
CAMPBELL BIO-MOD.MASTERING ACCESS
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780135351789
Author: Urry
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 11TYU
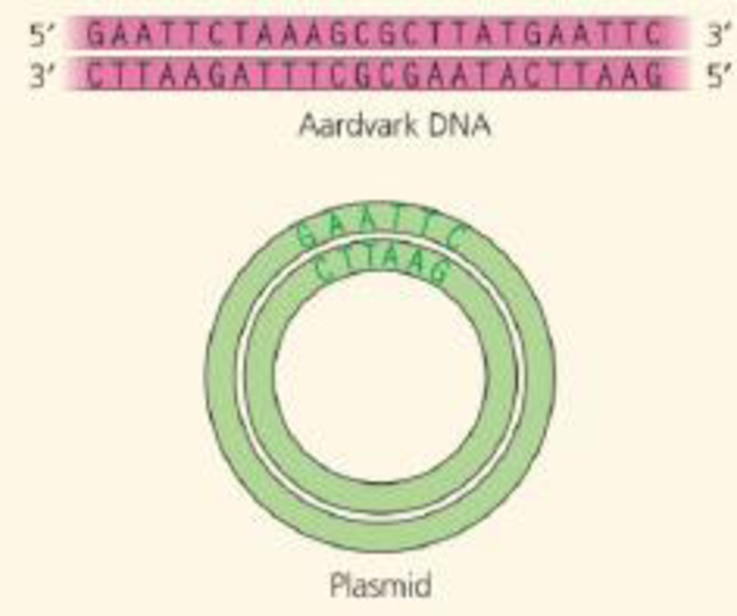
DRAW IT You are cloning an aardvark gene, using a bacterial plasmid as a vector. The green diagram shows the plasmid, which contains the restriction site for the enzyme used in Figure 20.5. Above the plasmid is a segment of linear aardvark DNA that was synthesized using PCR. Diagram your cloning procedure, and show what would happen to these two molecules during each step. Use one color for the aardvark DNA and its bases and another color for those of the plasmid. Label each step and all 5' and 3' ends.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
As you know, restriction enzymes evolved in different bacterial species independently. The adaptive significance of having a restriction enzyme is that the bacterium has the ability to cut the injected viral DNA into small segments. This destruction of viral DNA prevents the virus from taking over the bacterial cell and killing the cell.
What is one benefit of using a restriction enzyme with staggered ends (such as EcoRI) to cut both the DNA insert and the plasmid?
Which types of cut sites (staggered with “sticky ends” or blunt ends) are most useful in cloning DNA?
Would you expect restriction enzymes in different bacteria genera (Streptococcus, Lactobacter, Escherichia) to have the same recognition sites (DNA sequences). Why or why not?
You’re working in a research lab, and your current task is to clone the gene that codes for tyrosinase from potatoes. You grind up some potato, extracts the DNA from it and digests the DNA with two different restriction enzymes (separately, not together): EcoRI and BamHI. You then obtain the cloning vector, pUC19, and digest it with the same two enzymes. You then run a gel which is shown to the right.
You mix the potato DNA (digested with the enzyme you specified in part B) with cloning vector DNA (digested with the same enzyme). You then add the mixture to E. coli cells and carry out a transformation procedure so that the cells can each update a plasmid. You then plate the cells on a plate containing antibiotic. What antibiotic would be in the plate? Why would there be antibiotic in the plate? Be specific!
Unfortunately, you don’t get a single bacterial colony to grow on the plate. Not even one! You review your procedure and realize that when mixing the digested potato DNA…
Give typed full explanation
you made a recombinant plasmid (it is circular) that contains the sequence 5' AAGCTT in the middle of the inserted or cloned gene. that is the only place where this sequence occurs. the entire plasmif does not have 5' GAATTC. When putting this plasmid into E. coli (transformstion) what will happen?
1. plasmid will cut into several fragments
2. nothing the plasmif with remain circular
3. plasmid will be cut once making a linear dna fragment
4. will be cut once but will becomr two linear fragments
Chapter 20 Solutions
CAMPBELL BIO-MOD.MASTERING ACCESS
Ch. 20.1 - Prob. 1CCCh. 20.1 - DRAW IT One Strand of a DNA molecule has the...Ch. 20.1 - What are some potential difficulties in using...Ch. 20.1 - VISUAL SKILLS Compare Figure 20.7 with Figure...Ch. 20.2 - Prob. 1CCCh. 20.2 - Prob. 2CCCh. 20.3 - Based on current knowledge, how would you explain...Ch. 20.3 - Prob. 2CCCh. 20.3 - Prob. 3CCCh. 20.4 - What is the advantage of using stem cells for gene...
Ch. 20.4 - Prob. 2CCCh. 20.4 - Prob. 3CCCh. 20 - Describe how the process of gene doning results in...Ch. 20 - What useful Information is obtained by detecting...Ch. 20 - Describe how, using mice. a researcher could carry...Ch. 20 - What factors affecf whether a given genetic...Ch. 20 - In DNA technology, the term vector can refer to...Ch. 20 - Which of the following tools of DNA technology is...Ch. 20 - Prob. 3TYUCh. 20 - A paleontologist has recovered a bit of tissue...Ch. 20 - DNA technology has many medical applications....Ch. 20 - Which of the following is not true of cDNA...Ch. 20 - Expression of a cloned eukaryotic gene in a...Ch. 20 - Which Ii of the following sequences in...Ch. 20 - Prob. 9TYUCh. 20 - MAKE CONNECTIONS Looking at Figure 20.15, what...Ch. 20 - DRAW IT You are cloning an aardvark gene, using a...Ch. 20 - EVOLUTlON CONNECTION Ethical considerations aside,...Ch. 20 - Prob. 13TYUCh. 20 - Prob. 14TYUCh. 20 - The water in the Yellowstone National Park hot...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Cloning Genes Is a Multistep Process In cloning human DNA, why is it necessary to insert the DNA into a vector such as a bacterial plasmid?arrow_forwardFigure 17.7 You are working in a molecular biology lab and, unbeknownst to you, your lab partner left the foreign genomic DNA that you are planning to clone on the lab bench overnight instead of storing it in the freezer. As a result, it was degraded by nucleases, but still used in the experiment. The plasmid, on the other hand, is fine. What results would you expect from your molecular cloning experiment? There will be no colonies on the bacterial plate. There will be blue colonies only. There will be blue and white colonies. The will be white colonies only.arrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes the process of DNA sequencing? a. DNA is separated on a gel, and the different bands are labeled with fluorescent nucleotides and scanned with a laser. b. A laser is used to fluorescently label the nucleotides present within the DNA, the DNA is run on a gel, and then the DNA is broken into fragments. c. Nucleotides are scanned with a laser and incorporated into the DNA that has been separated on a gel, and then the DNA is amplified with PCR. d. Fragments of DNA are produced in a reaction that labels them with any of four different fluorescent dyes, and the fragments then are run on a gel and scanned with a laser. e. DNA is broken down into its constituent nucleotides, and the nucleotides are then run on a gel and purified with a laser.arrow_forward
- Which statement is NOT the function of restriction enzyme? Group of answer choices It cuts the vector’s plasmid and the desired gene from the original DNA. It ligates the desired to gene to vector’s plasmid. It acts as scissors of DNA that cut along a specific sequence. It serves as degrading proteins that cut plasmid on specific target site.arrow_forwardYou have two PCR primers: Forward- 5' TGAGCTAGGC 3' and Reverse- 5' GGTTCAGTCAG 3'. Show the binding sites of the primers to their Double strand DNA template. As the primer sizes are 10 and 11 bp, just write a 30 bp double stranded DNA (making sure the 5' and 3' ends of the double strand DNA in all 4 ends) and show where in the 30 bp double stranded DNA, these two primers would bind in correct orientation.arrow_forwardYou isolated a 10,500 base pair plasmid (supercoiled, cccDNA) from E. coli. The plasmid contains one unique recognition site for EcoRI, a restriction enzyme. Restriction enzymes recognize a specific sequence and cut both strands of the DNA at that sequence (Chapter 7). Brief DNase I treatment breaks one (or very few) phosphodiesterbonds in each DNA molecule, leaving the double-stranded DNA with one strand broken but the other strand intact, i.e “nicked.” You briefly incubated the cccDNA at 37°C in four separate reactions containing the components listed below. You ran each reaction sample on an agarose gel and visualized the DNA using ethidium bromide and UV light. The reactions included the appropriate buffer and ATP when required. An agarose gel containing four lanes of possible products is given below. Please refer to Figs. 4-26 and 4-27 in Watson for reference. For each reaction, indicate which lane of the gel contains the products that you would expect to see on your…arrow_forward
- Why is it important to sequence positive clones derived from PCR cloning? Group of answer choices Errors could have been incorporated during restriction enzyme digestion and so it is important to verify that only the expected protein is produced. Errors could have been incorporated during plasmid DNA extraction and so it is important to verify that only the expected protein is produced. Errors could have been incorporated during PCR and so it is important to verify that only the expected protein is produced. Errors could have been incorporated during cloning and so it is important to verify that only the expected protein is produced.arrow_forwardWhat's the cloning process from the first step to the last? Put the steps in order based on the following options: -Cut out the gene of interest with a restriction enzyme -Transform the E. coli with the plasmid. -Ligate the backbone of the DNA from the plasmid to the gene of interest. -Allow the gene of interest to anneal at the insertion site in the plasmid. -Select colonies based on the reporting system used in the plasmid. -Cut open the multiple cloning site on a plasmid with a restriction enzyme.arrow_forwardAn important feature of restriction enzymes is that each enzyme only recognizes a specific palindrome and cuts the DNA only at that specific sequence of bases. A palindromic sequence can be repeated a number of times on a strand of DNA, and the specific restriction enzyme will cut all those palindromes, no matter what species the DNA comes from. A linear DNA molecule is represented below. The DNA is represented by one line, although in actuality, DNA has two strands. If the DNA molecule has two restriction sites, specifically two repeats of a specific palindrome sequence, A and B, for a specific restriction enzyme: How many fragments would be produced if the DNA is cut by that enzyme? Number each fragment Which fragment would be the largest? Which fragment would be the smallest?arrow_forward
- On the gel shown below are four DNA samples. Samples A to C are taken from tissues of landslide victims that are being identified, while sample D came from a hair sample brought by a mother looking for the remains of her son. (see img) i. If similar band patterns in a gel are created using the same restriction enzyme, what does that tell you about the DNA sequence of the samples? ii. In sample C, only two fragments were created. How many restriction sites (regions where enzymes cut) are present in sample C?arrow_forwardYou want to make a recombinant DNA in which aPCR product amplified from the human genome is inserted into a plasmid vector. The polylinker of thisvector includes recognition sites for the enzymesEcoRI (5′ G^AATTC 3′) and BamHI (5′ G^GATCC3′). (The ^ symbolizes the cut site in the DNA.) PCRprimers that could amplify the fragment of humanDNA are: 5′ GCTACTTCGCGTATTCCA 3′ and5′ CCCAAGTCCTAGCCGATA 3′.a. Describe in detail how these primers would need tobe modified to create a fragment of the human genome flanked by EcoRI sticky ends so that thisfragment could be cloned easily into the plasmidvector. You will need to consider the fact that mostrestriction enzymes, including EcoRI, cannot cutDNA if the restriction site is directly at the end ofthe DNA molecule; the restriction enzyme recognition site must be at least six base pairs distant fromthe end.b. Describe a potential feature of the PCR-amplifiedregion of the human genome that could prevent youfrom using the strategy you described in…arrow_forwardAfter you design the PCR primers, you run the PCR on fluid from the patient’s nasal swab. Next, you need to evaluate the results. PCR makes billions of copies of just one sequence in a sample. Since you know the sequence, you also know the length (number of nucleotides) of the region you copied. There are about 130 nucleotides in the N gene fragment. This is typically stated as 130 base pairs. How can you visualize DNA and estimate its size? Load the DNA sample into an agarose gel (similar in consistency to jello) and apply an electric current to the gel. The DNA is charged and will move through the gel. The longer the DNA fragment, the more slowly it moves. The DNA is visualized by adding a fluorescent dye to your sample that sticks to DNA. When you look at the gel under UV light, the DNA should glow. What is the charge of a DNA molecule? Based on #1, would you expect DNA to be drawn to the (+) or (-) electrode of the gel electrophoresis chamber?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax
Molecular Techniques: Basic Concepts; Author: Dr. A's Clinical Lab Videos;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7HFHZy8h6z0;License: Standard Youtube License