
Concept explainers
In a population of rabbits, you find three different coat color
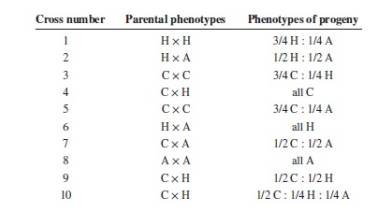
| a. | What can you conclude about the inheritance of coat color in this population of rabbits? |
| b. | Ascribe genotypes to the parents in each of the 10 crosses. |
| c. | What kinds of progeny would you expect, and in what proportions, if you crossed the chinchilla parents in crosses 9 and 10. |
a.
To determine:
The inheritance of coat color in this population of rabbits.
Introduction:
The gene refers to the functional and structural unit of life. The gene consists of two alleles. The increase in the number of alleles allows the generation of different phenotypes. There are four different alleles which are determining the coat color in rabbits.
Explanation of Solution
The four alleles determine the phenotype of rabbits. These are albino, wild type, chinchilla, and Himalayan. The phenotype of chinchilla rabbits have white hairs with black tips on the body, black hairs on extremities are present on Himalayan rabbits, albino has colorless hairs, and wild type has colored hairs.
The chinchilla rabbits are 75%, and the Himalayan rabbit is 25% from cross 3 data. This indicates that the dominant phenotype is chinchilla. The cross 5 contains 75% chinchilla and 25% albino rabbits. The chinchilla is dominant over albino phenotype. The cross 1 indicates Himalayan rabbits are 75% and 25% are albino rabbits. Thus Himalayan phenotype is dominant. This means inherited order is from chinchilla (cch) to Himalayan (ch) to albino (ca ) phenotype.
b.
To determine:
The genotypes of the parents in each of the ten crosses.
Introduction:
The genotype and phenotype are the two terms which describe the genetic makeup of the organism and also the physical character provided by a particular allele. The known genotype of parents helps in determining the genotype of offsprings.
Explanation of Solution
The two Himalayan individuals were crossed (cross-1). The phenotypic ratio is 3:1 of Himalayan and albino. This indicates complete dominance. The genotype of both parents is cchca. Thus the gametes would be cch and ca
| ♂/ ♀ | cch | ca |
| cch | cchcch Himalayan |
cchca Himalayan |
| ca | ca cch Himalayan |
ca ca Albino |
The cross (cross 2) between Himalayan and albino results in 1:1 phenotype. This indicates dominance. Thus the genotype of Himalayan parents is cchca (female), and albino is caca (male).
| ♂/ ♀ | cch | ca |
| ca | cchca Himalayan |
caca Albino |
| ca | cchca Himalayan |
ca ca Albino |
The cross (cross 3) between two chinchilla rabbits that results in a 3:1 ratio (chinchilla:Himalayan). The cross ( I case) have parental genotype Ccch (female) and Cca (male) and for II case is Ccch(male) and Ccch(female).
Cross for Condition I:
| ♂/ ♀ | C | cch |
| C | CC Chinchilla |
Ccch Chinchilla |
| ca | caC Chinchilla |
cacch Himalayan |
Cross for Condition II:
| ♂/ ♀ | C | cch |
| C | CC Chinchilla |
Ccch Chinchilla |
| cch | cchC Chinchilla |
cchcch Himalayan |
The cross (cross 4) between chinchilla and Himalayan parents results in all chinchilla phenotype. This is also a case of complete dominance. The genotype is CC (female) and cchcch or cchca (male).
Cross for Condition I:
| ♂/ ♀ | C | C |
| cch | Ccch Chinchilla |
cchC Chinchilla |
| ca | Cca Chinchilla |
caCa Chinchilla |
Condition II
| ♂/ ♀ | C | C |
| cch | Ccch Chinchilla |
Ccch Chinchilla |
| cch | Ccch Chinchilla |
Ccch Chinchilla |
The cross (cross 5) between two chinchilla parents results in 3:1 phenotype, i.e., chinchilla and albino. This is also a case of complete dominance. The genotype is Cca for both parents
| ♂/ ♀ | C | ca |
| C | CC Chinchilla |
Cca Chinchilla |
| ca | Cca Chinchilla |
caca Albino |
The cross (cross 6) between albino and Himalayan parents results in all Himalayan phenotype. This is also a case of complete dominance. The genotype is cchcch(female) and caca (male).
| ♂/ ♀ | cch | cch |
| ca | cchca Himalayan |
cchca Himalayan |
| ca | cchca Himalayan |
cacch Himalayan |
The cross (cross 7) between albino and chinchilla parents results in chinchilla and albino in 1:1 ratio. This is also a case of complete dominance. The genotype is Cca(female) and caca (male).
For cross 7:
| ♂/ ♀ | C | ca |
| ca | Cca Chinchilla |
caca Albino |
| ca | Cca Chinchilla |
caca Albino |
The cross (cross 8) between two albino parents results in all albino. This is also a case of complete dominance. The genotype of both parents is caca
| ♂/ ♀ | ca | ca |
| ca | ca ca Albino |
ca ca Albino |
| ca | ca ca Albino |
ca ca Albino |
The cross (cross 9) between himalayan and chinchilla parents results in chinchilla and chinchilla in 1:1 ratio. This is also a condition of complete dominance. The genotype of chinchilla parent is Ccch, and albino parent is cchcch or cchca.
| ♂/ ♀ | C | cch |
| cch | C cch Chinchilla |
cch cch Himalayan |
| cch | C cc Chinchilla |
cch cch Himalayan |
| ♂/ ♀ | C | cch |
| cch | Ccch Chinchilla |
cchcch Chinchilla |
| ca | Cca Chinchilla |
cchCa Himalayan |
The cross (cross 10) between Himalayan and chinchilla parents results in 2 chinchillas, 1 albino, and 1 Himalayan phenotype. The genotype of chinchilla parent is Cca and cchca.
For cross 10 :
| ♂/ ♀ | C | ca |
| cch | Ccch Chinchilla |
cchca Himalayan |
| ca | Cca Chinchilla |
ca ca Albino |
c.
To determine:
The progeny of chinchilla parents 9 and 10.
Introduction:
The dominant allele always expresses itself either homozygous or in heterozygous condition. The recessive allele is only expressed in homozygous condition, not in heterozygous condition.
Explanation of Solution
The cross between chinchilla 9 and 10 have gametes C and ca also C and cch. This cross results in chinchilla ¾ and Himalayan offsprings in ¼ ratio.
| ♂/ ♀ | C | cch |
| C | CC Chinchilla |
cchC Chinchilla |
| ca | C ca Chinchilla |
cchca Himalayan |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
GENETICS:FROM GENES TO GENOMES-ACCESS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Prescott's Microbiology
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
Biology: Life on Earth
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- Below is a pedigree of a human genetic disease in which solid color indicates affected individuals. Assume that the disease is caused by a gene that can have the alleles A or a. a) Based on this pedigree, what is the most likely mode of inheritance? b) What is/are the possible genotype/s of person 1? c) What is/are the possible genotype (s) of person 4 ? Explain your answers.arrow_forwardTo determine the recombination frequency between body color and wing genes in flies, you perform several crosses where you cross an F1 having red body and smooth wings with a yellow-bodied, crinkle-winged fly. You get the following results. What is the distance between the genes for body color and wing surface in map units?arrow_forwardIn pedigrees, individuals are usually specified by using a Roman numeral for their generation in the chart and an Arabic number for their position (reading left to right) within that generation. If we use the letter c for the allele that causes cystic fibrosis, what are the genotypes of individuals III-3 and III-4 (the third and fourth individuals shown in generation III) in the pedigree that shows this disease?arrow_forward
- Hemophilia and color blindness are both recessive conditions caused by genes on the X chromosome. To calculate the recombination frequency between the two genes, you draw a large number of pedigrees that include grandfathers with both hemophilia and color blindness, their daughters (who presumably have one chromosome with two normal alleles and one chromosome with two mutant alleles), and the daughters sons. Analyzing all the pedigrees together shows that 25 grandsons have both color blindness and hemophilia, 24 have neither of the traits, 1 has color blindness only, and 1 has hemophilia only. How many centimorgans (map units) separate the hemophilia locus from the locus for color blindness?arrow_forwardIndividuals of genotype AaBb were mated to individuals of genotype aabb. One thousand offspring were counted, with the following results: 474 Aabb, 480 aaBb, 20 AaBb, and 26 aabb. What type of cross is it? Are these loci linked? What are the two parental classes and the two recombinant classes of offspring? What is the percentage of recombination between these two loci? How many map units apart are they?arrow_forwardThe following pedigree shows the pattern of inheritance of red-green color blindness in a family. Females are shown as circles and males as squares; the squares or circles of individuals affected by the trait are filled in black. What is the chance that a son of the third-generation female indicated by the arrow will be color blind if the father is not color blind? If he is color blind?arrow_forward
- If you are working to solve for the relative distances between a cat's genes for fur color, where gene X has alleles X and x and gene Y has alleles Y and y that follow an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, which test-cross should you perform to determine a genetic map? A. XxYy x XxYy B. XXYY x xxyy C. XxYy x xxYy D. XxYy x xxyyarrow_forwardLet us suppose that two long-winged flies were crossed and that 77 long-winged and 24 short-winged specimens were counted in the offspring. a. Will the short-winged character be dominant or recessive?B. What will the genotypes of the parents be?C. What is the observed genotype ratio?arrow_forwardWhen a white guinea pig is crossed to a yellow guinea pig, all the progeny are cream-colored. From a cross of two such F1’s, the F2 showed 32 white, 66 cream, and 30 yellow guinea pigs. How is this trait inherited? _______________ Identify the genotype of the white guinea pig. ________ Identify the genotype of the yellow guinea pig. ________ Identify the genotype of the cream-colored guinea pig. ________ Identify the genotypes and the corresponding phenotypes of the F2 progeny. Give the genotypic ratio. __________________ Give the phenotypic ratio. ___________________arrow_forward
- This pedigree traces the inheritance of a trait in humans. Based on this pedigree, is the allele for this disease dominant or recessive? Is it sex-linked? Explain. What genotypes are most probable for the individuals labeled 4, 7, and 10?arrow_forwardPigment in mouse fur is only produced when the C allele is present. Individuals of the cc genotype are white. If color is present, it may be determined by the A, a AA or Aa results in agouti color, while aa results in black coats. What F1 and F2 genotypic and phenotypic ratios are obtained from a cross between AACC and aacc mice? (F2: intercross between F1 offspring) Explain briefly the pattern of inheritance in this problem set and how you determined the phenotypic ratios in the offspring.arrow_forwardIn mice, black color (B) is dominant to white (b). On different homologous chromosomes, a dominant allele (A) produces a band of yellow just below the tip of each hair in mice with black fur. This gives a frosted appearance known as agouti. Expression of the recessive allele (a) results in a solid coat color. If mice that are heterozygous at both locations are crossed, what is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? Use the rules of probability instead of a huge Punnett square.arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College



