
(a)
Interpretation:
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Concept introduction:
The H atom with the weakest bond and leads to the formation of stable ion is the most reactive H atom i.e. likely is abstracted by radical. The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond
Answer to Problem 25.37P
The H atom which is likely to be abstracted by bromine radical
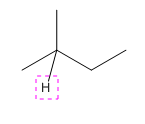
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
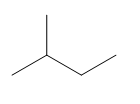
In the above compound there are three types of C atom; methyl, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms. Hydrogen atoms attached to respective carbons are also methyl H, secondary H and tertiary H atoms.
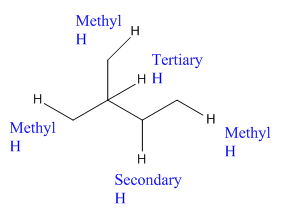
The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond

Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
(b)
Interpretation:
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Concept introduction:
The H atom with the weakest bond and leads to the formation of stable ion is the most reactive H atom i.e. likely is abstracted by radical. The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond
Answer to Problem 25.37P
The H atom which is likely to be abstracted by bromine radical
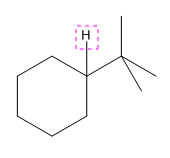
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
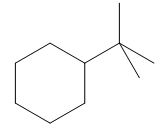
In the above compound there are three types of C atom; methyl, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms. Hydrogen atoms attached to respective carbons are also methyl H, secondary H and tertiary H atoms.
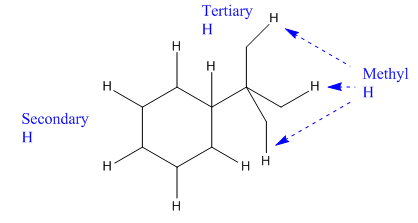
The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond

Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
(c)
Interpretation:
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Concept introduction:
The H atom with the weakest bond and leads to the formation of stable ion is the most reactive H atom i.e. likely is abstracted by radical. The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond
Answer to Problem 25.37P
The H atom which is likely to be abstracted by bromine radical
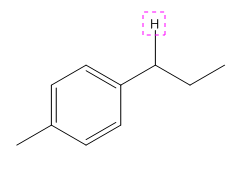
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
In the above compound there are four types of C atom; methyl, secondary, secondary benzylic and
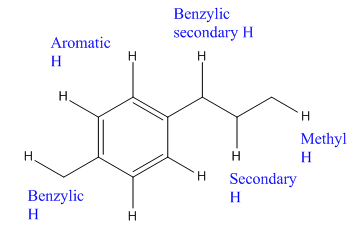
The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond

Here, the another benzylic radical could form by abstracting a H atom from the benzylic
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
(d)
Interpretation:
Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Concept introduction:
The H atom with the weakest bond and leads to the formation of stable ion is the most reactive H atom i.e. likely is abstracted by radical. The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond
Answer to Problem 25.37P
The H atom which is likely to be abstracted by bromine radical
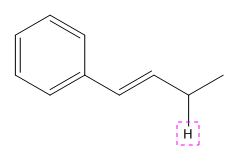
Explanation of Solution
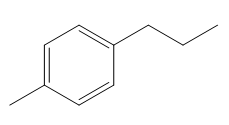
The given compound is:
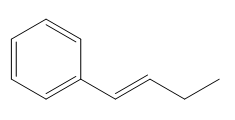
In the above compound there are three types of C atom; methyl, allylic, and aromatic carbon atoms. Hydrogen atoms attached to respective carbons are also methyl H, allylic, and aromatic H atoms.
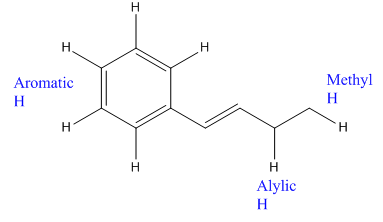
The H atom attached to the carbon with more number of alkyl group form weaker bond

Which H would most likely be abstracted by bromine radical
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





