
Concept explainers
What hydrogen atoms in each compound have a
a.
 e.
e.
b d.
d. ![]() f.
f. 
(a)
Interpretation: Hydrogen atoms with
Concept introduction: Acidic strength can be measured by a factor known as
Answer to Problem 23.34P
The highlighted hydrogens have
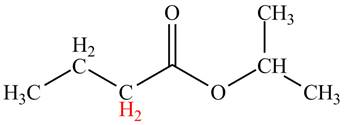
Explanation of Solution
The
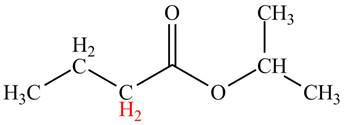
Figure 1
The hydrogen atoms having
(b)
Interpretation: Hydrogen atoms with
Concept introduction: Acidic strength can be measured by a factor known as
Answer to Problem 23.34P
The highlighted hydrogen atoms have
Explanation of Solution
The

Figure 2
The hydrogens having
(c)
Interpretation: Hydrogen atoms with
Concept introduction: Acidic strength can be measured by a factor known as
Answer to Problem 23.34P
The highlighted hydrogen atoms have
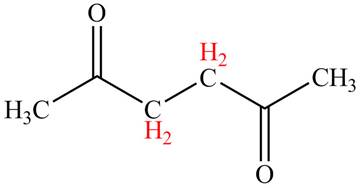
Explanation of Solution
The
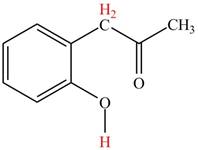
Figure 3
The hydrogens having
(d)
Interpretation: Hydrogen atoms with
Concept introduction: Acidic strength can be measured by a factor known as
Answer to Problem 23.34P
The highlighted hydrogens have
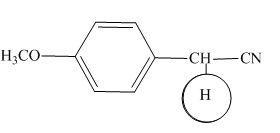
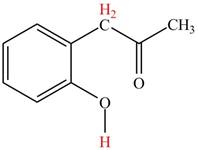
Explanation of Solution
The

Figure 4
The hydrogens having
(e)
Interpretation: Hydrogen atoms with
Concept introduction: Acidic strength can be measured by a factor known as
Answer to Problem 23.34P
The highlighted hydrogens have
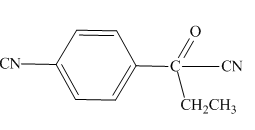
Explanation of Solution
The

Figure 5
The hydrogens having
(f)
Interpretation: Hydrogen atoms with
Concept introduction: Acidic strength can be measured by a factor known as
Answer to Problem 23.34P
The highlighted hydrogens have
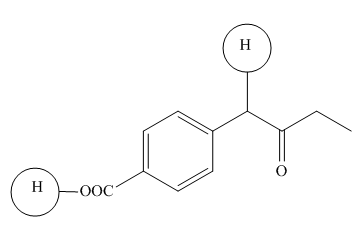
Explanation of Solution
The

Figure 6
The hydrogens having
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- how would doubling the concentration of HA affect the rate? Step 1: Fast, reversible HA = H+ + A- Step 2: Fast, reversible X + H+ = HX+ Step 3: Slow HX+ = products rate= k [X][HA]/ [A-]arrow_forwardExplain in your own words why reaction (a) would be faster than reaction (b). (a) H+(aq) + Cl¯(aq) --> HCl(aq) (b) H2(g) + Cl2(g) --> 2 HCl(g)arrow_forwardThis reaction has K = 2.3 * 10-18. Are the reactants or the products favored?arrow_forward
- What is the [H+] of a soln with a pOH of 2.9? A. 1.3 E -3 B. 7.9 E -12 C. 7.0 D. 1 E -7arrow_forwardCalculate the µg/L of the following:(a) 0.0500 N H2CO3(b) 0.0010 M CHCl3arrow_forwardAcetic acid, CH3COOH, is a weak organic acid, pKa 4.76. Write an equation for the equilibrium reaction of acetic acid with each base. Which equilibria lie considerably toward the left? Which lie considerably toward the right? Q.) NaOHarrow_forward
- Which of the following reactions result in a positive ∆ Ssys? A. Pb(NO3)2 (aq) +KCl (aq) ---> PbCl2 (s)+ KNO3 (aq) B. HCl (g) + H2O (l) ---> HCl (aq) C. H2 (g) + I2 (g) ---> 2HI (g) D. 2H2O (g) ---> 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) E. H2O (g) ---> H2O (l)arrow_forwardCO(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) + H2O(g) If the reaction above has a Keq of 72, the reaction is in favor of:arrow_forwardStep 1: Fast, reversible HA = H+ + A- Step 2: Fast, reversible X + H+ = HX+ Step 3: Slow HX+ = products What effect would adding A- to the solution have on the reaction rate?arrow_forward
- O3(g) ⇌ O2(g) + O(g)To which direction will the reaction shift if additional O3 is added?arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the ionization of HSO3? A. H3O+ B. SO32- C. H2O D. HSO4 a. C&D b. A & B c. B&C d. A&Darrow_forwardCo(H2O)6+2 +2 + 4 Cl- <----> CoCl4-2 + 6 H2O Based on the above equation, explain where the equilibrium shifted when the following reagents were added: H2O HCl AgNO3arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

