
Concept explainers
A block on a frictionless table is connected to a spring as shown. The spring is initially unstretched. The block is displaced to the right of point R and is then released.
1. When the block passes point R, is the spring compressed or stretched?
Does your answer depend on the direction in which the block is moving? Explain.
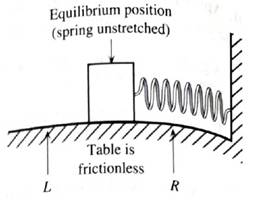
2. In the space provided, draw a free-body diagram for the block at the instant the block passes point R moving to the left. Draw arrows to represent the directions of the velocity, the acceleration, and the net force on the block, all at that instant. If any quantity is zero, state so explicitly.

Is the net work done on the block from point of release to point R, positive, negative, or zero? Explain.
At some instant, the block passes point L moving to the left. Draw a free-body diagram for the block at that instant. Also, draw arrows to represent the direction of the velocity, the net force, and the acceleration, all at that instant. If any quantity is zero, state so explicitly.

During a small displacement of the block from the right of point L to take the left of point L:
Is the net work done on the block positive, negative, or zero? Explain.
Does the speed of the block increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain how your answer is consistent with the work-energy theorem.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 3 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
University Physics Volume 2
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- Water going over a fall splashes on the rocks 20 m below. (a) What is the water’s velocity at the bottom of the fall, assuming ? = 0 at the top? (b) If 20 kg of water flows over the fall per second, how much force do the rocks exert on the falling water? (Assume the water comes to a stop once it hits the rocks.) please show your work, including diagrams, algebraic equations, and enough written explanations that somebody who is not familiar with the problem could understand what you are doing.arrow_forward36 Please use energy to solve Please label all free body diagrams and any formulas used Thanks!arrow_forwardA ball of mass 2.0 kg is attached to the end of a 2.2 m long string and whirled around in a circle thatdescribes a horizontal plane.a. What is the frequency of rotation of the ball if the string makes an angle of 15◦ with respect to the vertical?Provide a free-body diagram. b. At this speed (solved from part a), what is the tension in the string?arrow_forward
- Given the following information, how would you find the magnitude of the acceleration of the system. Express youranswer in terms of known quantities such as m1, m2, theta, k, xs, x0, and g. "A ball of mass m1 and block of mass m2 are attached by a lightweight cord that passes over a frictionless pulley of negligible mass, as shown in the figure below. The block lies on a smooth plane inclined at an angle 'theta'. The ball is attached to a spring whose spring constant is k and equilibrium position x0. The spring is then stretched so it measures a length xs. You may use the fact that the force due to a spring is opposite the stretch and equal to −kΔxstretch. The system is then released. You can assume that the acceleration due to gravity is given as g, and use the consistent coordinate system specified for each object."arrow_forwardA tie of uniform width is laid out on a table, with a fraction of its length hanging over the edge. Initially, the tie is at rest. (a) If the fraction hanging from the table is increased, the tie eventually slides to the ground. Explain. (b) What is the coefficient of static friction between the tie and the table if the tie begins to slide when one-fourth of its length hangs over the edge? Show your work and explain.arrow_forwardA man whose mass is 80 kg and a women whose mass is 50 kg sit at opposite ends of a canoe 5m long, whose mass is 30kg. (a) Relative to the man, where is the center of mass of the system consisting of man, women, and canoe? (Hint: choose a specific coordinate system with a specific origin.) (b) Suppose that the man moves quickly to the center of the canoe and sits down there. How fr does the canoe move in the water? Explain your work and your assumptions.arrow_forward
- I would like to know if you can break down step 2 part b I know it has to do with some trigonometry, but how do you set up the equation? Like can you do a free body diagram, and explain a little bit more detail?arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 0.62 kg attached to a spring with force constant 125 N/m is free to move on a frictionless, horizontal surface as in the figure below. The block is released from rest after the spring is stretched a distance A = 0.13 m. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer. Assume that the positive direction is to the right.) At that instant, find the force on the block. ___N At that instant, find its acceleration. ___m/s^2arrow_forwardConsider a pair of masses m1 and m2 connected by a non-stretchable string that runs over a frictionless pulley as shown on the figure on the right. If the coefficient of the kinetic friction between m1 and on the horizontal surface on which it initially rest is μk, find its resulting acceleration magnitude in terms of m1, m2, and μk, when the system is released. Assume that air resistance is negligible and m2 > μk m1. Show the complete and thorough solution in a clean paperarrow_forward
- Please refer to the picture with the formulas and constants that need to be used in this problem. Harzan wants to swing from one bank of the river to the other using an overhaning vine. As he swings, he traces out an arc of a circle. Part 1) Please draw and label a free body diagram of Harzan at the bottom of the swing. Part 2) What forces act as the radial force in the circular motion? Part 3) Is this uniform circular motion? Explain Part 4) The vine is 6.2 m long, and Harzan's mass is 85 kg. At the bottom of his swing, he is travelling at 4.3 m/s. What is the magnitide of the radial acceleration that Harzan experiences? Part 5) How much tension must the vine support in order to safely transport Harzan over the river? Please answer all partsarrow_forwardAn object moves on a flat surface with an acceleration of constant magnitude. If the acceleration is always perpendicular plane and measures the angle at which the block begins to slide. He reports that the coefficient of static friction was 0.25 in his experiments. At what angle did Leonardo’s blocks begin to slide? Show your work and explain.arrow_forward(Figure 1)Block 1, of mass m1, is connected over an ideal (massless and frictionless) pulley to block 2, of mass m2, as shown. Assume that the blocks accelerate as shown with an acceleration of magnitude a and that the coefficient of kinetic friction between block 2 and the plane is μ. Find the ratio of the masses m1/m2. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables a, μ, and θ, as well as the magnitude of the free-fall acceleration g.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





