
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Among molecules mentioned in the question, it is to be determined which has shorter
Concept introduction:
Hybridization affects both bond length and bond strength. The two
Answer to Problem 3.27P
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the molecules mentioned in the question is shown below:
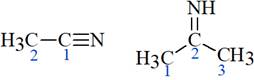
The two
In the first molecule, according to VSEPR theory, the
In the second molecule, according to VSEPR theory, the
This shows that in the first molecule, the percentage s character in
Bond length and bond strength is determined from the hybridization involved in the molecule.
(b)
Interpretation:
Among the molecules mentioned in the question, it is to be determined which has shorter
Concept introduction:
Hybridization affects both bond length and bond strength. The two
Answer to Problem 3.27P
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the molecules mentioned in the question is shown below:
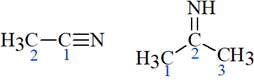
The two
In the first molecule, according to VSEPR theory, the
In the second molecule, according to VSEPR theory, the
This shows that in the first molecule, the percentage s character in C-N bond is more than that in the second molecule. Therefore, the C-N bond is shorter and stronger in the first molecule.
Bond length and bond strength is determined from the hybridization involved in the molecule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY:PRINCIPLES...(CL)
- Please answer this NEATLY, COMPLETELY, and CORRECTLY for an UPVOTE. Write the resonance structure that would result from pushing the electrons as indicated by the curved arrow.arrow_forwardWhich of the molecules are polar in attached problem?arrow_forwardb. and c.?? I'm so confused help pleasearrow_forward
- can you answer this please with an explainationarrow_forwardPlease draw a more stable resonance structure for the following molecule. Use a curved arrow to show how to transform the original structure to the new one and please specify charges.arrow_forwardUse curved arrow notation to show how the rst resonance structure can be converted to the second.arrow_forward
- Problem is on the picture.arrow_forwardFor the same molecule, which of the images corresponds to the correct Newman projection along the indicated bond? Need help understaniding how to answer question?arrow_forwardDraw the resonance structure for the following molecule: Just started with resonance, where would the arrows go? I'm unsure of this problem.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
