
Concept explainers
Draw electron-dot structures for the following molecules, indicating any unshared electron pairs. Which of the compounds are likely to act as Lewis acids and which as Lewis bases?
(a) AlBr3
(b) CH3CH2NH2
(c) BH3
(d) HF
(e) CH3SCH3
(f) TiCl4
a) AlBr3
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for AlBr3 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus aluminum has three dots to represent its 3s23p1electrons, bromine has seven dots to represent its 4s24p5 electrons. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for AlBr3 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for AlBr3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as
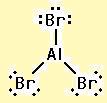
It will act as a Lewis acid.
Explanation of Solution
Aluminum atom has three electrons (3s23p1) in its valence shell. It has used all the three electrons in forming three Al- Br bonds. So it has no lone pair of electrons. The bromine atom has seven electrons in its valence shell (4s24p5). Out of these seven electrons, each bromine has used one electron for forming Al-Br bond and thus has the remaining six electrons as three lone pairs. AlBr3 will act as Lewis acid since the central aluminum atom requires two more electrons to complete its octet.
The electron–dot structure for AlBr3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as

It will act as a Lewis acid.
b) CH3CH2NH2
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for CH3CH2NH2 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus hydrogen has one dot to represent its 1s1 electron, carbon has four dots to represent its 2s22p2 electrons, and nitrogen has five dots to represent its 2s22p3 electrons. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for CH3CH2NH2 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for CH3CH2NH2 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,
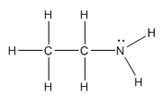
It will act as a Lewis base.
Explanation of Solution
Carbon atom has four electrons (2s22p2) in its valence shell. Both carbons have used all the four electrons in forming four bonds with other atoms. So they do not possess any lone pair of electrons. The nitrogen atom has five electrons in its valence shell (2s22p3). Out of these five electrons, nitrogen has used three electrons for forming one C-N and two N-H bonds and thus has the remaining two electrons as a lone pair. CH3CH2NH2 will act as Lewis base since the nitrogen atom can donate a pair of electrons to other species.
The electron–dot structure for CH3CH2NH2 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,

It will act as a Lewis base.
c) BH3
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for BH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus boron has three dots to represent its 2s22p1electrons, hydrogen has one dot to represent its 1s1 electron. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for BH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for BH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,
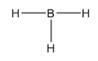
It will act as a Lewis acid.
Explanation of Solution
Boron atom has three electrons (2s22p1) in its valence shell. It has used all the three electrons in forming three B- H bonds. So it has no lone pair of electrons. Each hydrogen atom has one electron in its valence shell (1s1) which they utilize in forming the B-H bonds. BH3 will act as Lewis acid since the central boron atom requires two more electrons to complete its octet.
The electron–dot structure for BH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,

It will act as a Lewis acid.
d) HF
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for HF indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus fluorine has seven dots to represent its 2s22p5 electrons, hydrogen has one dot to represent its 1s1 electron. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors. To give: The electron dot structure for HF indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for HF indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as
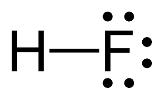
It will act as a Lewis acid.
Explanation of Solution
Fluorine atom is the most electronegative element and hence the H-F bond is highly polarized. The electrons in the bond are more concentrated on F rather than on H. The hydrogen is thus electron deficient and it can accept a pair of electrons from a Lewis base. Hence HF is likely to behave as Lewis acid.
The electron–dot structure for HF indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as
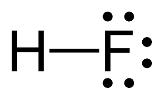
It will act as a Lewis acid.
e) CH3SCH3
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for CH3SCH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. Thus hydrogen has one dot to represent its 1s1 electron, carbon has four dots to represent its 2s22p2 electrons and sulfur has six dots to represent its 3s23p4 electrons. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for CH3SCH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for CH3SCH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,
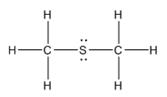
It will act as a Lewis base.
Explanation of Solution
Carbon atom has four electrons (2s22p2) in its valence shell. Both carbons have used all the four electrons in forming four bonds with other atoms. So they do not possess any lone pair of electrons. The sulfur atom has six electrons in its valence shell (3s23p4). Out of these six electrons, sulfur has used two electrons for forming two C-S bonds and thus has the remaining four electrons as two lone pairs. CH3SCH3 will act as Lewis base since the sulfur atom can donate a pair of electrons to other species.
The electron–dot structure for CH3SCH3 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,

It will act as a Lewis base.
f) TiCl4
Interpretation:
Electron dot structure for TiCl4 indicating any unshared electron pairs is to be drawn. Whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A covalent bond formed by sharing of two electrons between two atoms in a molecule is usually indicated by electron-dot structures in which valence electrons are represented as dots. A stable molecule results whenever all the atoms except hydrogen in a molecule achieve in their valence shell eight dots and hydrogen achieve two dots. The electrons present in the inner shells of the atoms are not shown.
Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors while Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
To give:
The electron dot structure for TiCl4 indicating any unshared electron pairs and to state whether it will act as Lewis acid or Lewis base.
Answer to Problem 42AP
The electron–dot structure for TiCl4 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,
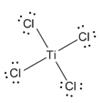
It will act as a Lewis acid.
Explanation of Solution
The chlorine atom has seven electrons in its valence shell (3s23p5). Out of these seven electrons, each chlorine has used one electron for forming Ti-Cl bond and thus have the remaining six electrons as three lone pairs. Titanium is a transition element. Transition elements utilize the d orbitals in the penultimate shell also along with orbitals of the valence shell during bonding. It has the configuration 3d24s2. It has used all the four electrons in forming four Ti-Cl bonds.
The d orbitals can have a maximum of ten electrons. In TiCl4, the titanium atom has empty d orbitals to accommodate electrons donated by a Lewis base. Hence TiCl4 will act as Lewis acid.
The electron–dot structure for TiCl4 indicating any unshared electron pairs can be given as,

It will act as a Lewis acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM.(LL)-W/OWL V2 >CUSTOM<
- The following reactions illustrate Brnsted acid-base behavior. Complete each equation. a.HI(aq)+?H3O+(aq)+I(aq) b.NH3(l)+?NH4++NH2 c.H2C2O4(aq)+H2O(l)?+HC2O4(aq) d.H2N2O2(aq)+H2O(l)H3O+(aq)+? e.?+H2O(l)H3O+(aq)+CO32(aq)arrow_forwardFollowing is a structural formula for imidazole, a building block of the essential amino acid histidine (Chapter 27). It is also a building block of histamine, a compound all too familiar to people with allergies and takers of antihistamines. When imidazole is dissolved in water, proton transfer to it gives a cation. Is this cation better represented by structure A or B? Explain.arrow_forwardWrite the Lewis structures of the reactants and product of each of the following equations, and identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base in each: (a) CS2+SHHCS3 (b) BF3+FBF4 (c) I+SnI2SnI3 (d) Al(OH)3+OHAl(OH)4 (e) F+SO3SFO3arrow_forward
- For oxyacids, how does acid strength depend on a. the strength of the bond to the acidic hydrogen atom? b. the electronegativity of the element bonded to the oxygen atom that bears the acidic hydrogen? c. the number of oxygen atoms? How does the strength of a conjugate base depend on these factors? What type of solution forms when a nonmetal oxide dissolves in water? Give an example of such an oxide. What type of solution forms when a metal oxide dissolves in water? Give an example of such an oxide.arrow_forwardHow do the components of a conjugate acid—base pair differ from one another4? Give an example of a conjugate acid—base pair to illustrate your answer.arrow_forwardCoal and other fossil fuels usually contain sulfur compounds that produce sulfur dioxide, SO2, when burned. One possible way to remove the sulfur dioxide is to pass the combustion gases into a tower packed with calcium oxide, CaO. Write the equation for the reaction. Identify each reactant as either a Lewis acid or a Lewis base. Explain how you arrived at your answer.arrow_forward
- In the following net ionic reaction, identify each species as either a Brnsted-Lowry acid or a Brnsted -Lowry base: CH3COO(aq)+HS(aq)CH3COOH(aq)+S2(aq). Identify the conjugate of each reactant and state whether it is a conjugate acid or a conjugate base.arrow_forwardNatural gas frequently contains hydrogen sulfide, H2S. H2S is removed from natural gas by passing it through aqueous ethanolamine, HOCH2CH2NH2 (an ammonia derivative), which reacts with the hydrogen sulfide. Write the equation for the reaction. Identify each reactant as either a Lewis acid or a Lewis base. Explain how you arrived at your answer.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds or ions has the weakest conjugate base? Briefly explain your choice. a) HCN b) HClO c) NH4+arrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





