
Concept explainers
The crate shown in Fig. 4-60 lies on a plane tilted at an angle
v
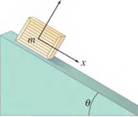
Figure 4-60
Part(a)To Determine:
The acceleration of the crate when it slides down an inclined plane when force of kinetic friction acts on it.
Answer to Problem 57P
Solution:
The acceleration of the crate down the inclined plane is found to be 2.5 m/s2.
Explanation of Solution
The crate of mass slides down a plane inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The free body diagram of the crate is shown below.
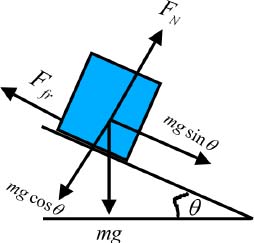
The weight mg of the crate acts vertically downwards. The normal force acts perpendicular to the inclined plane. The weight mg is resolved into two components, parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane. The force of kinetic friction acts opposite to the direction of motion of the box. There is a net force acting on the box in the downward direction parallel to the inclined plane accelerating it at a rate a.
Since there is no motion perpendicular to the incline,
…… (1)
The force of kinetic friction is related to the normal force as,
…… (2)
Since the crate slides down the incline, there is a net force F that acts downwards. This is given by,
…… (3)
Substitute equations (1)and (2)in (3).
……. (4)
From Newton’s second law,
Here, a is the resultant acceleration of the crate down the incline.
Therefore,
……(5)
Given:
The length of the incline
The angle at which the incline is inclined
The coefficient of kinetic friction
The initial velocity of the crate
Formula used:
Calculation:
Calculate the acceleration of the crate down the incline by substituting 9.8 m/s2for g and the given values for and .
Part(b)To Determine:
The speed of the crate when it reaches the bottom of the incline.
Answer to Problem 57P
Solution:
The speed of the crate at the bottom of the incline is found to be 6.3 m/s.
Explanation of Solution
To calculate the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the incline of length s is calculated using the equation of motion,
……(6)
Given:
The length of the incline
The angle at which the incline is inclined
The coefficient of kinetic friction
The initial velocity of the crate
Formula used:
Calculation:
Calculate the speed of the crate when it reaches the bottom of the incline by substituting the calculated value of a and the given values of s and in the equation,
Chapter 4 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





