
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
In
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
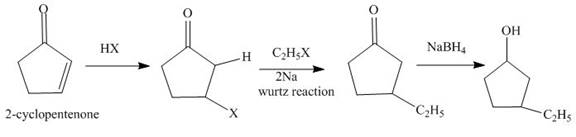
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
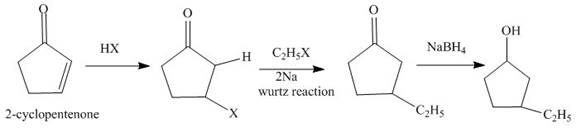
Figure 1
The synthesis of
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
In organic chemistry, the class of functional group which is derived from conjugated diene by replacing one double bond with a carbonyl group. The dienone compound is in conjugation to each other.
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
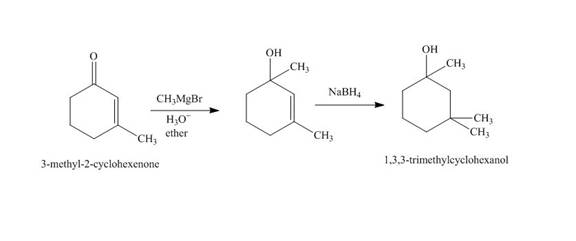
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
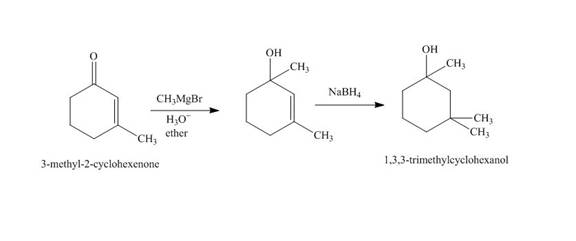
Figure 2
The synthesis of
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
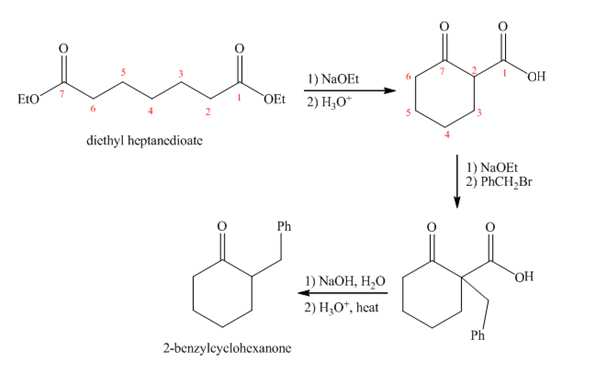
Explanation of Solution
Diethyl heptanedioate in presence of

Figure 3
The synthesis of
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
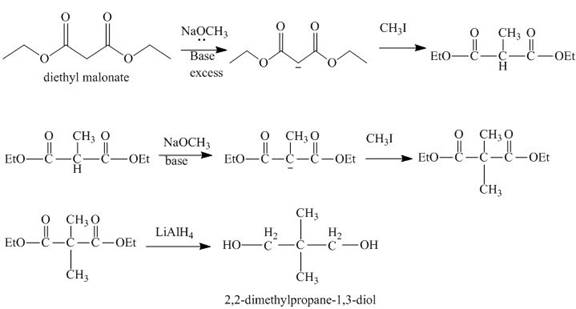
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of diethyl malonate in presence of base and then

Figure 4
The synthesis of
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic acid which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
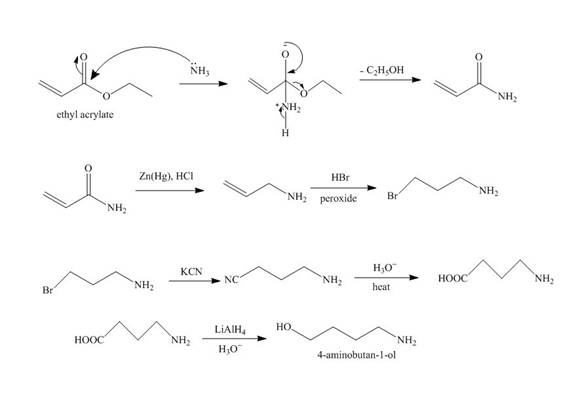
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ethyl acrylate with ammonia forms amide derivative. It undergoes reduction reaction with

Figure 5
The synthesis of
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
In organic chemistry, the compound with the molecular formula
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
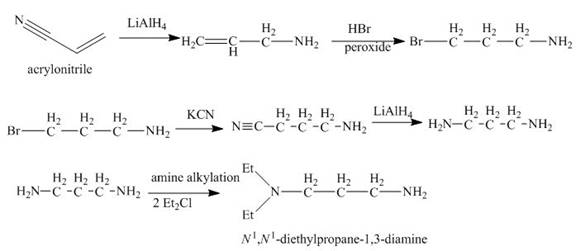
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of acrylonitrile with
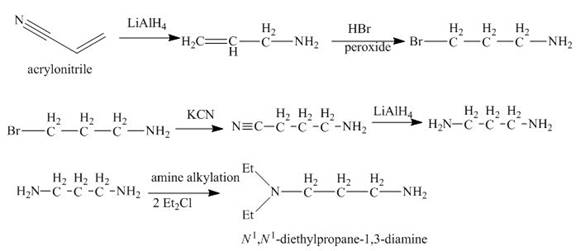
Figure 6
The synthesis of
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound contains a
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
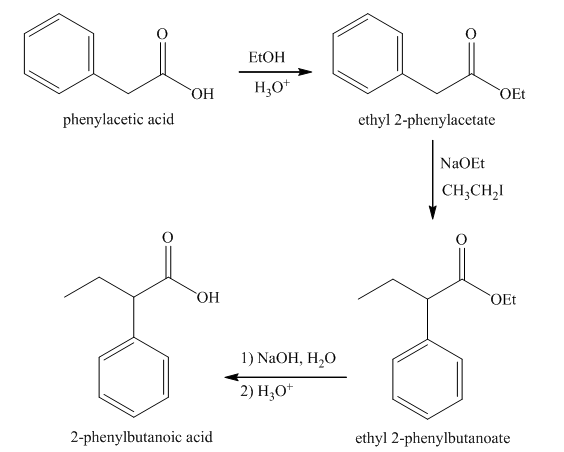
Explanation of Solution
Esterification of phenylacetic acid forms ethyl

Figure 7
The synthesis of
(h)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
In Aldol condensation reaction, the base abstracts an acidic proton from the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
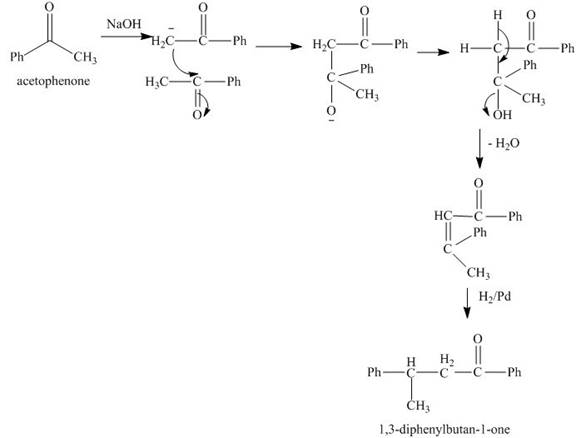
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of acetophenone in presence of base abstracts a

Figure 8
The synthesis of
(i)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of deuterium substituted diphenylethanol from phenylacetic acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of di-deuterium substituted diphenyl ethanol from phenylacetic acid is shown below.
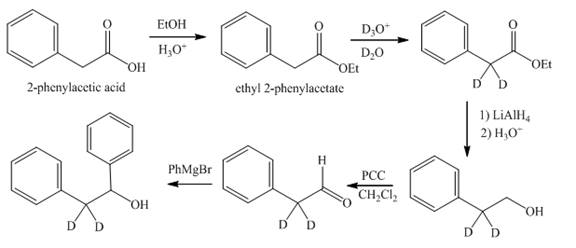
Explanation of Solution
Reaction of

Figure 9
The synthesis of deuterium substituted diphenyl ethanol from phenylacetic acid is shown in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of tetra-deuterium substituted product from cyclohexanone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In organic chemistry, the carbonyl compound is a class of functional group which contains a
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of tetra-deuterium substituted product from cyclohexanone is shown below.
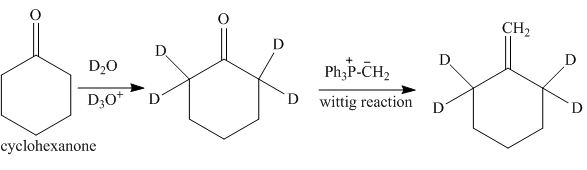
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of cyclohexanone with

Figure 10
The synthesis of tetra-deuterium substituted from cyclohexanone is shown in Figure 10.
(k)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
Friedel Craft acylation is an electrophilic
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
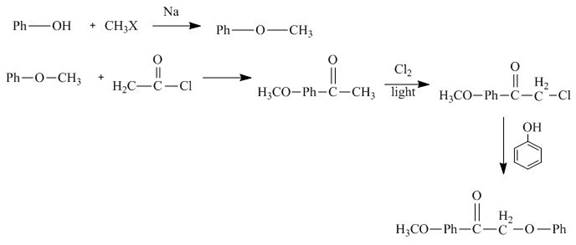
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of phenol with methyl halide forms methylphenyl ether. It reacts with acetyl chloride followed by chlorination in sunlight. Then it reacts with phenol to give the desired product. The synthesis of

Figure 11
The synthesis of
(l)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
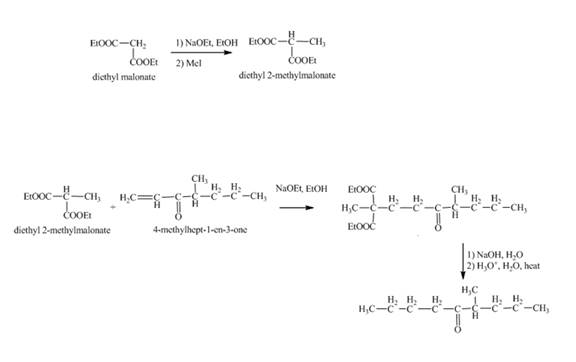
Explanation of Solution
Methylation of diethyl malonate in the presence of sodium ethoxide and

Figure 12
The synthesis of
(m)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
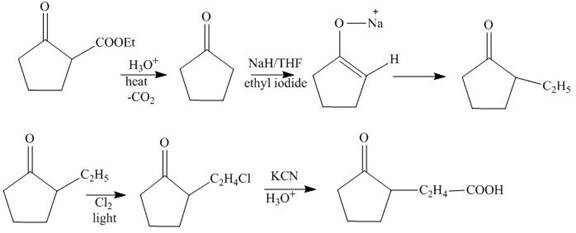
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis reaction of

Figure13
The synthesis of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Nonconjugated , -unsaturated ketones, such as 3-cyclohexenone, are in an acid-catalyzed equilibrium with their conjugated , -unsaturated isomers. Propose a mechanism for this isomerization.arrow_forwardCyclohexene can be converted to 1-cyclopentenecarbaldehyde by the following series of reactions. Propose a structural formula for each intermediate compound.arrow_forwardA step in a synthesis of PGE1 (prostaglandin E1, alprostadil) is the reaction of a trisubstituted cyclohexene with bromine to form a bromolactone. Propose a mechanism for formation of this bromolactone and account for the observed stereochemistry of each substituent on the cyclohexane ring. Alprostadil is used as a temporary therapy for infants born with congenital heart defects that restrict pulmonary blood flow. It brings about dilation of the ductus arteriosus, which in turn increases blood flow in the lungs and blood oxygenation.arrow_forward
- Amines are converted into alkenes by a two-step process called Hofmann elimination. SN2 reaction of the amine with an excess of CH3I in the first step yields an intermediate that undergoes E2 reaction when treated with silver oxide as base. Pentylamine, for example, yields 1-pentene. Propose a structure for the intermediate, and explain why it readily undergoes elimination.arrow_forwardShow the products you would obtain by acid-catalyzed reaction of cyclohexanone with ethylamine, CH3CH2NH2, and with diethylamine, (CH3CH2) 2NH.arrow_forwardAldehydes and ketones react with thiols to yield thioacetals just as they react with alcohols to yield acetals. Predict the product of the following reaction, and propose a mechanism:arrow_forward
- Compound I (C11H14O2) is insoluble in water, aqueous acid, and aqueous NaHCO3, but dissolves readily in 10% Na2CO3 and 10% NaOH. When these alkaline solutions are acidified with 10% HCl, compound I is recovered unchanged. Given this information and its 1H-NMR spectrum, deduce the structure of compound I.arrow_forwardPropose suitable reagent(s) to accomplish the following transformations.arrow_forwardPrepare the following compounds : 1-Starting with benzene or any other reagents , prepare 3-phenyl -1-propanolarrow_forward
- Propose a synthesis for the following compound starting with benzene. Write out the reagents and intermediates of each step. (Assume ortho and para isomers can be seperated)arrow_forwardPredict the major products (including stereochemistry) when cis-3-methylcyclohexanol reacts with the following reagents.(a) PBr3arrow_forwardIn a strongly acidic solution, cyclohexa-1,4-diene tautomerizes to cyclohexa-1,3-diene.Propose a mechanism for this rearrangement, and explain why it is energetically favorablearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

