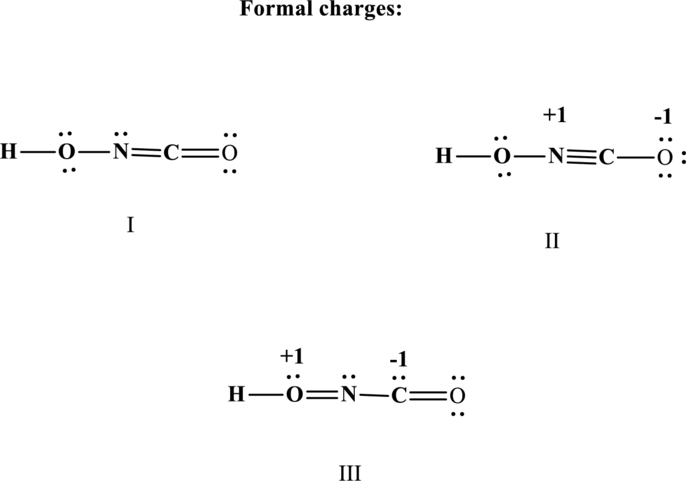
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure is calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 4 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 4 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 1 for
Therefore the non-zero formal charges can be assigned as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The most important Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure possible for
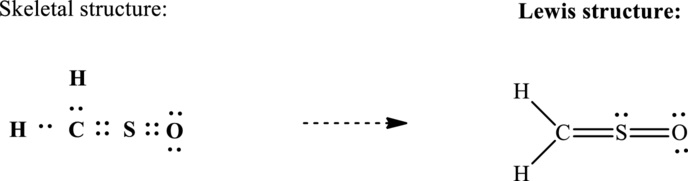
Since the double and triple bonds can conjugate therefore delocalization occurs that results in various equivalent resonance structures as indicated below:
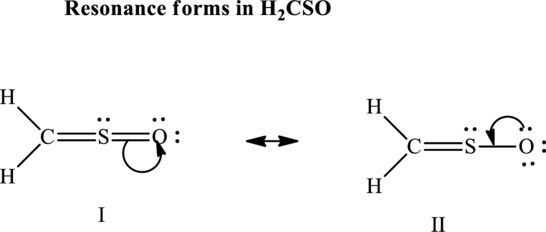
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure is calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 1 for
Therefore the formal charges can be assigned as follows:
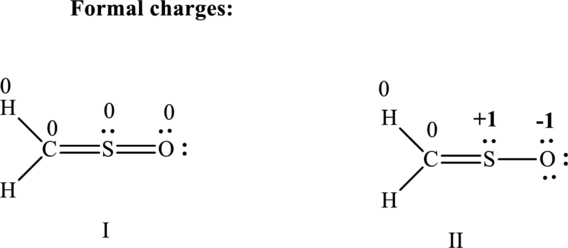
(c)
Interpretation:
The most important Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
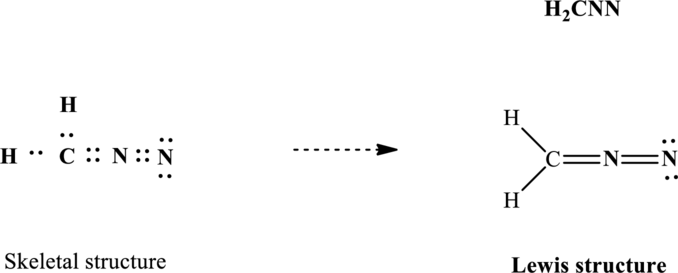
Since the double and triple bonds can conjugate therefore delocalization occurs that results in two equivalent resonance structures as indicated below:
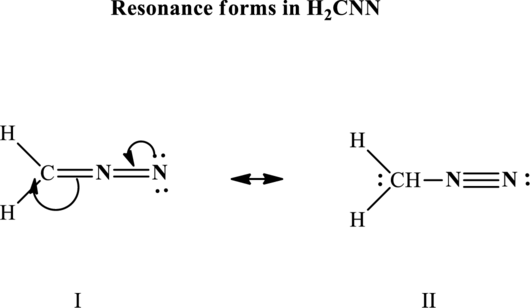
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure is calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 4 for
Substitute 1 for
Therefore the formal charges in
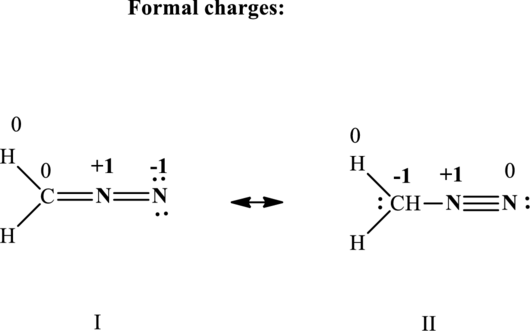
(d)
Interpretation:
The most important Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
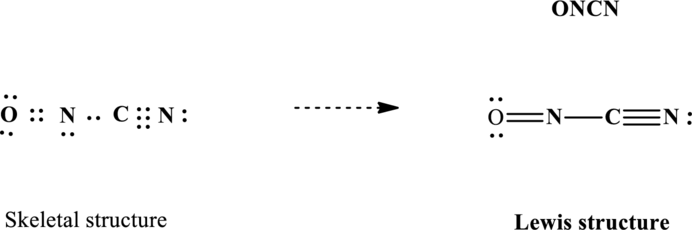
Since the double and triple bonds can conjugate therefore delocalization occurs that results in two equivalent resonance structures as indicated below:
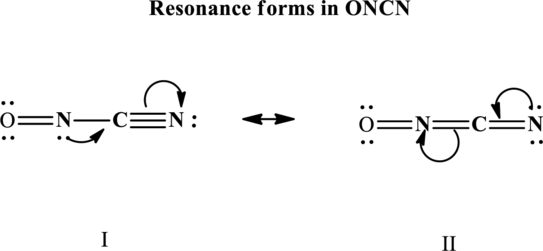
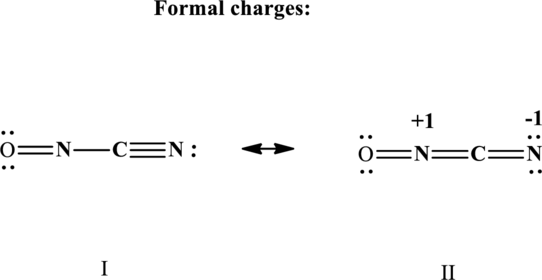
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure is calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Therefore the non-zero formal charges in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
- Carbon monoxide (CO) is an example of an overall neutral molecule (netcharge=0) that hasnon-zero formal charges. Draw a Lewis structure of carbon monoxide (CO).arrow_forwardDraw 2 resonance structures for [CH2CHCH2]+ and show all nonzero formal structuresarrow_forwardHow many lone pairs are there on the central Br atom in the Lewis structure of BrF2-?arrow_forward
- Does your molecular exhibit resonance? If so, show all possible forms. Does your molecule have any isomers? If so, show Lewis structures of them as well. for CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardDraw the major resonance form of fulminic acid, HCNO, with the atoms connected as indicated in the formula. Your structure should have nonzero formal charges minimized, and it should include all nonzero formal charges and all nonbonding electrons.arrow_forwardNOx and SOx are industrial air pollutants of grave concern. Draw the correct Lewis diagrams including formal charges on the atoms and resonance structures as appropriate for the following examples of these species: (Hint: don't use any Lewis structures with formal changes exceeding +1 or -1) Nitrous oxide, N2O, and disulfur monoxide, S2O The nitrogen trioxide radical, NO3- and sulfur trioxide, SO3; Use VSERP to assign the shape to these 4 molecules. Describe the polarity of each molecule. Which one is more polar? Justify your answer in terms of dipole moments and geometry.arrow_forward
- Draw Lewis structures for these ions and show which atom (or atoms) in each bears the formal charge. Q.) CH3NH3+arrow_forwardDetermine the number of valence electrons in sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and then draw the corresponding Lewis structure (with minimized formal charges).arrow_forwardWrite Lewis structures for these ions. Show all valence electrons and all formal charges. (Q) Acetate ion, CH3COO-arrow_forward
- 3. Write a Lewis structure suitable for crotonaldehyde, CH3CHCHCHO, used as tear gas and insecticide.arrow_forwardstructure of CH2O showing the unshared electron pairs and nonzero formal chargesarrow_forwardThe compound SF3N has been synthesized. (a) Draw the Lewis diagram of this molecule, supposing that the three fluoride atoms and the nitrogen atom surround the sulfur atom. Indicate the formal charges. Repeat, but assume that the three fluorine atoms and the sulfur atom surround the nitrogen atom. (b) From the results in part (a), speculate about which arrangement is more likely to correspond to the actual molecular structurarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

