
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.66P
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
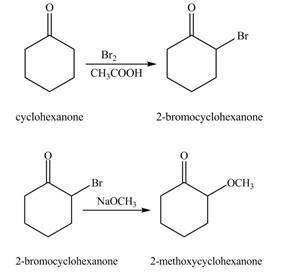
Explanation of Solution
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
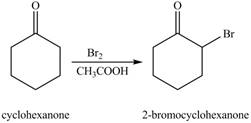
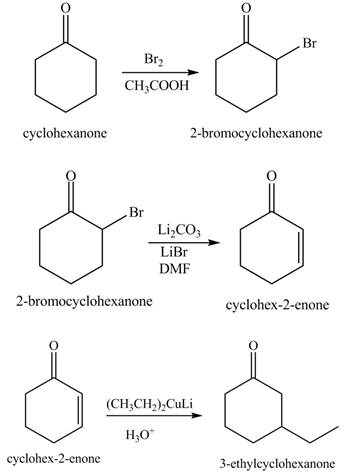
Figure 1
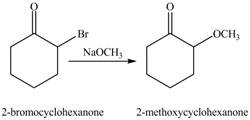
Figure 2
The first step of the reaction involves the bromination of cyclohexanone in the presence of acetic acid. It results in the formation of
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.66P
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
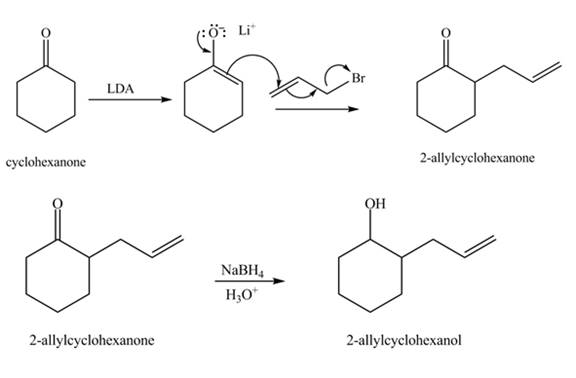
Explanation of Solution
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
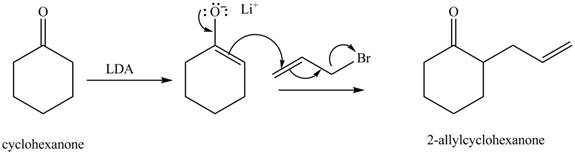
Figure 3
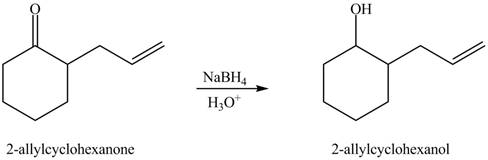
Figure 4
The full form of LDA is lithium diisopropylamide. It is a strong base. In the first step, cyclohexanone reacts with LDA to form an intermediate, which is followed by a reaction with allyl bromide to produce
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.66P
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
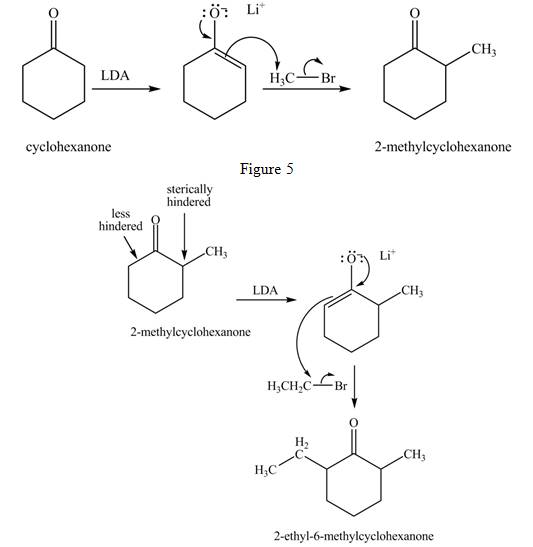
Explanation of Solution
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
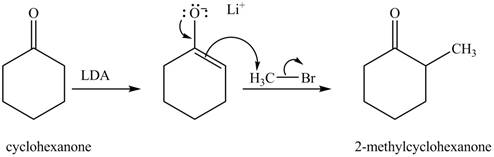
Figure 5
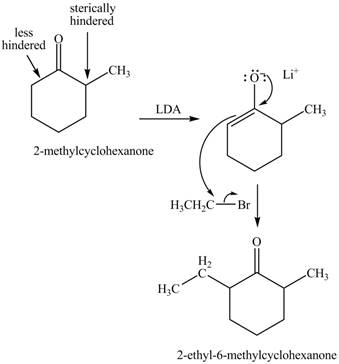
Figure 6
The full form of LDA is lithium diisopropylamide. It is a strong base. In the first step, cyclohexanone reacts with LDA to form an intermediate, which is followed by a reaction with methyl bromide to produce
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.66P
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Explanation of Solution
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
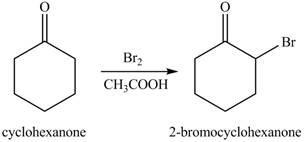
Figure 7
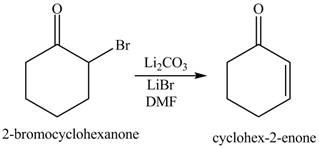
Figure 8
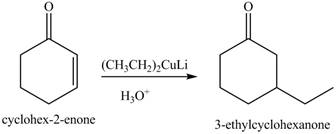
Figure 9
The first step of the reaction involves the bromination of cyclohexanone in the presence of
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.66P
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Explanation of Solution
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
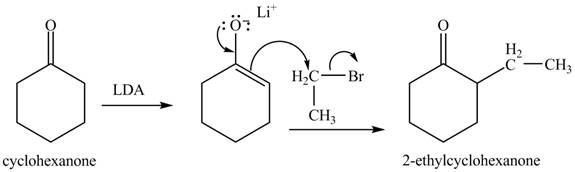
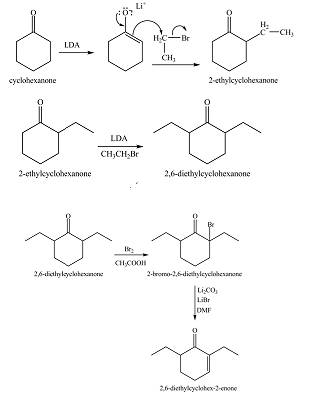
Figure 10
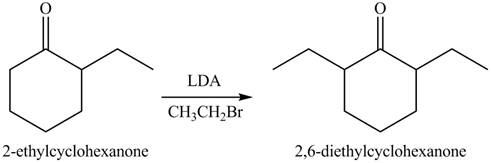
Figure 11
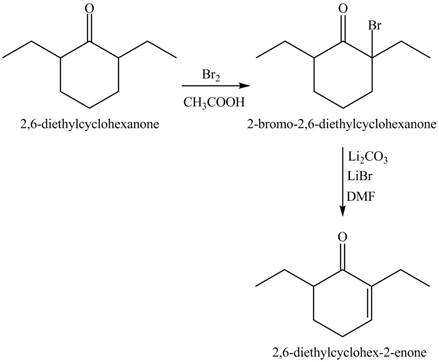
Figure 12
The full form of LDA is lithium diisopropylamide. It is a strong base. In the first step, cyclohexanone reacts with LDA to form an intermediate, which is followed by a reaction with ethyl bromide to produce
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of the products relies upon the type of reactants and reagents that are used during the reactions. The energy of a target molecule should be low because it increases the stability of a molecule that results in the formation of a molecule with high yield. The reagents perform numerous functions in reactions like proton abstraction, oxidation, reduction, catalysis, and dehydrogenation.
Answer to Problem 23.66P
The synthesis of a given compound from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Explanation of Solution
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
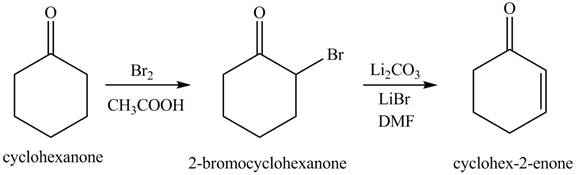
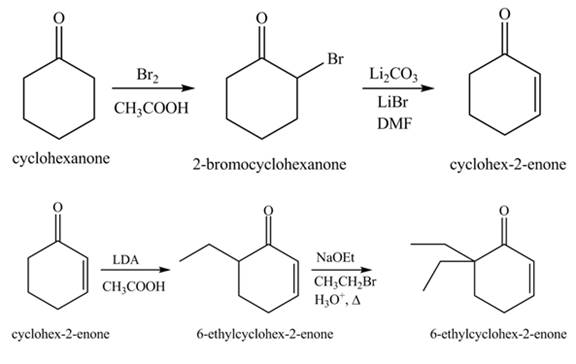
Figure 13
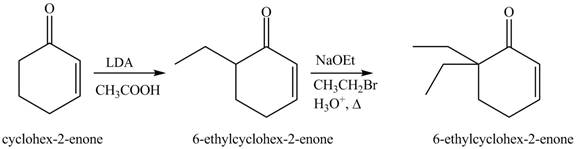
Figure 14
The first step involves the bromination of cyclohexanone to give bromo product, which on reaction with
The formation of the given product from cyclohexanone and organic halides having
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Devise a synthesis of each compound from benzene. You may usealcohols with one or two carbons and any inorganic reagents.arrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of attached acetal from 1-bromo-2-methylhexane,alcohols (and diols) containing one or two carbons, and any neededinorganic reagents.arrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of each compound from cyclohex-2-enone and organic halides having one or two carbons. You may use any other required inorganic reagents.arrow_forward
- Devise a synthesis of each compound using 1-bromobutane(CH3CH2CH2CH2Br) as the only organic starting material. You may useany other inorganic reagents.arrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of X from the given starting materials. You may useany organic or inorganic reagents. Account for the stereochemistryobserved in X.arrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of each compound from CH3CH2CH2CO2Et, benzene, andalcohols having ≤ 2 C's. You may also use any required organic or inorganic reagents.arrow_forward
- Hydrogenation of alkene A with D2 in the presence of Pd-C affords a single product B. Keeping this result in mind, what compound is formed whenA is treated with each reagent: (a) mCPBA; (b) Br2, H2O followed by base? Explain these results.arrow_forwardDimethyl cyclopropanes can be prepared by the reaction of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound X with two equivalents of a Wittig reagent Y. Draw a stepwise mechanism for this reaction.arrow_forwardDimethyl cyclopropanes can be prepared by the reaction of an α, β- unsaturated carbonyl compound X with two equivalents of a Wittig reagent Y. Draw a stepwise mechanism for this reaction.arrow_forward
- Devise a stepwise synthesis of each compound from dicyclopentadiene using a Diels–Alder reaction as one step. You may also use organic compounds having ≤ 4 C's, and any required organic or inorganic reagents.arrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of each compound from benzene and organicalcohols containing four or fewer carbons. You may also use anyrequired organic or inorganic reagents.arrow_forwardA key step in the synthesis of the antidepressant paroxetine (trade name Paxil) involves a Williamson ether synthesis of the acyclic ether in X. Draw two different routes to this ether and state which is preferred.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
