
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
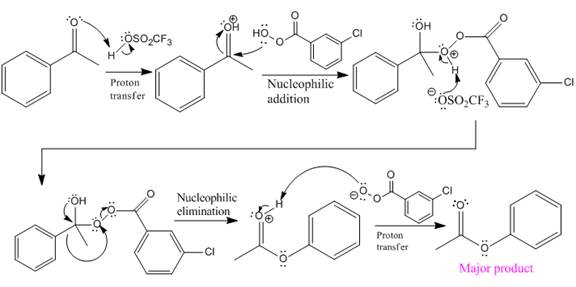
Explanation of Solution
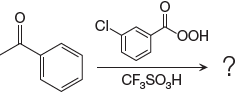
The given reaction is:
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a primary alkyl group and an aryl group. According to migratory aptitude, the aryl group has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction, an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and phenyl group, initially bonded to the carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:
The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of the given reaction conditions.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
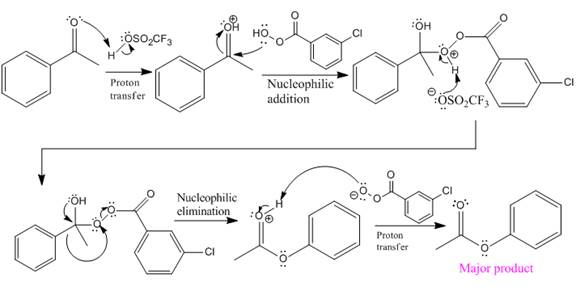
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
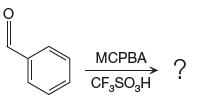
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a H atom and an aryl group. According to the migratory aptitude, the H atom has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction, an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and the H atom, initially bonded to carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:
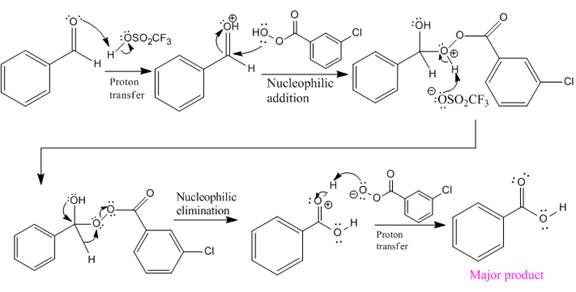
The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of given reaction conditions.
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
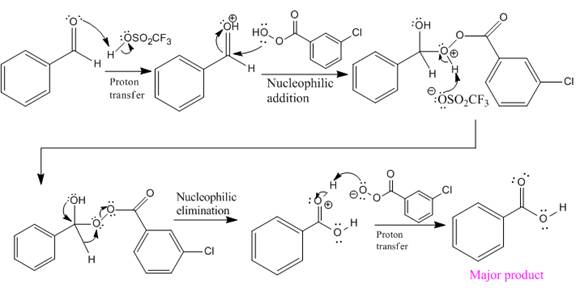
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
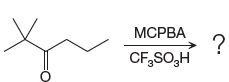
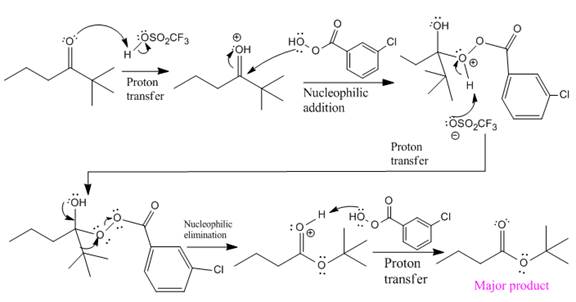
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a primary alkyl group and tertiary alkyl group. According to migratory aptitude, the tertiary alkyl group has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and the tertiary alkyl group, initially bonded to carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:

The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of given reaction conditions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





