
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism, for base catalyzed exchange of hydrogen
Concept introduction:
A carbonyl group has
Answer to Problem 22.74AP
The curved arrow mechanism for base catalyzed exchange of hydrogen
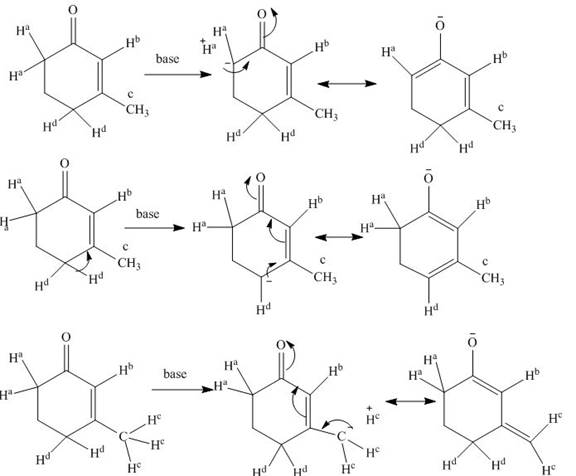
Explanation of Solution
The structure of compound is given below.
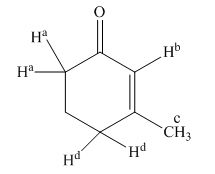
Figure 1
When a base is present in the medium, it easily removes the
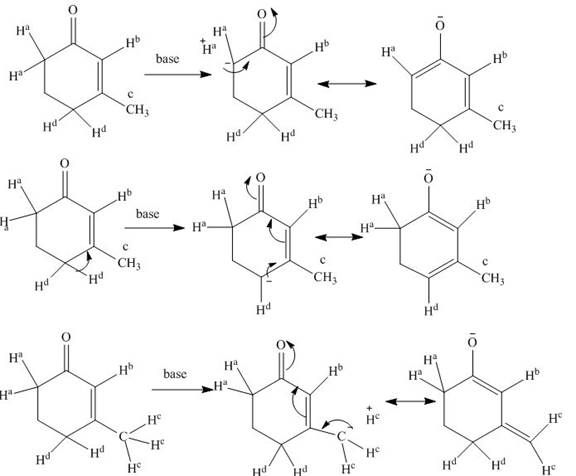
Figure 2
The base catalyzed exchange of hydrogen
(b)
Interpretation:
The less acidic character of
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.74AP
The proton,
Explanation of Solution
The
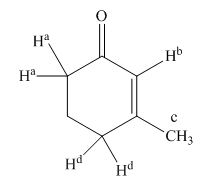
Figure 3
The
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for exchange of
Concept introduction:
In presence of the acid or base, the enone compounds remain in equilibrium with their isomers. Due to this, acidity of
Answer to Problem 22.74AP
The isomer
Explanation of Solution
The equilibrium of isomers,
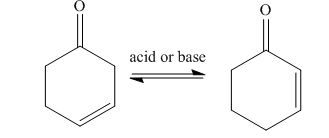
Figure 4
The
The reaction mechanism is shown in figure below.
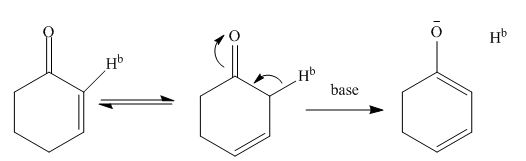
Figure 5
The
(d)
Interpretation:
The hydrogen that is replaced by deuterium in sex hormone, testosterone is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 22.74AP
The hydrogen at position “a” in vicinity to carbonyl carbon can be exchanged for deuterium in
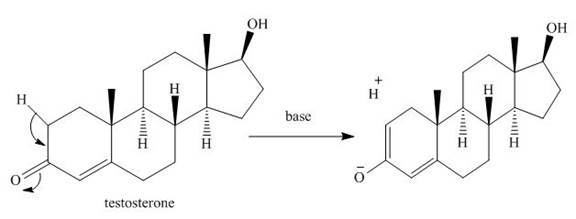
Explanation of Solution
The structure of sex hormone testosterone is given below.
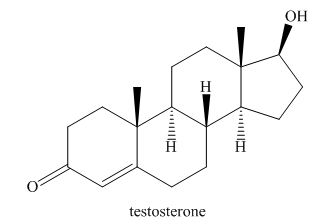
Figure 6
The hydrogen present at position “a” can be exchanged with deuterium, in sex hormone testosterone. This hydrogen, being at
The mechanism for the same can be shown as given below.

Figure 7
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- From 1 being the least acidic and 4 being the most acidic, arrange the following organic compounds in terms of increasing acidityarrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium-constant expressions and obtainnumerical values for each constant in. (a) the basic dissociation of aniline, C6H5NH2. (b) the acidic dissociation of hypochlorous acid,HClO. (c) the acidic dissociation of methyl ammoniumhydrochloride, CH3NH3Cl. (d) the basic dissociation of NaNO2. (e) the dissociation of H3AsO3to H3O+and AsO33-. (f) the reaction of C2O42-with H2O to give H2C2O4and OH-. show solutionarrow_forwardThe following three derivatives of succinimide are anticonvulsants that have found use in the treatment of epilepsy, particularly petit mal seizures. Q. Of these three anticonvulsants, one is considerably more acidic than the other two. Which is the most acidic compound? Estimate its pKa and account for its acidity. How does its acidity compare with that of phenol? with that of acetic acid?arrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity (1 = least acidic, 3 = most acidic) and in the space provided use resonance (of the conjugate base) to explain why the compound you have labelled “3” is the most acidic.arrow_forwardS.2. List the following compounds by discussing their basicity.arrow_forwardThe structure of hydrocodone is provided below: 2a) Give the sterochemistry of hydrocodone while focusing on E/Z, chirality, eclipsed/staggered, equatorial/axial2b) Describe the acidity/basticity of hydrocodone and find the most acidic Hydrogenarrow_forward
- Treatment of indene with NaNH2 forms its conjugate base in a Brønsted– Lowry acid–base reaction. Draw all reasonable resonance structures for indene's conjugate base, and explain why the pKa of indene is lower than the pKa of most hydrocarbons.arrow_forwardRank each of the following sets of nitrogen bases in terms of basicity and explain your answerarrow_forwardArrange the following organic molecules in order of increasing acidity, starting with the least acidic and explain your answer CH3CH3, HC≡CH and CH2=CH2arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

