
(a)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with
Concept introduction:
Tollens test is the chemical test for the identification of the presence of the aldehyde group in the compound.
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
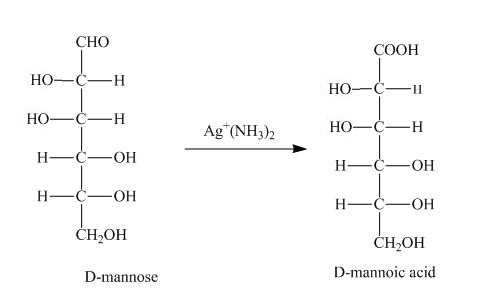
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with

Figure 1
The Tollens reagent oxidizes the aldehyde group into carboxylic acid. The D-mannose is oxidized by the
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
(b)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
Concept introduction:
There are two forms of sugars that is
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
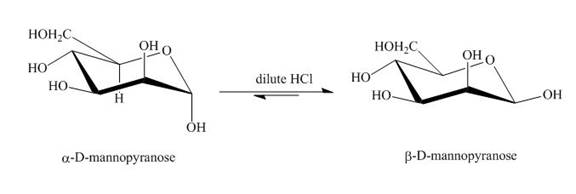
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
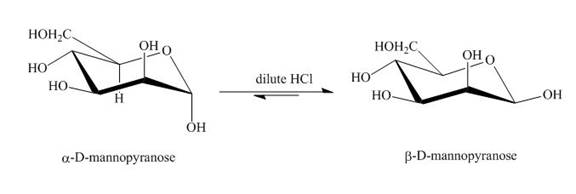
Figure 2
The conversion of both forms of sugar into each other in the presence of acid and base. That is the alpha form is converted beta and vice-versa. This change occurs until an equilibrium mixture of both compounds is obtained.
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
(c)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
Concept introduction:
There are two forms of sugars that is
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
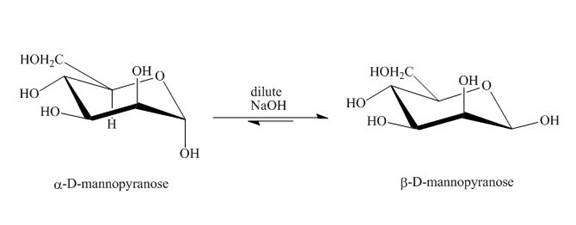
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute

Figure 3
The conversion of both forms of sugar into each other in the presence of acid or base. That is the alpha form is converted beta and vice-versa. This change occurs until an equilibrium mixture of both compounds is obtained.
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
(d)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with
Concept introduction:
The aldehyde group on oxidation changes into a carboxylic acid. The oxidation of the aldehyde group present in the aldoses is done by the bromine and water into carboxylic acids. The carboxylic acid of the aldoses thus formed is converted into lactones form.
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
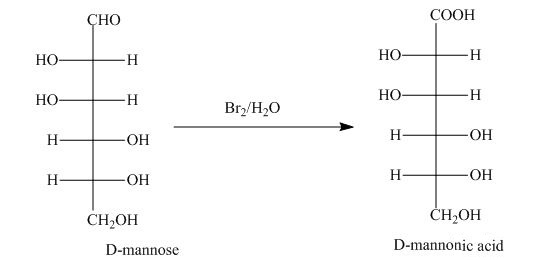
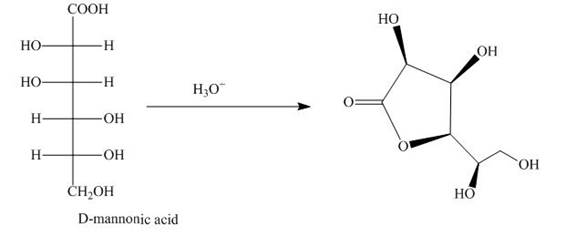
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with


Figure 4
Bromine and water oxidize the aldoses into carboxylic acids. The carboxylic acid thus formed is found in the form of lactones. Lactones formed are more stable in the five-membered
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
(e)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with
Concept introduction:
A monosaccharide is converted into cyclic acetals on reaction with alcohols in the presence of acidic conditions. The hydroxide group right to the oxygen atom in the pyranose ring structure is methylated and result in the formation of acetal.
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
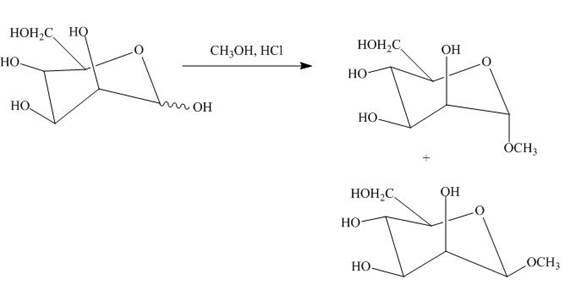
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with

Figure 5
The D-mannose on reaction with methanol and hydrochloric acid is converted into the acetal. The acetal formed is found in both forms alpha and beta regardless of the configuration of D-mannose.
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
(f)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with acetic anhydride/pyridine is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Esterification reaction of alcohol units of monosaccharide is also done. The esterification of the alcohol units is done in the presence of an excess of acetic anhydride and pyridine. All the alcohol units present are acylated.
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with acetic anhydride/pyridine is shown below.
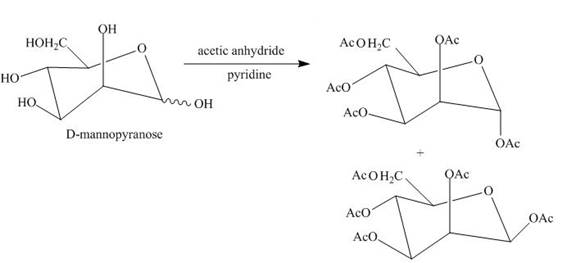
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with acetic anhydride/pyridine is shown below.

Figure 6
Esterification of all the alcohols units present in the D-mannose is done in the presence of acetic anhydride and pyridine.
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with acetic anhydride/pyridine is shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with
Concept introduction:
Ruff’s degradation is the degradation of the sugar molecule by one carbon unit. The aldose is oxidized to the carboxylic acids using bromine water. The carboxylic acid is converted into calcium salt using the calcium hydroxide base which on further reaction with
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with
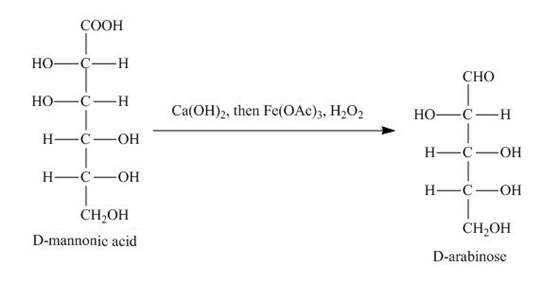
Explanation of Solution
The product of part (d) is shown below.
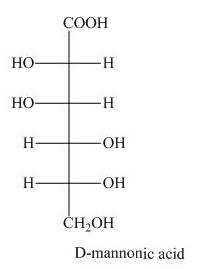
Figure 7
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with

Figure 8
The product obtained is the Ruff’s degradation product of the D-mannose. The D-mannonic acid is converted into calcium salt in the first step and then on reaction with
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with
(h)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when the product of part (e) is reacted with
Concept introduction:
The alkylation of the hydroxyl group of sugars is an important reaction. The alkylation of hydroxyl groups is done with the help of alkylating agent
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when the product of part (e) is reacted with
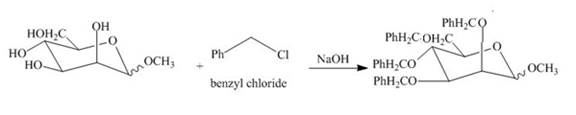
Explanation of Solution
The product of part (e) is shown below.
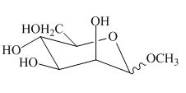
Figure 9
The product obtained when the product of part (e) is reacted with

Figure 10
The methyl D-mannopyranoside is alkylated in the strong base sodium hydroxide. The sodium hydroxide takes up the acidic proton of alcohol groups and converts them to alkoxide ion form. This alkoxide ion then substitutes the chloride group in the
The product obtained when the product of part (e) is reacted with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Naturally occurring compounds called cyanogenic glycosides, such as lotaustralin, release hydrogen cyanide, HCN, when treated with aqueous acid. The reaction occurs by hydrolysis of the acetal linkage to form a cyanohydrin, which then expels HCN and gives a carbonyl compound. (a) Show the mechanism of the acetal hydrolysis and the structure of the cyanohydrin that results. (b) Propose a mechanism for the loss of HCN, and show the structure of the carbonyl compound that forms.arrow_forwardOne of the later steps in glucose biosynthesis is the isomerization of fructose 6-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate. Propose a mechanism, using acid or base catalysis as needed.arrow_forwardChoose the product that is expected when the β-pyranose form of compound A is treated with excess ethyl iodide in the presence of silver oxide. The following information can be used to determine the identity of compound A: 1. The molecular formula of compound A is C6H12O6.2. Compound A is a reducing sugar.3. When compound A is subjected to a Wohl degradation two times sequentially, D-erythrose is obtained.4. Compound A is epimeric with D-glucose at C3.5. The configuration at C2 is R.arrow_forward
- When the gum of the shrub Sterculia setigera is subjected to acidic hydrolysis, one of the water-soluble components of thehydrolysate is found to be tagatose. The following information is known about tagatose:(1) Molecular formula C6H12O6(2) Undergoes mutarotation.(3) Does not react with bromine water.(4) Reduces Tollens reagent to give d-galactonic acid and d-talonic acid.(5) Methylation of tagatose (using excess CH3 I and Ag2O) followed by acidic hydrolysis gives1,3,4,5-tetra-O-methyltagatose.(a) Draw a Fischer projection structure for the open-chain form of tagatose.(b) Draw the most stable conformation of the most stable cyclic hemiacetal form of tagatosearrow_forwardProvide a step-wise mechanism for the hydrolysis of N,N-dimethyl formamide under basic conditionsarrow_forwardThe most stable conformation of most aldopyranoses is one in which the largest group, the CH2OH group, is equatorial. However, alpha-D-idopyranose exists primarily in a conformation with an axial CH2OH group. Write formulas for the two chair conformations of a-D-idopyranose (one with the CH2OH group axial and one with the CH2OH group equatorial) and provide an explanationarrow_forward
- Which of the following produces only butanoic acid (CH3CH2CH2 CO2H) being 'hydrolyzed in acid medium?arrow_forwardSuppose we aempt the conversion of fumaric acid to deuterated malic acid with BD3·THF,followed by oxidation with D2O2in NaOD(aq). Show all the possible stereoisomers (as Fisherprojections) that may be formed, and draw the mechanistic pathways (showing stereochemistry)that lead to these possible productsarrow_forwardHyaluronic acid, a component of connective tissue, is the fluid that lubricates joints. It is a polymer of alternating N-acetyl-d-glucosamine and d-glucuronic acid subunits joined by β-1,3'-glycosidic linkages. Draw a short segment of hyaluronic acid.arrow_forward
- Following is a retrosynthesis for the coronary vasodilator ganglefene. (a) Propose a synthesis for ganglefene from 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and 3-methyl-3-buten-2-one. (b) Is ganglefene chiral? If so, which of the possible stereoisomers are formed in this synthesis?arrow_forwardWhat is the product/s when Asetone is allowed to react with KMno4, H2O, NaOH while being heated in the presence of HCl. is there any sereochemistry associated with this reactionarrow_forwardExplain the products that would be formed when cholesterol is reacted with bromine in an organic solvent. Outline a mechanism for the reaction that takes place.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

