
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of C from the given illustration and the explanation for how it is obtained is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Trypsin is an enzyme that is found in the
Answer to Problem 27.53AP
The structure of C from the given illustration is
Explanation of Solution
The molecular mass of amino acid
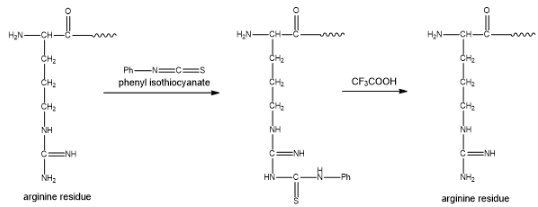
Figure 1
As a result, the phenyl hydantoin derivative is not formed. Due to this, the peptide C remain unchanged on Edman degradation. When the peptide C reacts with trypsin enzyme, it forms a single peptide D. Also, the trypsin enzyme cleaves at lysine and arginine residue. The peptide D gives the same amino acid analysis as peptide C. This confirms that the peptide D does not contain arginine residue, due to this the amino acid analysis of the peptide C is similar to that of the peptide D. The partial structure of peptide D is found to be
The structure of C from the given illustration is
(b)
Interpretation:
The b-type fragmentation for
Concept introduction:
In mass spectroscopy, compounds can be identified on the basis of the mass of the compound. When the compound breaks into fragment then they can be distinguished from the other compounds. This technique is also used to differentiate the isotopes of compounds. In amino acids, three types of fragments are observed in low energy collisions are a, b and y ions. It is known as tandem mass spectrometry.
Answer to Problem 27.53AP
The b-type fragmentation for
The b-type fragmentation for
where
Explanation of Solution
In amino acids, b-type fragments appear due to an amino group or in other words charge is being carried by N-terminal. That is why it is also known as the N-terminus amino acid fragment. The b-type fragment is shown below.
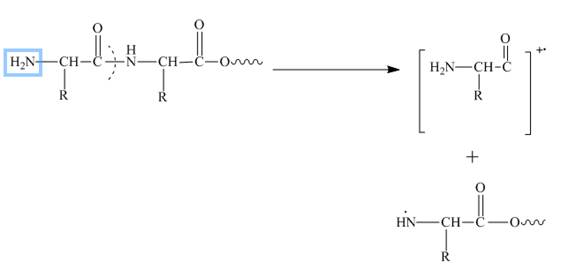
Figure 2
The peptide C is
The peptide D is
The b-type fragmentation for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- 22-35 Why is histidine considered a basic amino acid when the pKa of its side chain is 6.0?arrow_forwardDeduce the amino acid sequence of an undecapeptide (11 amino acids) from the experimental results shown in the table.arrow_forwardOxytocin, a nonapeptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland, functions by stimulating uterine contraction and lactation during childbirth. Its sequence was determined from the following evidence: 1. Oxytocin is a cyclic compound containing a disulfide bridge between two cysteine residues. 2. When the disulfide bridge is reduced, oxytocin has the constitution Asn, Cys2, Gln, Gly, Ile, Leu, Pro, Tyr. 3. Partial hydrolysis of reduced oxytocin yields seven fragments: Asp-Cys, Ile-Glu, Cys-Tyr, Leu-Gly, Tyr-Ile-Glu, Glu-Asp-Cys, and Cys-Pro-Leu. 4. Gly is the C-terminal group. 5. Both Glu and Asp are present as their side-chain amides (Gln and Asn) rather than as free side-chain acids. What is the amino acid sequence of reduced oxytocin? What is the structure of oxytocin itself?arrow_forward
- On complete hydrolysis, a polypeptide gives two alanine, one leucine, one methionine, one phenylalanine, and one valine residue. Partial hydrolysis gives the following fragments: Ala-Phe, Leu-Met, Val-Ala, Phe-Leu. It is known that the first amino acid in the sequence is valine and the last one is methionine. What is the complete sequence of amino acids?arrow_forward22-61 Polyglutamic acid (a polypeptide chain made only of glutamic acid residues) has an a-helix conformation below pH 6.0 and a random-coil conformation above pH 6.0. What is the reason for this conformational change?arrow_forwardDetermine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from the following data: Complete hydrolysis of the peptide yields Ala, Arg, Gly, 2 Lys, Met, Phe, Pro, 2 Ser, Tyr, and Val. Treatment with Edman’s reagent releases PTH-Val. Carboxypeptidase A releases Ala. Treatment with cyanogen bromide yields the following two peptides: 1. Ala, 2 Lys, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr 2. Arg, Gly, Met, Ser, Val Treatment with trypsin yields the following three peptides: 1. Gly, Lys, Met, Tyr 2. Ala, Lys, Phe, Pro, Ser 3. Arg, Ser, Val Treatment with chymotrypsin yields the following three peptides: 1. 2 Lys, Phe, Pro 2. Arg, Gly, Met, Ser, Tyr, Val 3. Ala, Serarrow_forward
- Three peptides were obtained from a trypsin digestion of two different polypeptides. indicate the possible sequences from the given data and tell what further experiment should be carried out in order to determine the primary structure of the polypeptide. polypeptide I: 1. Val-Gly-Asp-Lys 2. Leu-Glu-Pro-Ala-Arg 3. Ala-Leu-Gly-Asparrow_forwardA decapeptide undergoes partial hydrolysis to give peptides whose amino acid compositions are shown. Reaction of the intact decapeptide with Edman’s reagent releases PTH-Gly. What is the sequence of the decapeptide? 1. Ala, Trp 3. Pro, Val 5. Trp, Ala, Arg 7. Glu, Ala, Leu 2. Val, Pro, Asp 4. Ala, Glu 6. Arg, Gly 8. Met, Pro, Leu, Gluarrow_forwardDetermine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from the following data:Complete hydrolysis of the peptide yields Arg, 2 Gly, Ile, 3 Leu, 2 Lys, 2 Met, 2 Phe, Pro, Ser, 2 Tyr, and Val.Treatment with Edman’s reagent releases PTH-Gly.Carboxypeptidase A releases Phe. Treatment with cyanogen bromide yields the following three peptides:1. Gly-Leu-Tyr-Phe-Lys-Ser-Met 2. Gly-Leu-Tyr-Lys-Val-Ile-Arg-Met 3. Leu-Pro-Phearrow_forward
- Determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from the following data: Complete hydrolysis of the peptide yields Arg, 2 Gly, Ile, 3 Leu, 2 Lys, 2 Met, 2 Phe, Pro, Ser, 2 Tyr, and Val. Treatment with Edman’s reagent releases PTH-Gly. Carboxypeptidase A releases Phe. Treatment with cyanogen bromide yields the following three peptides: 1. Gly-Leu-Tyr-Phe-Lys-Ser-Met 2. Gly-Leu-Tyr-Lys-Val-Ile-Arg-Met 3. Leu-Pro-Phe Treatment with trypsin yields the following four peptides: 1. Gly-Leu-Tyr-Phe-Lys 3. Val-Ile-Arg 2. Ser-Met-Gly-Leu-Tyr-Lys 4. Met-Leu-Pro-Phearrow_forwardSomatostatin is a tetradecapeptide of the hypothalamus that inhibits the release of pituitary growth hormone. Its amino acid sequence has been determined by a combination of Edman degradations and enzymic hydrolysis experiments. On the basis of the following data, deduce the primary structure of somatostatin: 1. Edman degradation gave PTH-Ala. 2. Selective hydrolysis gave peptides having the following indicated sequences: Phe-Trp Thr-Ser-Cys Lys-Thr-Phe Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Cys Asn-Phe-Phe-Trp-Lys Ala-Gly-Cys-Lys-Asn-Phe 3. Somatostatin has a disulfide bridge.arrow_forwardUsing the information below, determine the amino acid sequence of the peptide, and explain how your structure is consistent with each piece of information. Complete hydrolysis by 6 M HCl at 110°C followed by amino acid analysis indicated the presence of Gly, Leu, Phe, and Tyr in a 2:1:1:1 molar ratio. Treatment of the peptide with1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene followed by complete hydrolysis and chromatography indicated the presence of the 2,4-dinitrophenyl derivative of tyrosine. No free tyrosine could be found. Complete digestion of he peptide with pepsin (which cleaves on the amino side of aromatic residues) followed by chromatography yielded a dipeptide containing Phe and Leu and a tripeptide containing Tyr and Gly in a 1:2 ratio.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





