
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-ribose is reacted with dilute ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
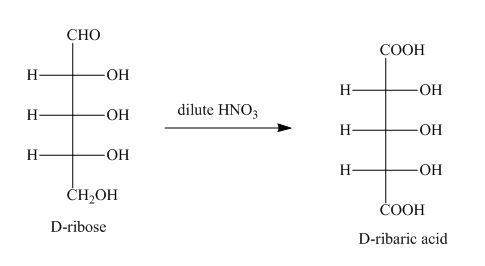
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with dilute ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with dilute ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.

Figure 1
The oxidation of D-ribose into D-ribaric acid occurs in the presence of dilute nitric acid.
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with dilute ![]() is shown in Figure 1.
is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Kiliani-Fischer process is is the reaction pathway by which an aldose is extended by one carbon unit. The first step of this reaction is the attack of the cyanide group on the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde group resulting in the formation of the cyanohydrins. The cyanohydrins thus formed is reduced to imine with catalytic hydrogenation. The imine thus formed can easily be hydrolyzed by into aldose and ammonium ion.
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
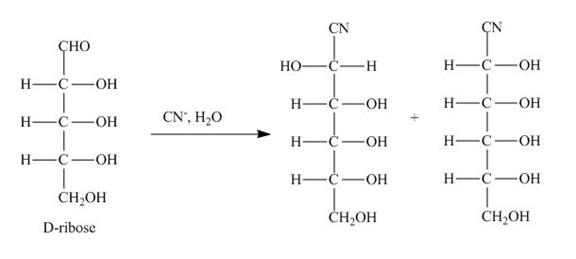
The products obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() are shown below.
are shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The products obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() are shown below.
are shown below.

Figure 2
The D-ribose is converted into cyanohydrins by the nucleophilic attack of the cyanide group on the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde group.
The products obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() are shown in Figure 2.
are shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The products expected when the product of part (b) is reacted with ![]() and
and ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Kiliani-Fischer process is is the reaction pathway by which an aldose is extended by one carbon unit. The first step of this reaction is the attack of the cyanide group on the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde group resulting in the formation of the cyanohydrins. The cyanohydrins thus formed is reduced to imine with catalytic hydrogenation. The imine thus formed can easily be hydrolyzed by into aldose and ammonium ion.
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
The products obtained when the product of part (b) is reacted with ![]() and
and ![]() are shown below.
are shown below.
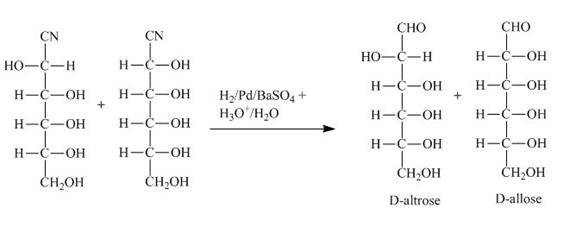
Explanation of Solution
The products obtained when the product of part (b) is reacted with ![]() and
and ![]() are shown below.
are shown below.

Figure 3
The product of part (b) is the cyanohydrin of D-ribose which is then converted into the extended aldose, altrose and allose. The catalytic hydrogenation of cyanohydrin into imine is done by ![]() . The imine then formed is hydrolyzed into the altrose and allose by
. The imine then formed is hydrolyzed into the altrose and allose by ![]() .
.
The products obtained when the product of part (b) is reacted with ![]() and
and ![]() are shown in Figure 3.
are shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A monosaccharide is converted into cyclic acetals on reaction with alcohols in the presence of acidic conditions. The hydroxide group right to the oxygen atom in the pyranose ring structure is methylated and result in the formation of acetal.
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
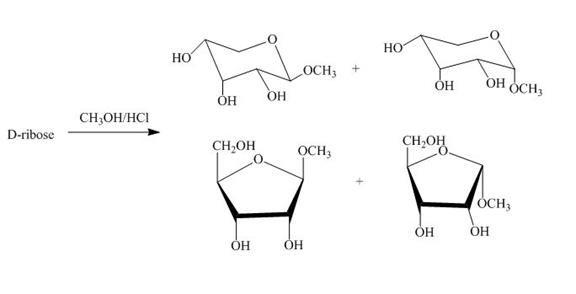
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
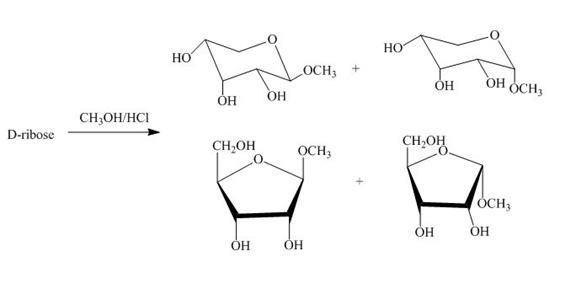
Figure 4
The D-ribose on reaction with methanol and hydrochloric acid is converted into the acetal. The acetal formed is found in both forms alpha and beta regardless of the configuration of D-ribose.
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is shown in Figure 4.
is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with ![]() (excess) and
(excess) and ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The methylation of the hydroxyl group of sugars is an important reaction. The methylation of hydroxyl groups is done with the help of methylating agent dimethyl sulfate in the presence of strong base sodium hydroxide.
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with ![]() (excess) and
(excess) and ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
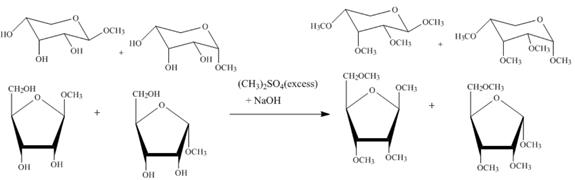
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with ![]() (excess) and
(excess) and ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.

Figure 5
The four products of part (d) are alkylated in the strong base sodium hydroxide. The sodium hydroxide takes up the acidic proton of alcohol groups and converts them to alkoxide ion form. This alkoxide ion then attacks on the dimethyl sulfate (also a methylating agent) and take up the methyl group simultaneously eliminating the methyl sulfate group.
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with ![]() (excess) and
(excess) and ![]() is shown in Figure 5.
is shown in Figure 5.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Trehalose, C12H22O11, is a nonreducing sugar that is only 45% as sweet as sugar. When hydrolyzed by aqueous acid or the enzyme maltase, it forms only d-glucose. When it is treated with excess methyl iodide in the presence of Ag2O and then hydrolyzed with water under acidic conditions, only 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methyl-d-glucose is formed. Draw the structure of trehalosearrow_forwarddoes structure E represent fructofuranose? explainarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for structure II? L-ketose D-ketose D-aldose L-aldosearrow_forward
- Show the structures of the following and give their names: C-2 epimer of D-galactose Beta anomer of alpha D-mannopyranose Alpha anomer of beta-D-lyxofuranose Enantiomer of L-ribulose Diastereomer of D-xylulose C-3 epimer of D-tagatose Illustrate what is asked for: Molecular formula of D-erythrulose Fischer projection formula of L-sorbose Haworth formula of alpha-D-idopyranose Number of stereoisomers formed by D-sorbosearrow_forwardIdentify the sugar in each description. a. An aldopentose that is not d-arabinose forms d-arabinitol when it is reduced with NaBH4. b. A sugar that is not D-altrose forms d-altraric acid when it is oxidized with nitric acid. c. A ketose that, when reduced with NaBH4, forms d-altritol and d-allitol.arrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes the structure below A. Dextrorotatory B. Ketose C. Hexose D. Levarotatory E. Pentose F. Aldose G. Terosearrow_forward
- Give the major organic product that is formed when the primary hydroxyl group of the following monosaccharide undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with acetic anhydridearrow_forwardProve that gentiobiose forms osazone and can undergo mutarotation can be hyrolyzed by Emulsin β-glycosidase forms these hydrolysis products following permethylation: 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methyl-D-glucose and 2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-D-glucosearrow_forwardTrehalose is a nonreducing disaccharide (C12H22O11) isolated from the poisonous mushroom Amanita muscaria. Treatment with an a@glucosidase converts trehalose to two molecules of glucose, but no reaction occurs when trehalose is treated with a b@glucosidase.When trehalose is methylated by dimethyl sulfate in mild base and then hydrolyzed,the only product is 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methylglucose. Propose a complete structure andsystematic name for trehalose.arrow_forward
- Draw Fischer projections for the product(s) formed by reaction of d-ribose with the following. In addition, state whether each product is optically active or inactive Q. NaBH4 in H2Oarrow_forwardPredict the products obtained when d-galactose reacts with each reagent.(a) Br2 and H2O (b) NaOH, H2O (c) CH3OH, H + (d) Ag(NH3) 2+ -OH(e) H2, Ni (f) excess Ac2O and pyridine (g) excess CH3 I, Ag2O (h) NaBH4(i) Br2, H2O, then H2O2 and Fe2(SO4)3 (j) (1) KCN/HCN; (2) H2, Pd/BaSO4; (3) H3O! (k) excess HIO42arrow_forwardIf H218O is used in the hydrolysis reaction catalyzed by lysozyme, which ring will contain the label, NAM or NAG?arrow_forward
