
Concept explainers
The diagrams at right show two identical gliders that move to the right without friction. The hands exert identical, horizontal forces on the gliders. The second glider experiences an additional, smaller force from a massless string held as shown.
Suppose the gliders move through identical displacements.
Is the work done on glider 1 by the hand greater than, less than, or equal to the work done on glider 2 by the hand? Explain.
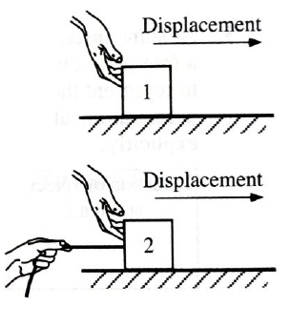
Is the change in kinetic energy of glider 1 greater than, less than, or equal to the change in kinetic energy of glider 2? Base your answer on your knowledge of the net work done on each object.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 3 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
- Please solve parts D, E, and F below and explain/show work for everything. A ski jumper starts from rest from point A at the top of a hill that is a height h1 above point B at the bottom of the hill. The skier and skis have a combined mass of 80 kg. The skier slides down the hill and then up a ramp and is launched into the air at point C that is a height of 10 m above the ground. The skier reaches point C traveling at 42m/s. The skier leaves the ramp at point C traveling at an angle of 25° above the horizontal. (d) Calculate the kinetic energy of the skier at the highest point in the skier's trajectory. (e) i Calculate the horizontal distance from the point directly below C to where the skier lands. If the angle is increased to 35°, will the new horizontal distance traveled by the skier be greater than, less than, or equal to the answer from part (e)(i) ? Justify your answer. After landing, the skier slides along horizontal ground before coming to a stop. The skier’s initial…arrow_forwardIf you start from A and move along the curvature through B,C and D and back to A as indicated. Explain how will you estimate the work done and whether the work is done onto the system by the surroundings or done by the system onto the surroundingsarrow_forwardCalculate the magnitude of motive and stabilizing/destabilizing force when a muscle attached to a bone at a distance d = 2.2 cm from the joint center exerts Fm = 250 N of tension at the following angles of attachment (λ): a) 30̊, b) 60̊, c) 90̊, d) 120̊, e) 150̊. Insert your results in the graph below. Interpret your findings. What does this result imply for muscle force generation? NOTE: You will have to create two curves in your graph. Label them clearly. Show your work.arrow_forward
- Write your solution and answer correctly. 1. After a leaf falls from a tree, an apple falls next. If the apple has a potential energy of 97 J and a kinetic energy of 420 J, how much energy is present on the apple?arrow_forwardPlease answer all components of the question: A teacher is planning to demonstrate the principle of energy conservation to his class by bungee jumping from the scaffolding in the school's gym. He has a mass of 120 kg, and the scaffolding is 25 m above the ground. a) How much potential energy would the teacher have at that location? Explain/Show your work. b) If the teacher wants to have the bungee stop his motion when he is 2 meters above the gym floor, how much energy will the bungee need to absorb? Explain/Show your work. c) If he orders a bungee cord with an unstretched length of 8 m, what spring constant should he be sure to get in order to safely perform this demonstration? Explain/Show your work.arrow_forwardPlease solve this problem and explain the trigonmetric situation with finding h - i am having trouble visualizing it - please draw an image as well Jeff of the Jungle swings on a 7.6-m vine that initially makes an angle of 37° with the vertical. If Jeff starts at rest and has a mass of 78 kg, what is the tension in the vine at the lowest point of the swing?arrow_forward
- A player kicks a soccer ball (0.5 kg mass) at the goal. It hits the crossbar at a height of 2.5 m, while moving at a speed of 30 m/s. a) What is the total energy of the ball when it hits the crossbar? Show your work. b) A soccer ball sits at rest on top of a building. How tall does the building have to be so that the ball has the same energy as the soccer ball in part a)? Show your work.arrow_forwardA box starts with a velocity of 10 m/s and falls along the frictionless path shown below.What is the velocity of the box at points B, C, D, and E?arrow_forwardChoose the correct answer: 1. We can distinguish three simple cases of action of a force and the work it does on a system: A. When the force acts in the same direction and sense as the displacement, the work it does is positive (W> 0) B. When the force acts in the same direction, but in the opposite direction to the displacement, the work that performs has a negative value (W <0) C. When the force acts in a direction perpendicular to the displacement, it does no work (W = 0) 2. An example of negative work is: A. Stop a ball. B. Push a car C. Walking with the backpack on the backarrow_forward
- B. Directions: Solve the given problem. Show your solution. 1. You joined a “dogsled” race during your winter break. To start, you pulled the sled (total mass of 85 kg) with a force of 195N at 45° above the horizontal. Find the work done on the sled after it moves at a distance of 7m. Plss answer my question. Thankyouarrow_forwardA block sliding along a frictionless, horizontal surface with a speed of 0.6 m/s collides with a spring attached to a wall. The spring is compressed 19.0 cm before the block is stopped. If the same block were to collide with the spring again while having a speed of 2.6 m/s, what would the spring's compression be before stopping the block this time, in centimetres? Be clear and show all your work. (HANDWRITTEN)arrow_forwardDirection: solve the given problem. Show your solution. 1. You joined a "dogsled" race during your winter break. To start you pulled the sled ( total mass of 85kg) with a force of 195N at 45° above the horizontal. Find the work done on the sled after it moves at a distance of 7m.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





