
(a)
Interpretation:
The group, period and the metallic character of element should be identified.
Concept introduction:
The periodic table is given below,
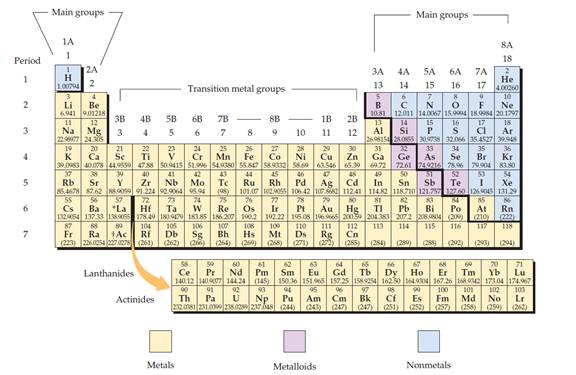
Figure 1
The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals.
Metal:
A metal is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, has a shiny appearance. Metal has the capacity to conducts the electricity and heat. Metals are malleable or ductile.
Non-metal:
Non-metal is an element that mostly absences metallic character.
Metalloid:
Metalloid is one of the types of chemical element, which has properties in between, or that are a mixture of metals and nonmetals.
Alkali metals:
Alkali metals are a group (column) in the periodic table is lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr).
Alkaline earth metals:
Alkaline earths metals are group two of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
(b)
Interpretation:
The group, period and the metallic character of element should be identified.
Concept introduction:
The periodic table is given below,
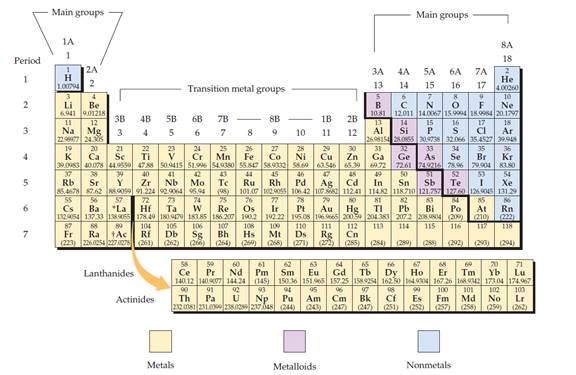
The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals.
Metal:
A metal is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, has a shiny appearance. Metal has the capacity to conducts the electricity and heat. Metals are malleable or ductile.
Non-metal:
Non-metal is an element that mostly absences metallic character.
Metalloid:
Metalloid is one of the types of chemical element, which has properties in between, or that are a mixture of metals and nonmetals.
Alkali metals:
Alkali metals are a group (column) in the periodic table is lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr).
Alkaline earth metals:
Alkaline earths metals are group two of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Modified Mastering Chemistry With Pearson Etext -- Standalone Access Card -- For Fundamentals Of General, Organic, And Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Chlorine is an element with the symbol Cl. Draw and label atomic structure of chlorine indicating the number and locations of protons, neutrons and electrons in one atom of chlorine.arrow_forwardWhat is the mass in grams of 6.022 * 1023 O atoms of mass 16.00 amu?arrow_forwardWhat is the smallest unit of an element that retains the properties of that element?arrow_forward
- Elemental analysis of a compound with molar mass 342.3 g/mol gives the following mass percent composition: C 42.11%, H 6.48%, O 51.41%. Find the molecular formula of the compound. Enter your answer in the space below using the following format: if the molecular formula of a compound containing elements X, Y, and Z is X2YZ3 enter your answer as X2YZ3.arrow_forwardIdentify the names of the following structure. (with alpha/beta and L-D designation)arrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning

