
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
It is stated that α-tocopherol is a natural antioxidant that terminates lipid peroxidation by donating H to a lipid radical (
Concept introduction:
In the body, free radicals play important roles in cell signaling and protecting against invading bacteria. Because they are highly reactive, however, these free radicals can lead to unwanted side reactions that damage or kill cells. The hydroxyl radical (
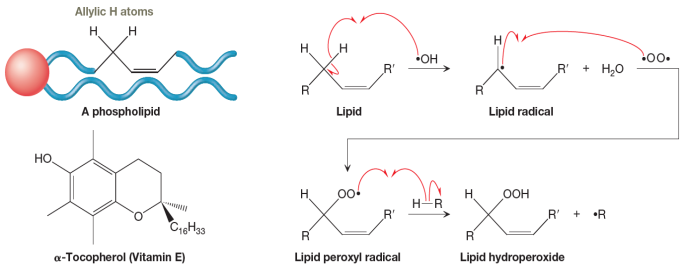
As shown in the scheme above on the right, hydrogen abstraction produces an allylic radical, which subsequently undergoes radical coupling with a molecule of
Lipid peroxides and the compounds they produce in subsequent reactions are very toxic. Fortunately, vitamin E (which is α-tocopherol), found abundantly in foods such as almonds, spinach, and avocados, is a natural antioxidant that is one of the body’s most important defenses against lipid peroxidation. A lipid radical can readily abstract the phenolic
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 25 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- Draw the structure(s) of the major organic product(s) obtained after workup of the following reaction. You do not have to consider stereochemistry. If no reaction occurs, draw the organic starting material. Include counter-ions, e.g., Na+, I-, in your submission, but draw them in their own separate sketcher. Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner.arrow_forwardComplete the mechanism of hydration of alkene below. Please follow curved arrows to predict the resulting structures in each step Step 1 of hydration of 2-methyl-1-propene (Note that the most stable carbocation is formed here) Step 2 of hydration of 2-methyl-1-propene(Note that the most stable carbocation is formed here) Step 3 of hydration of 2-methyl-1-propenearrow_forwardPlease help!! With some explanation. Which of the indicated functional groups or ions in the image below is the most basic?arrow_forward
- answer question and provide explanations that are easy to followarrow_forwardHelp finding the mechanism of this reaction as well as the intermediate molecule marked with the question mark?arrow_forwardBoth the Hydroboration and Free Radical addition reactions result in the Anti _________________ product. Complete the sentence above. Explain what it means.arrow_forward
- PLEASE ASAP Major products for electrophilic addition transformations. Clearly show stereochemistry where appropriate (using wedged or dashed bond lines, or by writing axial or equatorial bonds). If no reaction is expected, write “NR”.arrow_forwardPlease explain the reaction mechanism above to show how product is formed. The product is the borate coplymer .( Please include ALL lone pairs with the structures and provide an explanation of what is happening)arrow_forwardGive the major product of the reaction in the attached figure.Thanks.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
