
a.
To sketch: Electric field lines between two like charges of equal magnitude.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Electric field lines:
The electric field lines are actually the line of force. They are imaginary in nature. To determine the direction of net field at any point, a tangent is drawn at that point.
The lines of electric field originate from the positive charge and terminates in the negative charge.
The electric field lines between two like charges of equal magnitude is shown below,
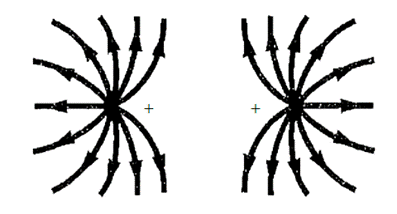
The lines of electric field are always perpendicular to the surface of the charge. Since the two charge are similar in nature and magnitude, so they will repel each other and hence the lines of electric field points away from the positive charge as shown above.
The lines of electric field are assumed to terminates at infinity.
b.
To sketch: Electric field lines between two unlike charges of equal magnitude.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Electric field lines:
The electric field lines are actually the line of force. They are imaginary in nature. To determine the direction of net field at any point, a tangent is drawn at that point.
The lines of electric field originate from the positive charge and terminates in the negative charge.
The electric field lines between two unlike charges that is a positive and negative charge is shown below,
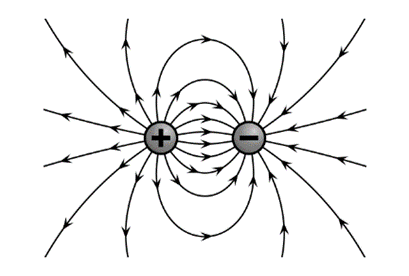
The lines of electric field are always perpendicular to the surface of the charge. Since the two charge are similar in magnitude but different in nature, so the lines of electric field originate from positive and terminate at negative charge as shown above.
c.
To sketch: Electric field lines between a positive charge and a negative charge of double magnitude.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Electric field lines:
The electric field lines are actually the line of force. They are imaginary in nature. To determine the direction of net field at any point, a tangent is drawn at that point.
The lines of electric field originate from the positive charge and terminates in the negative charge.
The electric field lines between a positive and negative charge of double magnitude is shown below,
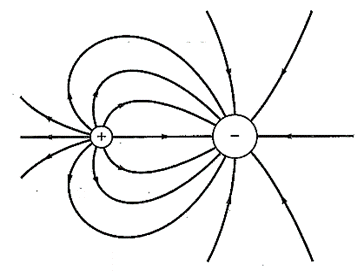
The lines of electric field are always perpendicular to the surface of the charge. Since the two charge differ in magnitude as well as nature, so the lines of electric field originate from positive and terminate at negative charge as shown above. As the negative charge is double in magnitude, so its electric field is high which is represented by more field lines.
d.
To sketch: Electric field lines between two oppositely charged parallel plates.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Electric field lines:
The electric field lines are actually the line of force. They are imaginary in nature. To determine the direction of net field at any point, a tangent is drawn at that point.
The lines of electric field originate from the positive charge and terminates in the negative charge.
The electric field lines between two oppositely charged parallel plates is shown below,
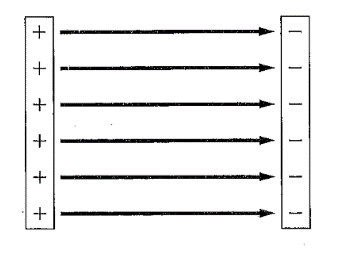
The lines of electric field are always perpendicular to the surface of the charge. Here, the lines of electric field originate from positive and terminate at negative charge as shown above.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
University Physics Volume 1
College Physics (10th Edition)
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





