
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the major organic product formed in the reaction of ethylamine and phenyl isothiocyanate with complete reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The nucleophilic addition reaction is a common reaction of
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The compound
Explanation of Solution
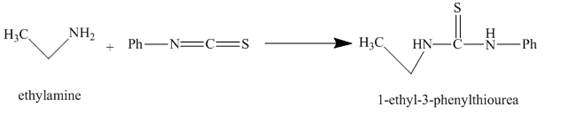
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
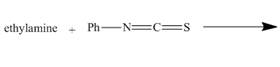
Figure 1
The carbon in phenyl isothiocyanate is electron deficient, because it is attached to nitrogen and sulfur atoms with double bonds. It easily accepts lone pair of electron present at nitrogen of ethylamine and undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction and as the result
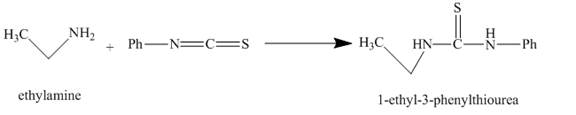
Figure 2
The major organic compound obtained, by the reaction of ethylamine and phenyl isothiocyanate, is
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the major organic product formed by the reaction of methylamine with benzaldehyde in presence of potassium cyanide, and afterwards hydrolyzing it and treating it with dilute base is to be drawn. The complete reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Under nucleophilic addition reaction of
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The structure of the major organic product formed by the reaction of methylamine with benzaldehyde in presence of potassium cyanide, and afterwards hydrolyzing it and treating it with dilute base along with complete reaction is shown below.
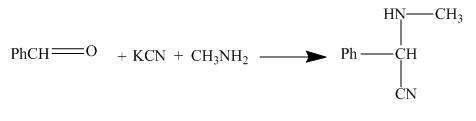
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
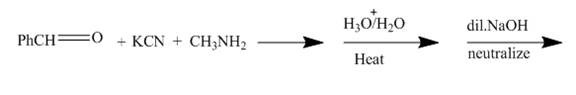
Figure 3
The reaction is a good example of Strecker synthesis. This is again a nucleophilic addition reaction. The compound formed is
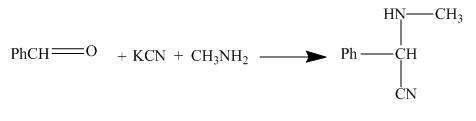
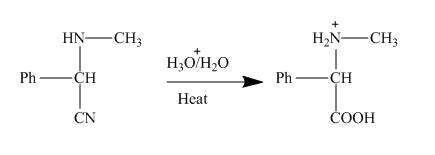
Figure 4
This nitrile group of

Figure 5
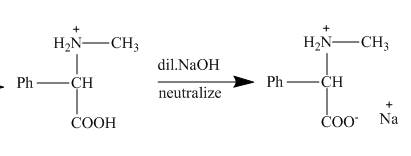
This amino acid is treated with base to neutralize it. Finally, the sodium salt of the acid is obtained as shown below.

Figure 6
The products of the reaction are
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete reactions and structures of the major organic products formed by the reaction sequence given for amine carboxylate ion are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amine being acidic can be neutralized with base. The salts thus formed easily undergo addition reactions to form a compound known as imine. This imine can be again reduced to higher amines. This is a method for alkylation of amines.
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The amine is first neutralised to form corresponding salt. This salt gives addition product with given aldehyde, known as imine which is again reduced to corresponding amine. The reaction sequence and structure of the compounds is shown below.
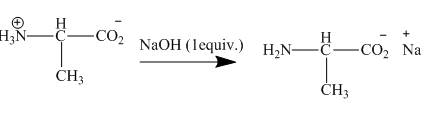
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
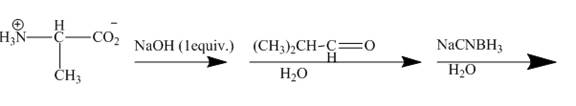
Figure 7
The amine group gets neutralized by

Figure 8
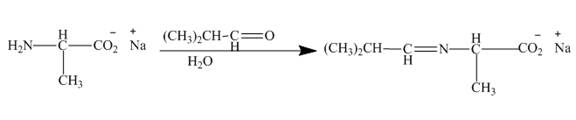
The carbonyl carbon of the dimethylacetaldehyde will be added to amino group of the above formed salt to give an imine product as shown below.

Figure 9
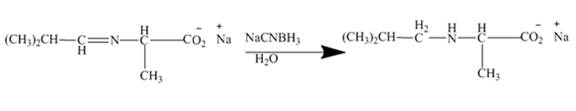
The mild reducing agent
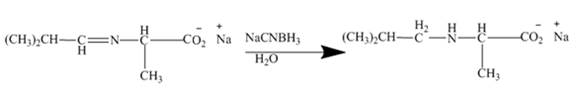
Figure 10
The amines easily undergo addition reaction. These addition reactions are useful to alkylate the amines to get higher amines as shown in Figures 8 to 10.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the major organic product formed by the neutralization of given amino diester with
Concept introduction:
Tertiary butyl groups are better leaving group than methyl group. Tertiary groups are highly substituted so they have more
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The tertiary butyl group of the diester leaves the molecule giving the corresponding alcohol and the rest of the cleaved molecule gets neutralized with
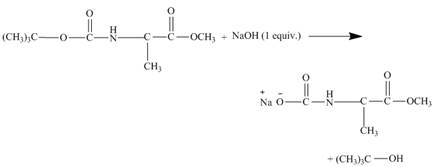
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
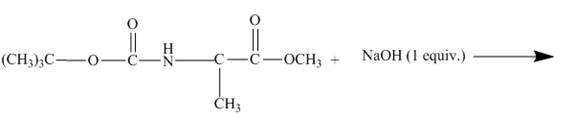
Figure 11
As the diester is treated with

Figure 12
The diester molecule cleaves to give alcohol and corresponding sodium salt of carboxylate ion as shown in Figure 12.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of the major organic product, formed by treating given acyl hydrazide with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid, and complete reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The primary
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The given acyl hydrazide gets diazotized with reagents
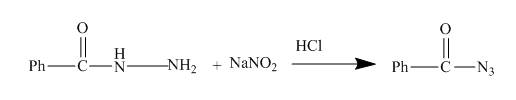
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
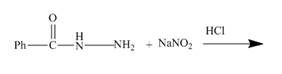
Figure 13
The acyl hydrazide being an aromatic amine easily undergoes diazotization reaction. As a result acyl azide is formed which is useful intermediate for formation of azo dyes and coupling reaction. The reaction is shown in the Figure below.
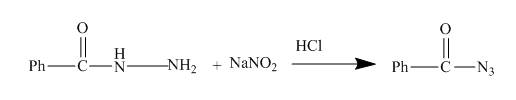
Figure 14
The given acyl hydrazide is converted to a compound acyl azide by the diazotization reaction of amines as shown in Figure 14.
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of the major organic product, formed by heating acyl azide (formed as in Figure 9) with benzene, and complete reaction are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The curtius rearrangement is the rearrangement of azide molecule to isocyanate. When azide molecules are heated, they undergo thermal decomposition to form isocyanate. A molecule of nitrogen is lost in this rearrangement. These isocyanates can easily be attacked by nucleophiles to give primary amines.
Answer:
The acyl azide (formed in Figure 9) upon heating with benzene gives isocyanate as shown below.
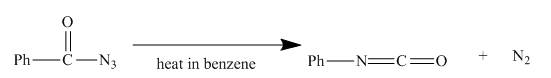
Explanation:
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
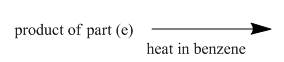
Figure 15
In the above reaction, the acyl azide molecule undergoes curtius rearrangement upon heating with benzene. It forms isocyanate and a molecule of nitrogen is lost.

Figure 16
The lone pair electron of nitrogen is shared with carbonyl carbon. Simultaneously the terminal nitrogens are lost away as a nitrogen molecule. Now the alkyl carbon bonds with nitrogen, to form isocyanate. The rearrangement is depicted in the Figure below.
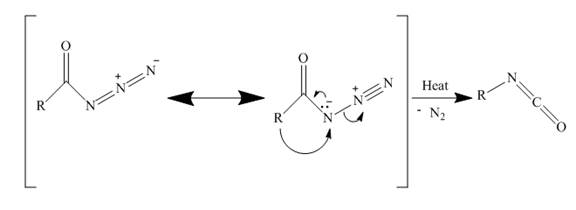
Figure 17
Conclusion:
The acyl azide by curtius rearrangement forms an isocyanate as shown in Figure 17. This can easily get attacked by nucleophiles. This method can be used to prepare primary amines.
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The acyl azide (formed in Figure 9) upon heating with benzene gives isocyanate as shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
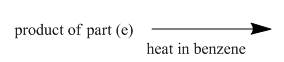
Figure 15
In the above reaction, the acyl azide molecule undergoes curtius rearrangement upon heating with benzene. It forms isocyanate and a molecule of nitrogen is lost.

Figure 16
The lone pair electron of nitrogen is shared with carbonyl carbon. Simultaneously the terminal nitrogens are lost away as a nitrogen molecule. Now the alkyl carbon bonds with nitrogen, to form isocyanate. The rearrangement is depicted in the Figure below.

Figure 17
The acyl azide by curtius rearrangement forms an isocyanate as shown in Figure 17. This can easily get attacked by nucleophiles. This method can be used to prepare primary amines.
(g)
Interpretation:
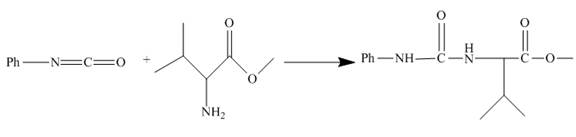
The structure of the major organic product, formed by heating isocyanate (formed as in Figure 10) with valine methyl ester, and complete reaction are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The isocyanate molecules have high electron density. They are prone to nucleophilic attack. Nucleophile like alcohols and amines attacks the isocyanate to give corresponding amines, carbamates and urea derivatives.
Answer:
The isocyanate reacts with valine methyl ester to give urethane derivative. The reaction and structure of the product is shown below.
Explanation:
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
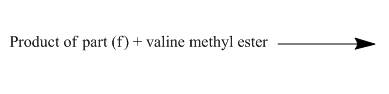
Figure 18
Phenyl isocyanate formed as in Figure 10 reacts with valine methyl ester. This is nucleophilic addition reaction. The lone pair of amino nitrogen attacks the isocyanate carbon. The molecule adds up and a urea derivative is the product of the reaction. The reaction is shown as below.
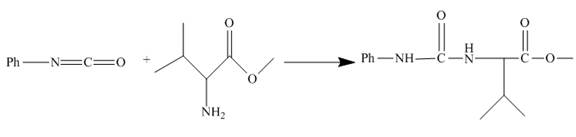
Figure 19
Conclusion:
Isocyanates are good intermediates to get higher amines and their derivatives as shown in Figure 19. They easily undergo nucleophilic addition reaction to forms new compounds as carbamates and urea derivatives.
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The isocyanate reacts with valine methyl ester to give urethane derivative. The reaction and structure of the product is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
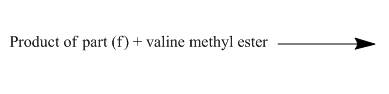
Figure 18
Phenyl isocyanate formed as in Figure 10 reacts with valine methyl ester. This is nucleophilic addition reaction. The lone pair of amino nitrogen attacks the isocyanate carbon. The molecule adds up and a urea derivative is the product of the reaction. The reaction is shown as below.

Figure 19
Isocyanates are good intermediates to get higher amines and their derivatives as shown in Figure 19. They easily undergo nucleophilic addition reaction to forms new compounds as carbamates and urea derivatives.
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of the major organic product, formed by treating given compound with sodium ethoxide in ethanol, and complete reaction are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
As the electrons of carbonyl carbon are more attracted to the oxygen. The carbon has low electron density. When two carboxylate groups are attached to same carbon it becomes very reactive as the electron density is even less. They become prone to nucleophilic attack.
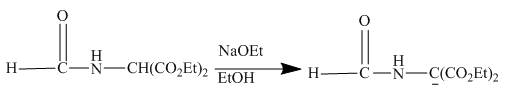
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The given compound being an active methylene compound gets deprotonated when reacts with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. The produced anion gives addition product with the given
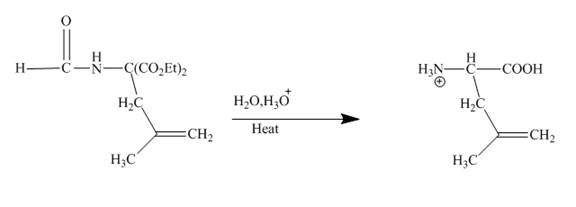
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
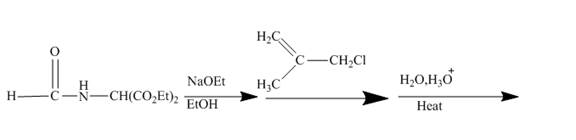
Figure 20
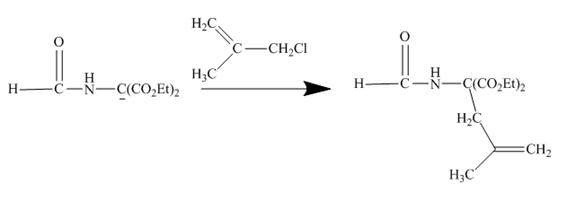
The sodium ethoxide in ethanol is a strong nucleophile. Having high electron density the oxygen of ethoxide attracts the proton of the given compound. The given compound is a very reactive methylene compound. Having two ester groups on the same carbon makes it electron deficient and it is easily attacked by the nucleophile like ethoxide. In this reaction, ethanol facilitates the reaction as a base. The anion formed undergoes addition reaction with the given alkene. Addition product formed under goes hydrolysis and gives the primary amine as the final product. The complete reaction is shown below.



Figure 21
An anion is formed as the reaction product of the reaction between the given compound with ethoxide in ethanol. This anion forms addition product with the alkene given in which upon hydrolysis produces primary amine. This is a very good method to obtain higher amines.
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure of the major organic product, formed by treating given cyanoester with hydrazine in sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid and the reaction sequences followed, with complete reactions is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having amino and carboxylic group are very reactive. They form nucleophilic addition reaction products to give intermediates like hydrazide, azide, isocyanate, which are very useful in synthesis of higher amines, azo dyes, urea derivatives and other products.
Answer to Problem 27.75AP
The ester group reacts with hdrazine to produce acyl hydrazide. This acyl hydrazide gets diazodized with
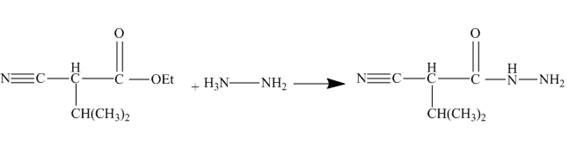
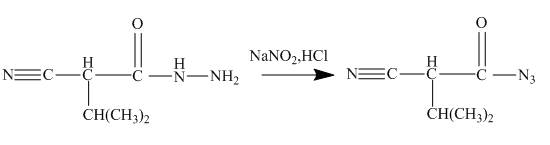
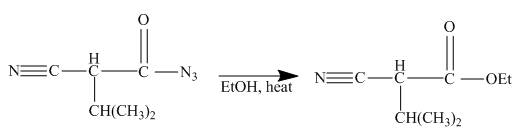
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
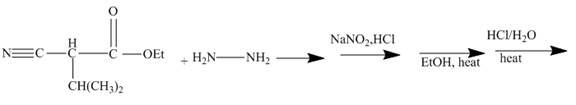
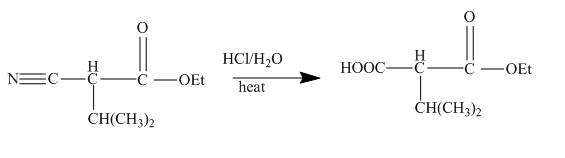
Figure 22
In the first step the ester by nucleophilic addition with hydrazin, give acyl hydrazide. This acyl hydrazide undergoes diazodization reaction with



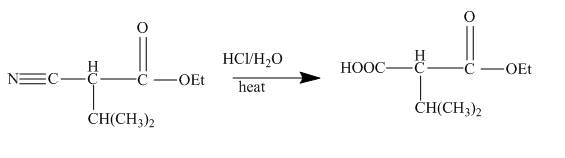
Figure 23
The cyanoester undergoes series of reaction to give different products like acyl hydrazide, acyl azide isocyanate, urea derivative. These reaction sequences are used for industrial preparations to get various useful compounds.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- A. Distinguish the amine component from the coupling component in the given azo dye. B. Sketch the azo dye that would be formed from the two given components.arrow_forwardprovide the structure for the product followin gthe reaction sequencearrow_forwardAssuming the oligopeptide ALPHAHELICKS forms one continuous alpha-helix, the carbonyl oxygen of the glutamic acid residue is hydrogen-bonded to the hydrogen in the amide nitrogen of??arrow_forward
- Thoroughly explain why (a)malthose is a reducing sugar while trehalose is not based on their structures. (b)Why is trehalose very resistant to acid hydrolysis while maltose can be acid-hydrolyzed with ease. Give clear explanations.arrow_forwardgive explanation in detailarrow_forwardGive only typing answer with explanation and conclusion Complete the Retrosynthesis for both structure: must provide steps and structures.arrow_forward
- Justify why do electrophilic substitution reaction in naphthalene take place at Alpha position. and write the short note of Asymmetric?arrow_forwardGive detailed Solution...Draw the following organic compoundarrow_forward(b) Classify the following alcohols in order of increasing ease of acid-catalyzed dehydration.Justify your answers.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

