Concept explainers
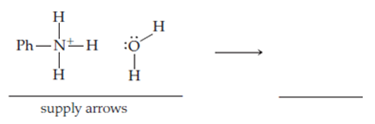
The reaction just described is reversible. Deprotonation of the conjugate acid of an organic base by water provides another example of simultaneous making and breaking of sigma bonds. Thus, in the deprotonation of anilinium ion by water, the base is water, which has unshared electrons on the ________ atom. The acid is ________ ion. A pair of ________ electrons on the oxygen atom of water is pushed toward the ________ atom. Simultaneously, the pair of ________ electrons between the hydrogen and ________ atom of the anilinium ion is pushed toward the ________ atom. Thus, the oxygen- ________ sigma bond is made and a hydrogen- ________ sigma bond is broken. The nitrogen atom, which possessed a positive charge, is now ________, and the oxygen atom, which was neutral, now possesses a formal ________ charge.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 3 Solutions
Pushing Electrons
- In the following reaction of tetrafluoroboric acid, HBF4, with acetate ion, C2H3O2-, the formation of tetrafluoroborate ion BF4-, and acetic acid, C2H4O2 is favored. HBF4 + C2H3O2- → BF4- + C2H4O2 Which is the weaker base, BF4- or acetate ion?arrow_forwardFor the reaction below, identify the acid, the base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. C5H5NH+ + H2O ↔ C5H5N + H3O+ C5H5N : base H2O : H3O+ : C5H5NH+ :arrow_forwardFor the following reaction, draw the Lewis Dot structure for each reactant and product including any formal charges. Also identify the Lewis Acid and the Lewis Base for this reaction. CH3CH2CCH + NH2- -> CH3CH2CC- + NH3 On the product side of the equation, one of the C atoms has 1 unshared pair of electrons and is (-) charged.arrow_forward
- Fosamax has six acidic groups. The active form of the drug, which has lost two of its acidic protons, is shown in the box. (Notice that the phosphorus atom in Fosamax and the sulfur atom in Problem 36 can be surrounded by more than eight electrons because P and S are below the second row of the periodic table.) a. Why are the OH groups bonded to phosphorus the strongest acids of the six groups? b. Which of the remaining four groups is the weakest acid?arrow_forwardThe following reaction is used for both HNO3 and KNO2. Based on what you know about acid dissociation constants, explain why this is the case. NO3- + 3H+ + 2e- ↔ HNO2 + H2Oarrow_forwardLabel the following reactions as Acid, Base, Conjugate Acid and Conjugate base using the Bronsted Lowry Model. Recall that an acid donates a proton to become a conjugate base, and a base accepts and proton to form a conjugate acid. HCO3- + NH3® CO3-2 + NH4+ HCl + H2O ® H3O+ + Cl- CH3COOH + H2O ® H3O+ + CH3COO- HOCl + NH3 ® NH4+ + ClO-arrow_forward
- Why is HCl so acidic? For example, why is H-Cl more acidic than H-S-CH3? Isn't the conjugate base's negative charge more stabilized with a sulfur and extra methyl group (by the induction effect)? While Cl is more electronegative than Sulfur, I would assume Cl being alone as its own ion would make it less stable.arrow_forwardFor each of the following reactions, highlight or circle the substance on the left hand side which is behaving as an acid and the substance on the right hand side which is its conjugate base. H2O + HCl ➡ H3O+ + Cl- CH3CO2H + OH ➡ CH3CO2- + H2O H2SO4 + HNO3 ➡ HSO4- + H2NO3+ CH3CO2H + HNO3 ➡ CH3CO2H2+ + NO3- Justify each of your choices with concrete explanations.arrow_forwardWrite the products of these reactions. Use single or double arrows as appropriate. When you are done, label the acid and base on the left side and the conjugate acid (CA) and conjugate base (CB) on the right side. (a) PO43- + CH3NH3+ (b) H2O + H2SO4arrow_forward
- Acids & Bases: Understanding Connections Between Descriptions if Weak Acid Dissociations For a certain acid pka is 3.58. Calculate the pH at which an aqueous solution of this acid would be 6.5% dissociated. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. *Photo included belowarrow_forwardIf enough of a monoprotic acid is dissolved in water to produce a 0.0124 M solution with a pH of 6.72, what is the equilibrium constant, p?a, for the acid? kindly consider the following when answering the question For weak acids that are so dilute or so weak that the pH of the solution lies between 6 and 7, the autoprotolysis of water must be taken into account when determining the p?a value. At equilibrium, there are four species in solution, the weak acid, HA, its conjugate, A−, H3O+, and OH−. Start by developing four equations that describe what is occurring in the solution at equilibrium.arrow_forwardPhenol Red: What is the purpose of this test? Why is a Durham tube inverted inside the test tube? At what pH does phenol red register an acidic result? What is the color? What is the color of an alkaline result? If you see an acid result, what does this mean? What about an alkaline result?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

