
Concept explainers
What product is formed when
(a)
(a)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alkenes on hydrogenation reaction in the presence of
Answer to Problem 20.15P
The product formed by the treatment of
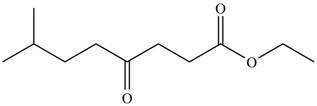
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The given compound
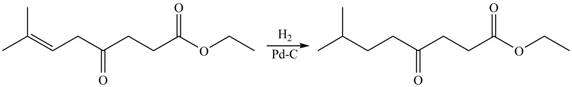
Figure 2
The product formed by the treatment of
(b)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alkenes on hydrogenation reaction in the presence of
Answer to Problem 20.15P
The product formed by the treatment of
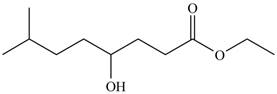
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The given compound
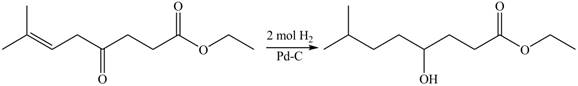
Figure 4
The product formed by the treatment of
(c)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alkenes on hydrogenation reaction in the presence of
Answer to Problem 20.15P
The product formed by the treatment of
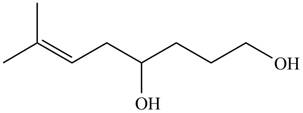
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
The given compound
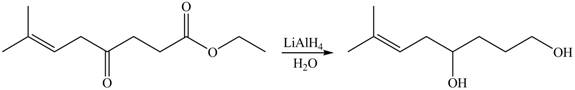
Figure 6
The product formed by the treatment of
(d)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alkenes on hydrogenation reaction in the presence of
Answer to Problem 20.15P
The product formed by the treatment of
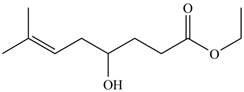
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The given compound
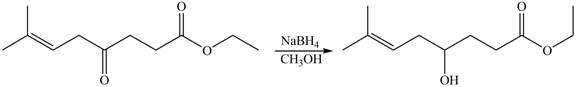
Figure 8
The product formed by the treatment of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Access (Custom)
- Eleostearic acid, C18H30O2, is a rare fatty acid found in the tung oil used for finishing furniture. On ozonolysis followed by treatment with zinc, eleostearic acid furnishes one part pentanal, two parts glyoxal (OHC-CHO), and one part 9-oxononanoic acid [OHC(CH2)7CO2H]. What is the structure of eleostearic acid?arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when phenol(C6H5OH) is treated with each reagent. Give an explanation. d. (CH3CH2)2CHCOCl, AlCl3 j. product in (d), then NH2NH2, – OHarrow_forwardDraw the products formed when (CH3)2C=CH2 is treated with following reagent. [1] BH3; [2] H2O2, HO−arrow_forward
- Draw the product formed when (CH3)2CHOH is treated with each reagent (a, b and c)arrow_forwardOximene and myrcene, two hydrocarbons isolated from alfalfa that have the molecular formula C10H16, both yield 2,6- dimethyloctane when treated with H2 and a Pd catalyst. Ozonolysis of oximene forms (CH3)2C = O, CH2 = O, CH2(CHO)2, and CH3COCHO. Ozonolysis of myrcene yields (CH3)2C = O, CH2 = O, (two equiv), and HCOCH2CH2COCHO. Identify the structures of oximene and myrcene.arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when p-methylaniline (p-CH3C6H4NH2) is treated with each reagent. a. HCl b. CH3COCl c. (CH3CO)2O d. excess CH3I e. (CH3)2C = O f. CH3COCl, AlCl3 g. CH3CO2H h. NaNO2, HCl i. Part (b), then CH3COCl, AlCl j. CH3CHO, NaBH3CNarrow_forward
- Draw the products formed when A is treated with each reagent: (a) H2 + Pd-C; (b) mCPBA; (c) PCC; (d) CrO3, H2SO4, H2O; (e) Sharpless reagent with (+)-DET.arrow_forwardWhat is the major stereoisomer formed when each alkyl halide is treated with KOC(CH3)3?arrow_forwardWhat product is formed when each compound is treated with either Ag2O, NH4OH or Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O?arrow_forward
